The British Klemm Aeroplane Company developed the B.K.1 Eagle, a three-seat light aircraft as a follow-up to the British Klemm Swallow, its licensed copy of the Klemm L.25. While similar to the Klemm Kl 32, it was an entirely independent design by G. Handasyde, the chief designer of British Klemm, first flying in early 1934.[1] The Eagle was a low-wing wooden monoplane with a retractable undercarriage. It had an enclosed cabin for the pilot and two passengers. Six of this initial version of the Eagle were built. As was the case with the Swallow, a revised version was introduced in 1935 when British Klemm was renamed the British Aircraft Manufacturing Co. This version, the B.A. Eagle II had a revised rudder and a deepened rear fuselage. A total of 37 Eagle IIs were built, including a single example fitted with a fixed undercarriage.
Eagles were mainly sold to private owners, with a few also being used by flying clubs or as executive transports. In India, the Nawab of Sachin operated an Eagle as his personal aircraft. Eagles were also used for air racing, with several being entered into the King's Cup Races between 1935 and 1937. Single examples were also entered into the MacRobertson Air Race of 1934 between Britain and Australia and the 1936 Schlesinger Race between England and South Africa. Neither aircraft completed the races
At the outbreak of the Second World War, seven Eagles were pressed into RAF service in the UK, with two in Australia and one in Kenya, but the undercarriages proved vulnerable in RAF service, with most airframes being written off due to undercarriage failure.Two aircraft survived the war to be flown by civil owners in Australia.Wikipedia
 Wikipedia BA Eagle ll
Wikipedia BA Eagle ll
426 (B) Sqn On wings of fire ("Thunderbird")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington III, Lancaster II, Halifax III, VII, Liberator VI, VIII:)
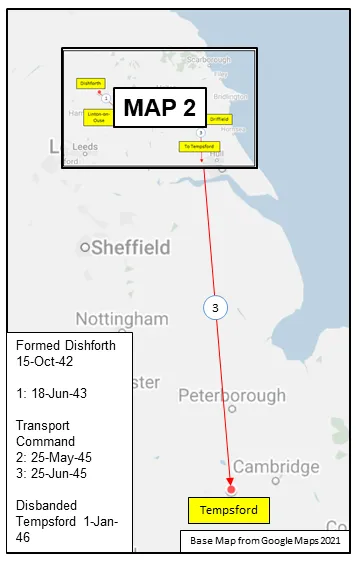
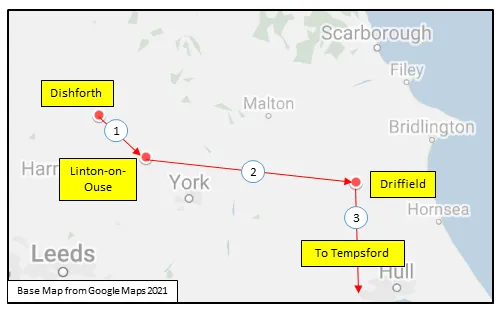
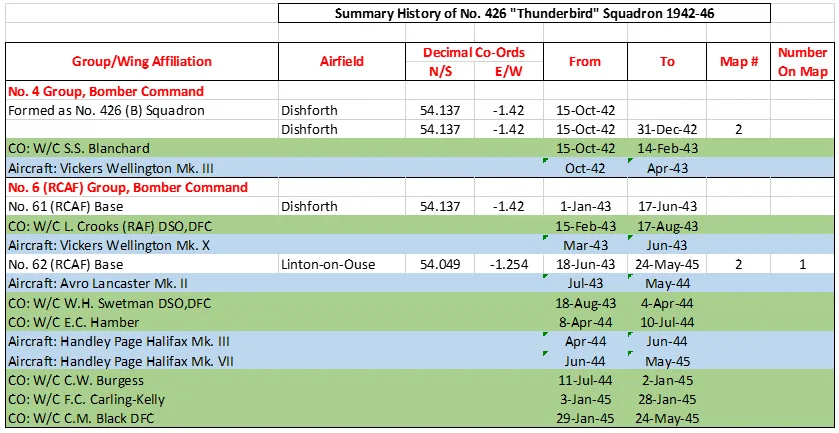
426 Squadron was formed at Dishforth, Yorkshire, UK 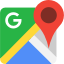 on October 15, 1942 as the 24th RCAF squadron and seventh bomber squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. Originally it was a member of No 4 Group, RAF Bomber Command, flying Vickers Wellington Mk III aircraft with the squadron code OW as part of the strategic bombing of Germany. On January 1, 1943 it became part of No 6 (RCAF) Group, while remaining at Dishforth until June 1943. On June 17, 1943 it moved to Linton-on-Ouse, Yorkshire.
