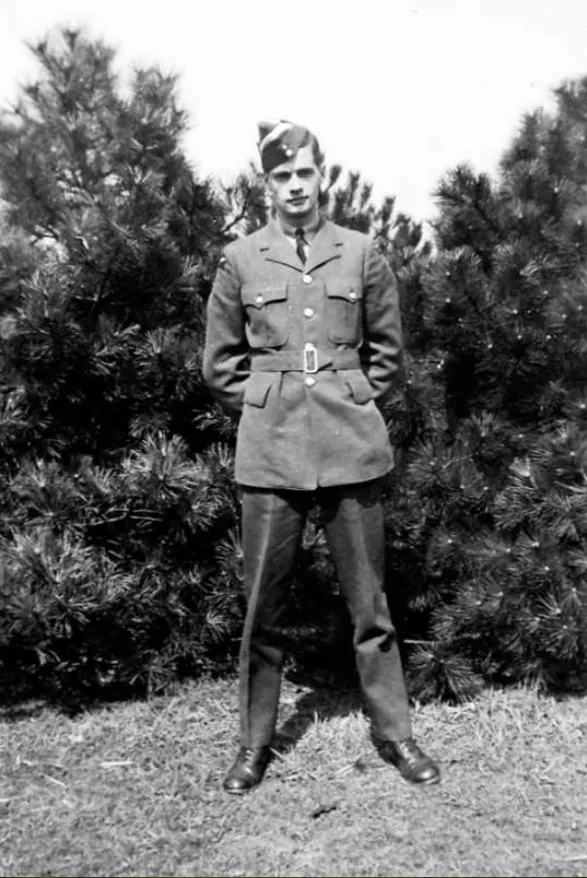
Johnson, Wilfred Sydney (Flying Officer)
Killed in Action 1943-November-20
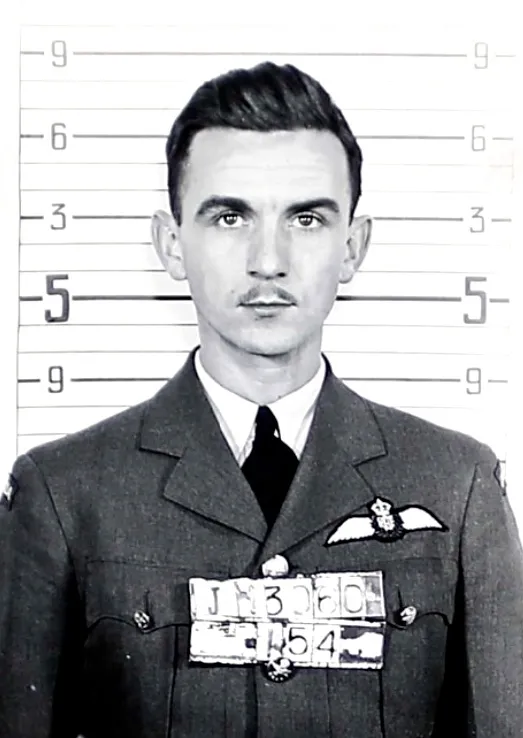


Birth Date: 1922
Born:
Parents:
Spouse:
Home: Toronto, Ontario
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
422 Sqn- Squadron
This Arm Shall Do It
Base
RAF St. Angelo, Fermanaugh, N. Ireland
Rank
Flying Officer
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
J/13060
Home
Target
Crew or Other Personnel
Sunderland W6031
Mission
Sunderland Mk. III W6031
Convoy Patrol 1943-November-20 to 1943-November-20
(GR) Sqn (RCAF) Castle Archdale
Operated by No. 422 (GR) Squadron, RCAF from 12 December 1942, coded "G". Operating from Castle Archdale on 16 June 1943, when it sighted 3 u-boats near 44-04N 13-42W, but lost them in haze before an attack could be started. Escorted convoys returning from Africa on 20(?) November 1943.
In the vicinity of combined convoy SL-139/MKS-30: forewarned by the Naxos radar detector, U-648 fought off the Sunderland with accurate AA fire. Approx. one hour later the aircraft sent a distress call saying it was about to ditch at 42°40N/19°30W. The crew of 11 were never found.
source: Malcolm Deeley, Ulster Aviation Society
R H Strauss, W.S. Johnson, J.D. Ulrichsen, C.G. Gorrie, FSs N. Barrett, B.G. Burton (RAF), R.A. Park (RAF), Sergeants N.P. Cook (RAF), and N.N. Lewis (RAF) were killed. Two others of the crew, not Canadians, missing believed killed.Sunderland serial: W6031

Short Sunderland, coded Z, 15 Apr 1943
The Short S.25 Sunderland was a British flying boat patrol bomber, developed and constructed by Short Brothers for the Royal Air Force (RAF). The aircraft took its service name from the town (latterly, city) and port of Sunderland in North East England.
