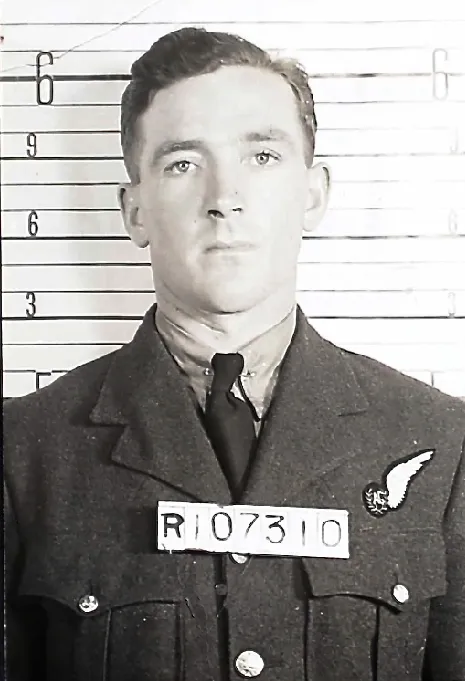
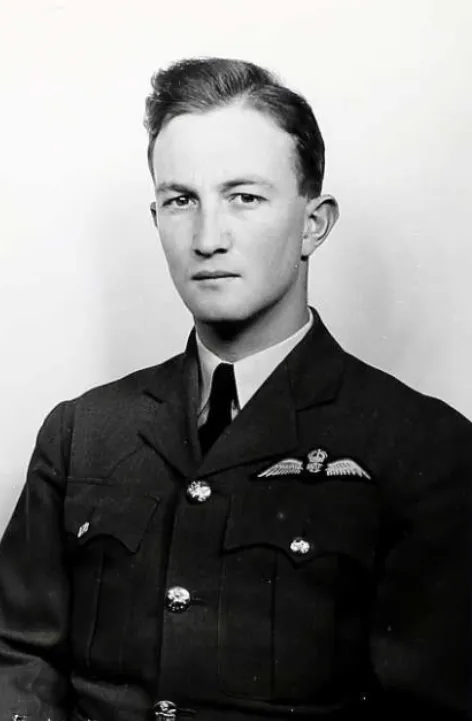
Doyle, Gordon James (Pilot Officer)
Killed in Action 1945-January-28
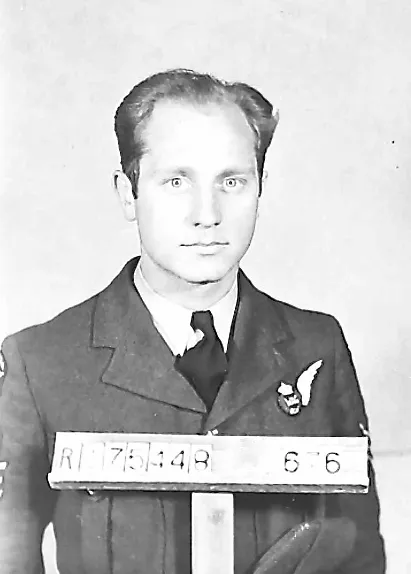


Birth Date: 1922
Born: Toronto, Toronto Municipality, Ontario, Canada
Parents: Son of Mr and Mrs J T Doyle, of Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Spouse:
Home: Toronto, Ontario
Enlistment: Toronto, Ontario
Enlistment Date: 1941-June
Service
RCAF
Unit
424 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Castigandos Castigamus Chastise those deserving
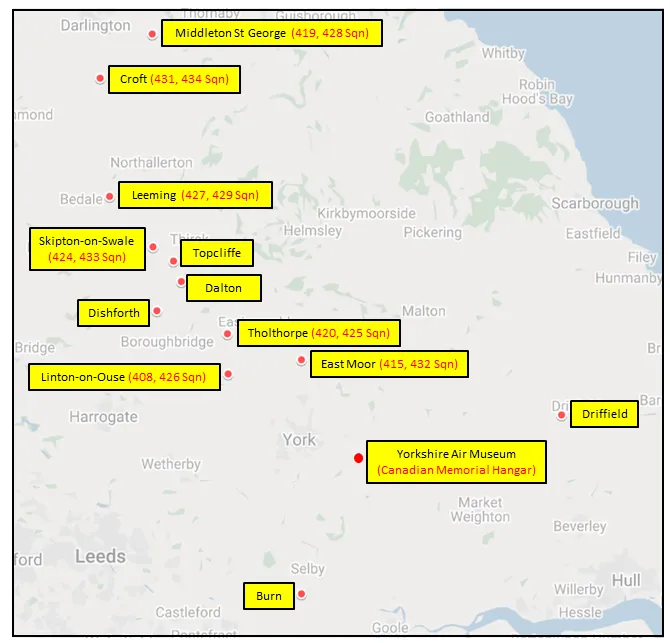
Base
RAF Skipton-on-Swale
Rank
Pilot Officer
Position
Wireless Operator/Air Gunner
Service Numbers
J/94856
Prev: R/175448
Crew or Other Personnel
Halifax LW164
Mission
Halifax B.Mk.III LW164
Bombing Stuttgart Germany 1945-January-28 to 1945-January-28
424 (B) Sqn (RCAF) RAF Skipton-on-Swale
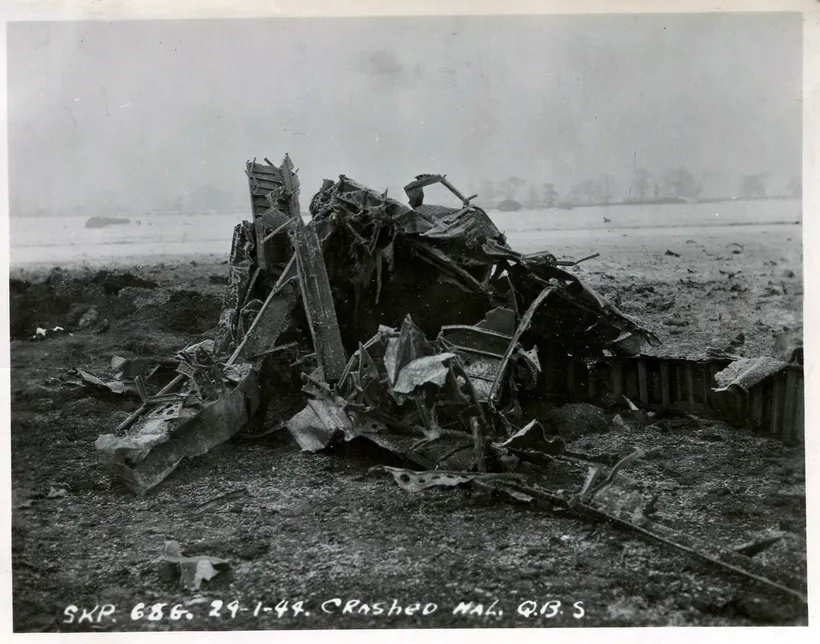
424 Tiger Squadron (Castigandos castigamus) RAF Skipton-on-Swale. Halifax BIII aircraft LW 164 QB-C swung on take-off for an operation against targets in Stuttgart, Germany, crashed and exploded, killing all members of the crew with the exception of the rear air-gunner, who was thrown clear. Flying Officer J E H B Tremblay (RCAF) survived, severely injured
Wing Commander E M Williams AFC (RCAF), Pilot Officer R E Chatfield (RCAF), Pilot Officer D J Doyle (RCAF), Flying Officer w Fleming (RCAF), Pilot Officer R J Nicolls (RCAF) and Sergeant L Tongue (RAFVR) were all killed in action in the crash
![]() Royal Air Force serial and Image Database
Royal Air Force serial and Image Database
![]() Aircraft accidents in Yorkshire
Aircraft accidents in Yorkshire


On 1945-01-28, Squadron Leader A. Ross Dawson, the Chief Technical Officer with 424/433 Sqns at Skipton on Swale, wrote in his diary:
Warning: The following material contains graphic content that may not be suitable for all readers
"Well, we had quite an exciting day (and tragic too) as seems to happen quite frequently on Sundays. We got 8 a/c from 424 & 6 from 433 all ready to go on an op to Stuttgart. The bomb load, 1 2000 pounder plus 12 500 lb clusters of incendiaries; 10% of these being the explosive type. Everything was shaping up well just before take off at 7:15 pm & all the kites were lined up raring to go. Old Sanders was off first in 424 in "O" for Oboe & then W/C Clyde Marshall in "T" Tare. The runway was pretty icy but it didn't seem to bother them much. I was up in the Control tower as per usual checking the kites as they took off. W/C Ted Williams who was to take over 424 Sqdn from Marshall when he finished his tour was third off in S for Sugar. I watched his lights down the runway & thought he was safely airborne when for some unaccountable reason the lights didn't seem to lift as they should & the thought flashed through my mind Oh oh, here it comes! Sure enough it did! If it hadn't been so horrible it might have been very pretty. A great blinding