on October 15, 1942 as the 24th RCAF squadron and seventh bomber squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. Originally it was a member of No 4 Group, RAF Bomber Command, flying Vickers Wellington Mk III aircraft with the squadron code OW as part of the strategic bombing of Germany. On January 1, 1943 it became part of No 6 (RCAF) Group, while remaining at Dishforth until June 1943. On June 17, 1943 it moved to Linton-on-Ouse, Yorkshire.  , as part of No 62 (RCAF) Base, at the same time re-equipping with Avro Lancaster Mk II aircraft. In April/May of 1944 , it again re-equipped, this time with Handley Page Halifax Mk III and VII aircraft, which it flew until the end of hostilities in Europe. At that time, to meet a need for long range transport in support of the proposed Tiger Force to attack Japan, it was re-designated as a Transport squadron in May 1945 and converted to Consolidated Liberator C Mk VI and VIII. After the surrender of Japan before the Tiger Force became operational, between October and December 1945 the squadron ferried troops from and around Egypt, India and the Far East. The squadron was disbanded at Tempsford, Bedfordshire, UK
, as part of No 62 (RCAF) Base, at the same time re-equipping with Avro Lancaster Mk II aircraft. In April/May of 1944 , it again re-equipped, this time with Handley Page Halifax Mk III and VII aircraft, which it flew until the end of hostilities in Europe. At that time, to meet a need for long range transport in support of the proposed Tiger Force to attack Japan, it was re-designated as a Transport squadron in May 1945 and converted to Consolidated Liberator C Mk VI and VIII. After the surrender of Japan before the Tiger Force became operational, between October and December 1945 the squadron ferried troops from and around Egypt, India and the Far East. The squadron was disbanded at Tempsford, Bedfordshire, UK  on January 1, 1946.
on January 1, 1946.
Overall, the squadron flew 268 bombing missions involving 3233 individual sorties, for the loss of 88 aircraft. 8997 tons of bombs were dropped. There were 242 Transport sorties. The squadron members were awarded 2 DSO's, 130 DFC's and 2 Bars to DFC, 1 CGM, 25 DFM's1 DFC(USA) and 13 MiD's. [Possibly, the most heroic act realized by a member of the squadron during the war took place on October 20, 1943, when Flight Sergeant Stuart (the pilot) and his crew were sent to bomb Leipzig. During the mission he was engaged by enemy fighters, Messerschmitt Bf 109 and Junkers Ju 88, initially managing to shake them off but not before having his aircraft rendered almost unfit to fly, leaving it with shattered cockpits and gun turrets; holes in the fuel tanks, damaged hydraulics and no navigation instruments. Against all odds Stuart decided to continue the mission and successfully bombed his target before guiding his crippled aircraft home. He was awarded the Conspicuous Gallantry Medal.] Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943, Baltic 1943, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1943-44, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1943-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1943. Wikipedia, Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 426 Squadron 1942-46
MAP 1: 426 Squadron Movements 1942-46 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
MAP 2: 426 Squadron Movements 1942-45 (detail of Map 1)
|
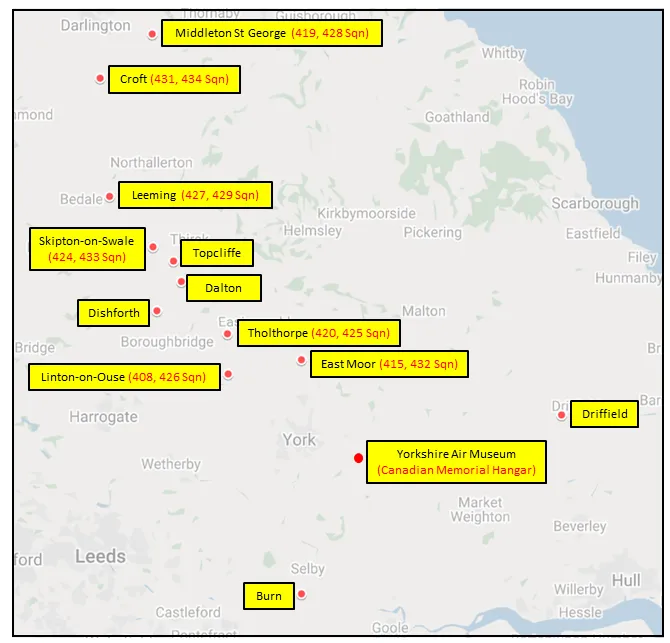
MAP 3: 6 Group Bomber Bases 1943-1945
|
426 Squadron History Summary 1942-46
426 Squadron History Summary 1942-46 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Dakota, North Star, Yukon, Hercules)
The squadron was re-formed as a Transport unit at Dartmouth, Nova Scotia  on 1 August 1946 from the Dartmouth portion of No. 164 (Transport) Squadron. It moved to Dorval (Montreal), Quebec
on 1 August 1946 from the Dartmouth portion of No. 164 (Transport) Squadron. It moved to Dorval (Montreal), Quebec  in March 1947 and was re-equipped from Dakota to four-engine North Star aircraft for long-range transport duty. From July 1950 to June 1954 the squadron was detached to McChord Air Force Base in Washington, USA
