Reineck, Leonard (Sergeant)
Prisoner of War 1943-July-28


Birth Date: unkown date
Born:
Parents:
Spouse:
Home:
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RAF
Unit
429 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Fortunae Nihil Nothing to chance
Base
East Moor
Rank
Sergeant
Position
Wireless Operator/Air Gunner
Service Numbers
1129400
PoW: 222443
Target
Crew or Other Personnel
Wellington JA114
Mission
Wellington B. Mk. X JA114
Bombing Hamburg Germany 1943-July-27 to 1943-July-28
429 (B) Sqn (RCAF) RAF East Moor
For this Hamburg op of the 9 crews dispatched including the CO and his crew, W/C Piddington and B Flight Commander, Squadron Leader French and his crew. There were 2 early returns, Sergeant Tighe with his Gee becoming US and Flight Lieutenant Pentony because the starboard engine became US. The crews returned from 0357 to 0423.
The squadron waiting, to no avail, W/C Piddington and his crew failed to return on this op. According to his tail gunner, Reg Scarth, they were flying a brand new kite that night and it was developing too much power. W/C Piddington couldn't throttle back enough because it would cause the engines to overheat. Because of the excessive power their kite was about two minutes ahead of the bomber stream and a sitting duck for the enemy radar and night fighters. They were attacked by Ofw. Karl Kades at 0049 hrs. The aircraft was on fire from the attack and the crew were attempting to exit the plane when it broke apart from an explosion. Sergeant L. Reineck was catapulted through the side of the fuselage. He didn't know what happened to the rest of the crew. He was told by the German interrogation officer, in Frankfurt on 6 Aug 1943 that W/C Piddington was found at the controls of the wrecked aircraft. Sergeant Reineck doesn't know what happened to the rest of the crew. Sergeant L Reineck (WAG) RAF and Sergeant R Scarth (AG) RAF would spend the rest of the war as POWs. Many recalled W/C Piddington as a very popular and well-liked officer. He was quiet, he had a sense of humour and he earned the respect of both his crew and the squadron. W/C Piddington's grave marker is at Hamburg Cemetery.
The story finally comes to life again when Ellen Renton, the wife of Flying Officer Paul Renton (BA) RAFVR age 27 typed a letter to the RAF on 6 July 1945 saying that a soldier friend of hers had made enquires for her in Germany and found that a plane was brought down at Rensdburg on July 27th, 1943. She goes on to describe that there were three airmen in the plane, 2 were identified as W/C Piddington, the other as DO NOT Remove 14805, this is Flying Officer Farquhar number, but the third in someway has been recorded as an American in the book and on the gravestone, yet my friend found a certificate confirming their death and on this they were down as English. She asked that if this unidentified airmen is her husband she would rather know and have his name on the cross, rather than being in the state of mind of not knowing anything for the past two years. She closed the letter by saying If my husband has made the supreme sacrifice, I would rather know where his body lies. She enclosed a photograph of the cross her friend found.
The MREU section, under Flight Lieutenant S.G. Uerdal, takes up the story in May 1946. Herr Oehme, the local policeman at the time of the crash, was looking skyward on the night of 26/27 July 1943. He said he saw a Dornier 217 attack a British aircraft. The Dornier crashed at the same time, presumably shot down by the British aircraft. Herr Oehme arrived at the scene of the crash about one and a half hours later, finding pieces of the aircraft scattered over a wide area and burning fiercely. He identified it as a twin engine aircraft. He placed a guard on the aircraft and reported it to the Landraft at Rendsburg and to the Luftwaffe airfield at Neumunster. The Luftwaffe came out and took charge of the crash scene. Herr Oehme stated that he was told by Hauptman Vollert, from Neumunster that the aircraft was identified as a Wellington. He stated that three bodies were recovered from the crash site with one badly burned. Two of the bodies were identified as Piddington rectly identifies Stovell,not Renton and Farquhar. The third body couldn't be identified. They were buried with full military honours on 30 Jul 1943 at Neumunster. The original graves, in 1946, showing Stovell on the marker.
Uerdal reports that the graves were extremely well cared for with flowers on them and a grass verge around them with two crosses of pine with the names of W/C Piddington and Flying Officer Allan Ronald Armitage Farquhar's (N) RCAF age 21 names on the crosses in white lettering. The third cross is marked at Flight Lieutenant C. Stovel 16835. The bodies were exhumed to confirm identities. The first body was badly burned and decapitated. Because of this there was no possible means of positively identifying it. The next body exhumed had false upper dentures and a dark moustache. Obviously W/C Piddington. Since Farquhar and Piddington were positively identified and the third body was part of the same crash. They came to the conclusion the grave was incorrectly labelled at Flight Lieutenant Stovel and was in fact Pilot Officer Paul Renton. (J16835 Flight Lieutenant C.C Stovel RCAF, of 408 sqn was also killed that night. He is buried at the Hamburg Cemetery). Based on their findings they considered the matter was closed and the graves registered.
