Adamson,William Ian (Flying Officer)
Killed in Action 1944-March-31
Service
RAFVR
Unit
101 (B) Sqn- Squadron (RAF)
Mens Agitat Molem Mind over matter
Base
RAF Ludford Magna
Rank
Flying Officer
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
148447)
Crew or Other Personnel
Lancaster DV264
Mission
Lancaster Mk.I/III DV264
Bombing Nuremberg Germany 1944-March-31 to 1944-March-31
101 (B) Sqn (RAF) RAF Ludford Magna
RAF Commands reports Lancaster DV264 Took off from Ludford Magna at 21:45 in Lancaster Mark III (Sqn code: SR-L Bomber Command), was hot down outbound by a Halifax and crashed near Gemund 5 km NNE of Schleiden
This would normally have been the moon stand-down period for the Main Force, but raid to the distant target of Nuremberg was planned on the basis of an early recast that there would be protective high cloud on the outward route, when the oon would be up, but that the target area would be clear for ground-marked imbing, A Meteorological Flight Mosquito carried out a reconnaissance and ported that the protective cloud was unlikely to be present and that there could be oud over the target, but the raid was not cancelled.
795 aircraft were dispatched- 572 Lancasters, 214 Halifaxes and 9 Mosquitoes. The German controller ignored all the diversions and assembled his fighters at 2 radio beacons which happened to be astride the route to Nuremberg. The first fighters appeared just before the bombers reached the Belgian border and a fierce battle in the moonlight lasted for the next hour. 82 bombers were lost on the outward route and near the target. The action was much reduced on the return flight, when most of the German fighters had to land, but 95 bombers were lost in all - 64 Lancasters and 31 Halifaxes, 11.9 per cent of the force dispatched. It was the biggest Bomber Command loss of the war. Most of the returning crews reported that they had bombed Nuremberg but subsequent research showed that approximately 120 aircraft had bombed Schweinfurt, 50 miles north-west of Nuremberg. This mistake was a result of badly forecast winds causing navigational difficulties. 2 Pathfinder aircraft dropped markers at Schweinfurt. Much of the bombing in the Schweinfurt area fell outside the town and only 2 people were killed in that area
The main raid at Nuremberg was a failure. The city was covered by thick cloud and a fierce cross-wind which developed on the final approach to the target caused many of the Pathfinder aircraft to mark too far to the east. A IO-mile-long creepback also developed into the countryside north of Nuremberg. Both Pathfinders and Main Force aircraft were under heavy fighter attack throughout the raid. Little damage was caused in Nuremberg; 69 people were killed in the city and the surrounding villages.The Bomber Command Wae Diaries, Martin Middlebrook and Chris Everitt
Lancaster serial: DV264
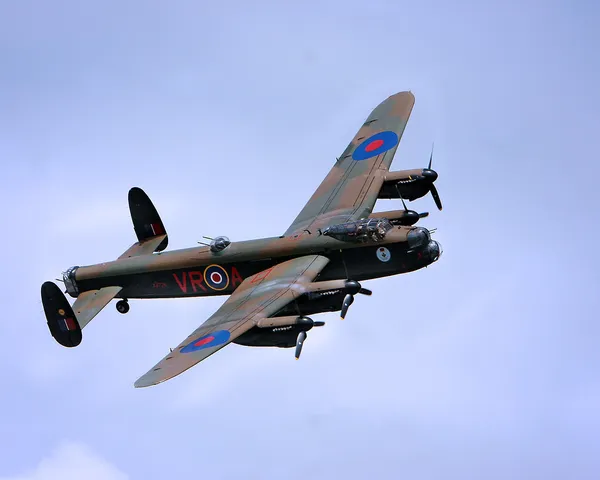

Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same wartime era.
The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use". Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one version, Bristol Hercules engines. It first saw service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942 and as the strategic bombing offensive over Europe gathered momentum, it was the main aircraft for the night-time bombing campaigns that followed. As increasing numbers of the type were produced, it became the principal heavy bomber used by the RAF, the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and squadrons from other Commonwealth and European countries serving within the RAF, overshadowing the Halifax and Stirling. Wikipedia
Unit Desciption
101 (B) Sqn Mens Agitat Molem ()
No. 101 Squadron RAF was originally formed within the RFC as a bomber unit in July 1917. It was disbanded in December 1919, then re-formed at Bircham Newton, Norfolk, in 1928, being the only operational squadron to fly the Boulton Paul Sidestrand and Overstrand aircraft. These were the first RAF bombers to have enclosed and power-operated turrets. When WWII broke out, the squadron was based at West Raynham, Norfolk, having now equipped with Bristol Blenheim aircraft. It was a reserve squadron until its first operation against Germany in July, 1940, and it later spent the greater part of its attacks on the barges in the channel and North Sea ports, which had been gathered for operation SEALION, the projected German invasion of Britain. In April 1941, a flight of the squadron's Blenheims was detached to Manston in Fighter Command's No. 11 Group, and from there it attacked enemy shipping during daylight, in an operation known as Channel Stop. In June, 1940 the squadron moved to Oakington, Cambridgeshire, where it remained until February 1942, when it moved to Bourne, Cambridgeshire.
During May and June 1941, the squadron converted to Vickers Wellingtons and flew with Bomber Command. It participated in all three 1000-bomber raids to Cologne, Essen and Bremen in 1942. In August 1942 the squadron moved to Stradishall, Suffolk, and in September to Holme-on-Spalding Moor, Yorkshire. Later in the year the squadron converted to Avro Lancaster aircraft, and continued the Bomber Command assault on Germany and Italy. In June 1943 the squadron moved again, to Ludford Magna, Lincolnshire. It participated in the raid on the rocket development centre at Peenemunde, and was fortunate enough to evade the enemy night fighters on that occasion.
In late 1943 the squadron was given a new function within Bomber Command, that of Radio Counter Measures, to attempt to cut the radio communications between the German night fighter controllers and the fighter pilots. Each aircraft was equipped with the radio device known as A.B.C. or Airborne Cigar. A special German-speaking radio operator in the aircraft used the ABC equipment to scan the appropriate frequencies, and when the German signals were detected, jamming was started by transmitting a warbling note. The Lancaster aircraft carrying ABC were easily distinguished because they carried three large aerials, two dorsally and one under the nose. In addition to the ABC equipment, the Lancasters carried a full bomb load. Unfortunately, because they transmitted strong signals, it was possible for night fighters to seek them out, and squadron losses were relatively high as a consequence; only three other Lancaster squadrons had higher losses. On the night of 5/6 June 1944, the squadron put up 21 ABC Lancasters to jam enemy wireless communications to prevent night fighters from being directed to the airborne invasion forces.
After its last operational mission, to Berchtesgaden in late April 1945, the squadron participated in operation MANNA, dropping food to help the staving populace of the Netherlands. It also was part of operation DODGE, bringing back British troops from Italy. The squadron moved to Binbrook, Lincolnshire in October 1945. It was successively equipped with Avro Lincoln, English Electric Canberra and Avro Vulcan aircraft.