in March 1947 and was re-equipped from Dakota to four-engine North Star aircraft for long-range transport duty. From July 1950 to June 1954 the squadron was detached to McChord Air Force Base in Washington, USA  , from where it was employed on the Korean airlift (Operation “Hawkâ€) and made 600 round trips across the North Pacific between Vancouver and Tokyo, logging 34,000 flying hours and carrying 13,000 personnel and 7,000,000 pounds of freight and mail without mishap. A typical Korean Air Lift route for 426 Squadron aeroplanes was a physically and mentally demanding fifty-hour round trip flight from McChord to Japan and back with stops at Elmendorf Air Force Base (Alaska), Shemya (Aleutian Islands), Handed and Misawa Air Base (Japan). In 1956 it airlifted United Nations Emergency Force personnel and equipment to the Middle East and, in 1960-62, to the Belgian Congo. The unit moved to Trenton, Ontario
, from where it was employed on the Korean airlift (Operation “Hawkâ€) and made 600 round trips across the North Pacific between Vancouver and Tokyo, logging 34,000 flying hours and carrying 13,000 personnel and 7,000,000 pounds of freight and mail without mishap. A typical Korean Air Lift route for 426 Squadron aeroplanes was a physically and mentally demanding fifty-hour round trip flight from McChord to Japan and back with stops at Elmendorf Air Force Base (Alaska), Shemya (Aleutian Islands), Handed and Misawa Air Base (Japan). In 1956 it airlifted United Nations Emergency Force personnel and equipment to the Middle East and, in 1960-62, to the Belgian Congo. The unit moved to Trenton, Ontario  in September 1959, and in January 1962 to St Hubert (Montreal) Quebec
in September 1959, and in January 1962 to St Hubert (Montreal) Quebec  . The squadron was disbanded on 1 September 1962.
. The squadron was disbanded on 1 September 1962.
It reformed again as 426 Transport Training Squadron on May 3, 1971, at Uplands, Ontario  . The squadron moved to Trenton in August 1971 where it remains today, conducting training on the CC-130 Hercules.The squadron has carried out many tasks since the end of Korean War, including casualty evacuations, Royal tours and other VIP transport, and United Nations air lift operations. Thunderbird has worked in many places: the Arctic, the Middle East and Europe, the Congo and Japan.
. The squadron moved to Trenton in August 1971 where it remains today, conducting training on the CC-130 Hercules.The squadron has carried out many tasks since the end of Korean War, including casualty evacuations, Royal tours and other VIP transport, and United Nations air lift operations. Thunderbird has worked in many places: the Arctic, the Middle East and Europe, the Congo and Japan.
426 Transport Training Squadron carries out classes of different courses every year to generate operationally effective air mobility aircrew and technicians in support of Canadian Armed Forces (CAF) operations. The squadron also has dedicated personnel assigned to provide operational test and evaluation and system support to Air Mobility fleets. In 1995, the Squadron’s school underwent extensive renovations and acquired state-of-the-art computerized training aids. In spring 2000, the Squadron completed an upgrade to its OFS-130H flight simulator. The changes included a new motion base, new visual system and upgraded avionics equipment. The Squadron also opened a new building housing the Cargo Compartment Trainer for the CC-130H Hercules. Anticipating the future needs of the Air Mobility community and the newly procured CC-130J Hercules, the school expanded its facilities in 2012. The Air Mobility Training Centre (AMTC) was designed and built to accommodate the latest in aircrew and technician simulation, making it one of the most advanced training facilities in the world. The building serves as the home of 426 Squadron staff, whose job it is to train and prepare aircrew, technicians and aeromedical personnel for employment on the CC-130J, CC-130H, and CC-150 Polaris aircraft. Wikipedia, Kostenuk & Griffin, and www.canada.ca/en/air-force/corporate/squadrons/426-squadron.html