Developed in parallel with the civilian S.23 Empire flying boat, the flagship of Imperial Airways, the Sunderland was developed specifically to conform to the requirements of British Air Ministry Specification R.2/33 for a long-range patrol/reconnaissance flying boat to serve with the Royal Air Force (RAF). As designed, it served as a successor to the earlier Short Sarafand flying boat. Sharing several similarities with the S.23, it featured a more advanced aerodynamic hull and was outfitted with various offensive and defensive armaments, including machine gun turrets, bombs, aerial mines, and depth charges. The Sunderland was powered by four Bristol Pegasus XVIII radial engines and was outfitted with various detection equipment to aid combat operations, including the Leigh searchlight, the ASV Mark II and ASV Mark III radar units, and an astrodome.
The Sunderland was one of the most powerful and widely used flying boats throughout the Second World War. In addition to the RAF, the type was operated by other Allied military air wings, including the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), South African Air Force (SAAF), Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF), French Navy, Norwegian Air Force, and the Portuguese Navy. During the conflict, the type was heavily involved in Allied efforts to counter the threat posed by German U-boats in the Battle of the Atlantic. Wikipedia
Unit Desciption
422 Sqn This Arm Shall Do It ("Flying Yachtsmen")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Lerwick I, Catalina IB, III, VB, Sunderland III, Liberator VI, VIII)

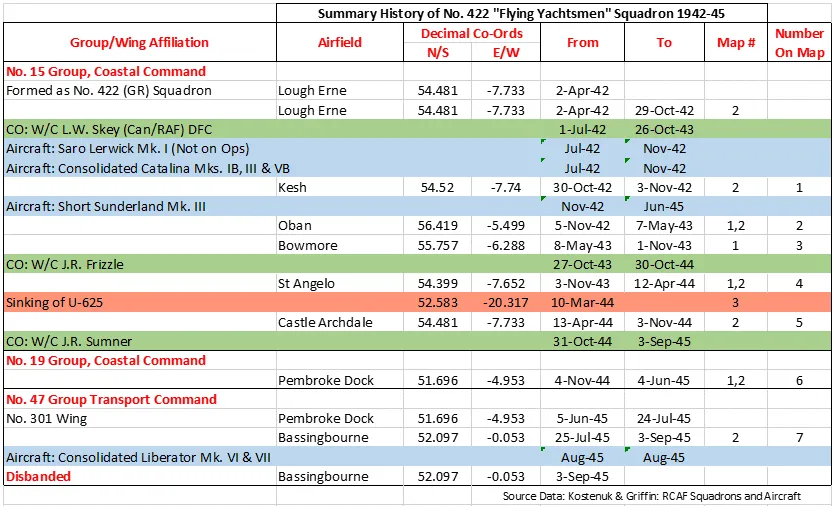
No. 422 (General Reconnaissance) Squadron was the 19th RCAF squadron formed overseas in WWII. It was the 5th Coastal squadron, and was formed at Lough Erne, Fermanagh, Northern Ireland ![]() on April 2, 1942. It flew Consolidated Catalina and Short Sunderland flying boats on convoy support and anti-submarine patrols over the North Atlantic shipping routes. When hostilities ended in Europe, the squadron was re-designated a Transport (T) unit and was converting to Consolidated Liberator aircraft when hostilities terminated in the Far East. The squadron was then disbanded at Bassingbourn, Cambridgeshire, England
on April 2, 1942. It flew Consolidated Catalina and Short Sunderland flying boats on convoy support and anti-submarine patrols over the North Atlantic shipping routes. When hostilities ended in Europe, the squadron was re-designated a Transport (T) unit and was converting to Consolidated Liberator aircraft when hostilities terminated in the Far East. The squadron was then disbanded at Bassingbourn, Cambridgeshire, England ![]() on September 3, 1945.
on September 3, 1945.
In the course of its operations, the squadron flew 1116 operational sorties for the loss of 9 aircraft and 70 aircrew, of whom 11 were killed, 31 presumed dead, 6 injured and 22 rescued. The squadron is credited with 1 U-boat (U-625), sunk by the crew of Sunderland EK591 from St. Angelo. Ireland on 10 March 1940. The captain, WO2 W.F. Morton, was on his first operation. Awards to squadron members were 1 OBE, 1 MBE, 6 DFCs,1 BEM, 1 Air Medal (USA) and 22 MiD. Battle Honours were: Atlantic 1942-45, English Channel and North Sea 1944-45, Normandy 1944, Biscay 1944-45, Arctic 1942.