source: Greg Kopchuck, Bomber Command Museum of Canada
Wellington serial: JA114
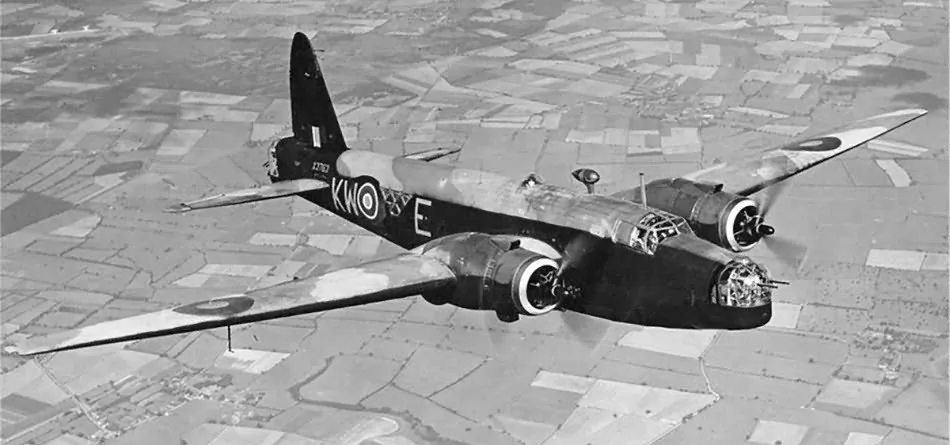

Vickers Wellington B. Mk. III (Serial No. X3763), coded KW-E, No. 425 'Alouette' (B) Squadron, RCAF, late summer of 1942
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson, a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design.
The Wellington was used as a night bomber in the early years of the Second World War, performing as one of the principal bombers used by Bomber Command. During 1943, it started to be superseded as a bomber by the larger four-engined "heavies" such as the Avro Lancaster. The Wellington continued to serve throughout the war in other duties, particularly as an anti-submarine aircraft.
It holds the distinction of having been the only British bomber that was produced for the duration of the war, and of having been produced in a greater quantity than any other British-built bomber. The Wellington remained as first-line equipment when the war ended, although it had been increasingly relegated to secondary roles. The Wellington was one of two bombers named after Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, the other being the Vickers Wellesley.
In August 1936, an initial order for 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft, powered by a pair of 1,050 hp (780 kW) Bristol Pegasus radial engines, was received by Vickers; it had been placed so rapidly that the order occurred prior to the first meeting intended to decide the details of the production aircraft. In October 1937, another order for a further 100 Wellington Mk Is, produced by the Gloster Aircraft Company, was issued; it was followed by an order for 100 Wellington Mk II aircraft with Rolls-Royce Merlin X V12 engines. Yet another order was placed for 64 Wellingtons produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. With this flurry of order and production having been assured by the end of 1937, Vickers set about simplifying the manufacturing process of the aircraft and announced a target of building one Wellington per day.
A total of 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft were built; 150 for the RAF and 30 for the Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) (which were transferred to the RAF on the outbreak of war and used by 75 Squadron). In October 1938, the Mk I entered service with 9 Squadron. The Wellington was initially outnumbered by the Handley Page Hampden (also ordered by the Ministry to B.9/32) and the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley (to B.34/3 for a 'night' bomber) but outlasted both rival aircraft in service. The Wellington went on to be built in 16 separate variants, in addition to two training conversions after the war. The number of Wellingtons built totalled 11,462 of all versions, a greater quantity produced than any other British bomber. On 13 October 1945, the last Wellington to be produced rolled out. Wikipedia
Unit Desciption
429 (B) Sqn Fortunae Nihil ("Bison")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington III, X, Halifax II, V, III, Lancaster I, III)

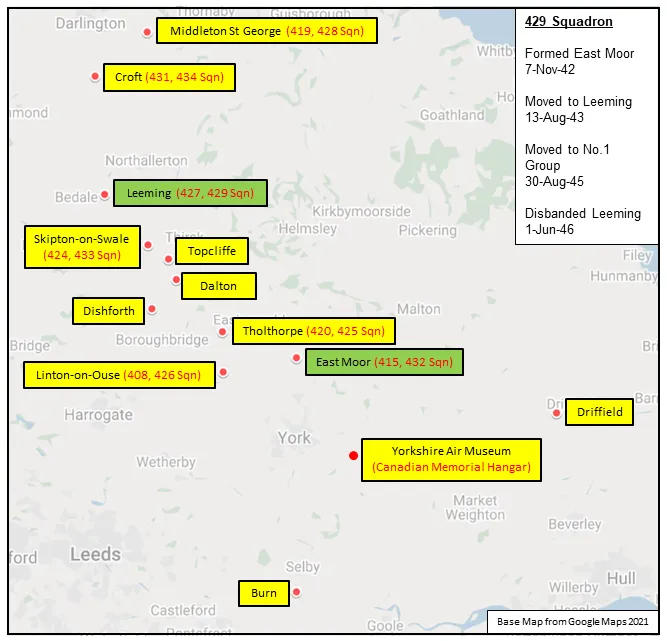
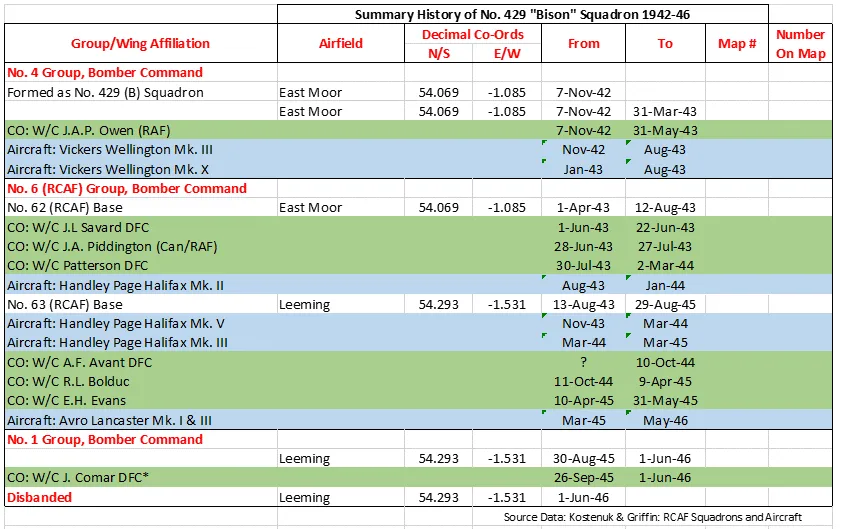