Maps for Movements of 422 Squadron 1942-45
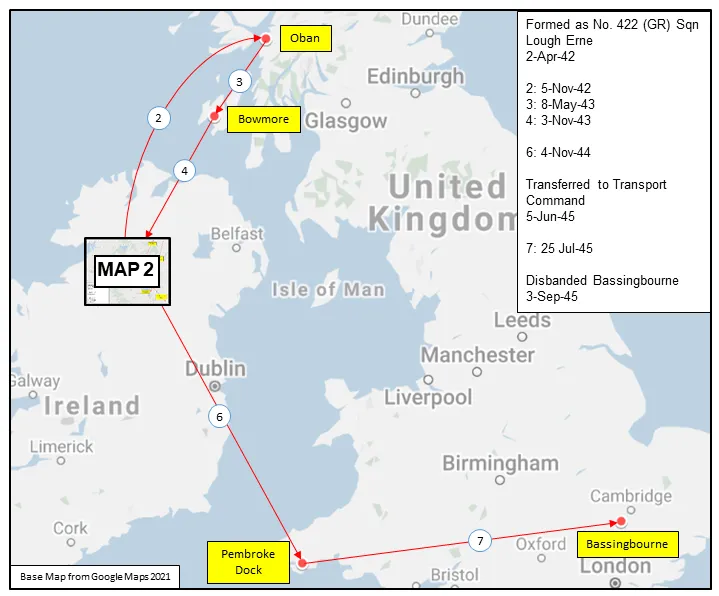
MAP 1: 422 Squadron Movements 1942-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
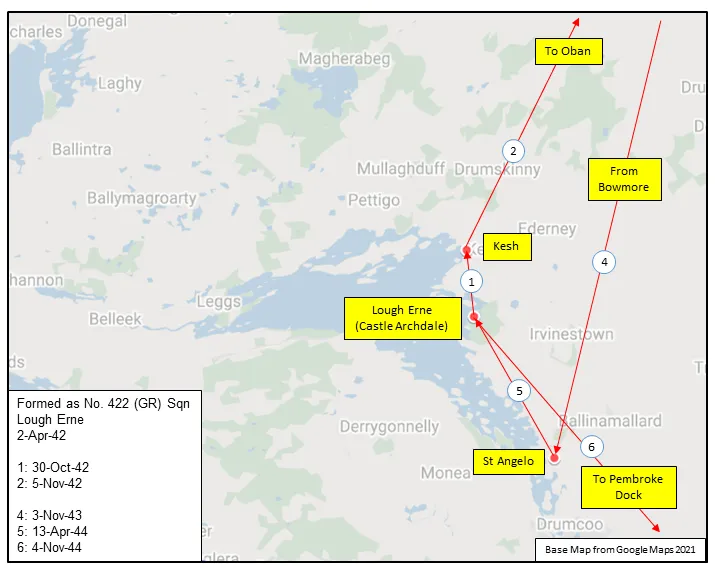
MAP 2: 422 Squadron Movements 1942-45 (detail of Map 1)
|
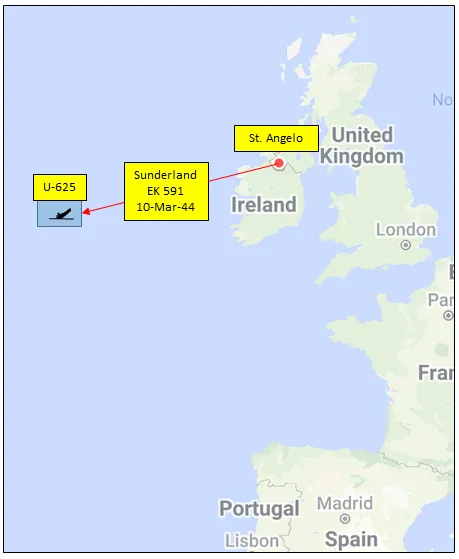
![]() 422 Squadron in the Battle of the Atlantic (RCAF Museum)
422 Squadron in the Battle of the Atlantic (RCAF Museum)
422 Squadron History Summary 1942-45
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Sabre Mk. 2, 4, 5, 6, Starfighter, Huey, Kiowa)
The squadron was re-formed as a Fighter unit at Uplands (Ottawa), Ontario ![]() on 1 January 1953 with Canadair Sabre aircraft, and joined No. 4 (Fighter) Wing at Baden-Soellingen, Germany
on 1 January 1953 with Canadair Sabre aircraft, and joined No. 4 (Fighter) Wing at Baden-Soellingen, Germany ![]() in August. Its nickname was changed to "Tomahawk". Selected as one of eight Sabre units in No. 1 Air Division Europe to be re-equipped with CF-104 Starfighter aircraft for a nuclear strike role, it was deactivated on 15 April 1963 and reactivated as Strike Attack on 15 July. On 1 February 1968 the squadron was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces. The squadron was deactivated in July, 1970. The squadron was reactivated as 422 Tactical Helicopter Squadron in January 1971, and remained a helicopter squadron until it was finally disbanded in August 1980.
in August. Its nickname was changed to "Tomahawk". Selected as one of eight Sabre units in No. 1 Air Division Europe to be re-equipped with CF-104 Starfighter aircraft for a nuclear strike role, it was deactivated on 15 April 1963 and reactivated as Strike Attack on 15 July. On 1 February 1968 the squadron was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces. The squadron was deactivated in July, 1970. The squadron was reactivated as 422 Tactical Helicopter Squadron in January 1971, and remained a helicopter squadron until it was finally disbanded in August 1980.