No 429 Squadron was the 10th bomber unit and 27th squadron formed by the RCAF overseas in WWII. It was formed in November 1942 at East Moor, Yorkshire, UK ![]() as part of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. On April 1, 1943 it became part of No 6 (RCAF) Group at No 62 (RCAF) Base, still remaining at East Moor until August 1943, when it moved to Leeming, Yorkshire
as part of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. On April 1, 1943 it became part of No 6 (RCAF) Group at No 62 (RCAF) Base, still remaining at East Moor until August 1943, when it moved to Leeming, Yorkshire ![]() as part of no 63 (RCAF) Base: it remained at Leeming until its disbandment in May 1946. It undertook strategic and tactical bombing operations. After the cessation of hostilities in Europe, it remained in England and transferred to No 1 Group, where it was engaged in transporting troops from Italy (Operation DODGE).
as part of no 63 (RCAF) Base: it remained at Leeming until its disbandment in May 1946. It undertook strategic and tactical bombing operations. After the cessation of hostilities in Europe, it remained in England and transferred to No 1 Group, where it was engaged in transporting troops from Italy (Operation DODGE).
The squadron, with squadron code AL, flew Vickers Wellington Mks III and X until August 1943, when it re-equipped with Handley-Page Halifax Mk II, which it flew between August 1943 and January 1944, and Mk V between November 1943 and March 1944. These were superseded by Halifax Mk III aircraft in March 1944. In March 1945, the squadron re-equipped with Lancaster Mk I and III. In summary of its activities, it flew 3221 sorties, including airlifting 1055 PoWs back to England, for the loss of 71 aircraft. 9356 tons of bombs were dropped. The squadron was awarded45 DFCs and 2 Bars to DFC, 1 AFC, 1 CGM and 7 DFMs. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943-45, Baltic 1943-45, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1943-44, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1943-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1943-44. Wikipedia,Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 429 Squadron 1942-46
429 Squadron History Summary 1942-46
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Buffalo, Hercules, Globemaster)
The squadron was reactivated at St. Hubert, Quebec ![]() on 21 August 1967 as a Tactical Transport Unit. It flew de Havilland CC-15 Buffalo aircraft for the Canadian Forces Mobile Command and was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces on 1 February 1968. In August 1981 it was renamed 429 Transport Squadron and moved to CFB Winnipeg
on 21 August 1967 as a Tactical Transport Unit. It flew de Havilland CC-15 Buffalo aircraft for the Canadian Forces Mobile Command and was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces on 1 February 1968. In August 1981 it was renamed 429 Transport Squadron and moved to CFB Winnipeg ![]() . The final move was in 1990 to 8 Wing in Trenton, Ontario
. The final move was in 1990 to 8 Wing in Trenton, Ontario ![]() . The squadron was disbanded in 2005.
. The squadron was disbanded in 2005.
Two years later in August 2007, 429 Squadron was again re-activated, this time operating the CC-177 Globemaster III strategic transport aircraft. It used these new aircraft in support of Canada's operations in Afghanistan.