flash of flame rose up followed by thick billowing clouds of black smoke right at the intersection of the two runways. At intervals of a second or so the pyrotechnics were going off in all colours of the rainbow & then the incendiaries started with their vivid white flames interspersed with the occasional explosive one which sent up streamers of white fire in all directions & silhouetted against the black clouds of smoke & reddened by the flames underneath. It looked very much like the Toronto Ex. fireworks especially with the sharp chattering of the machine gun ammunition going off in the background.
"The crash trucks & ambulance raced out immediately while we endeavored to think out a way of getting the other 11 a/c away on the op which of course always comes first. Unfortunately the crash blocked off the only two cleared runways while the third hadn't been cleared of snow yet so we were stuck & cancelled the rest of the op for good.
"When the crash occurred, it shook the building a little but not as much as if a big bomb had gone off so we decided that the 2000 pounder hadn't gone off yet. We knew from experience that it takes almost 1/2 hour for a 2000 pounder to heat up enough to blow up in a fire so we had to work fast to prevent any more damage to the aircraft parked near the crash. W/C Tambling & I raced out in his car to see what we could do with 15 minutes of our 1/2 hour grace already gone. We picked up Squadron Leader Stinson on the way & decided to start up and taxi the two nearest kites away from the vicinity. I climbed in with Tambling first to get him started & noticed he was so excited he tried starting the engines without turning on the fuel cocks nor his booster mag switches. For some reason or other I hadn't got too excited yet & fixed him up ok. The minutes just seem to tear by before we got him started up & away he went. I hopped out then to get Stinson going. He hadn't even got his engines started yet & there was less than 5 minutes to go! I had to make up my mind whether to start running for safety or go to help him which of course didn't leave much choice. Exactly on the 1/2 hour mark we got two of the four engines going but to get out of the dispersal area we had to taxi up nearer the blazing wreckage than ever; about 50' or so between me & a 2000 pounder ready to go up at any second; more darn fun. Anyway, after what seemed ages & ages we made it out ok & got well away from the crash.
Back at the control tower the crash truck had returned to say that there was one survivor; the tail gunner who was only slightly bruised but was quite dazed from shock & found wandering around on his feet amongst the debris. By the time an hour was up the fire almost out & still no bomb gone off, we ventured out to find a great crater about 20 feet deep & 40' across; it had gone off the moment of impact! All our taxiing a/c to safety was for nothing but still exciting enough when we didn't know what was going to happen. Blasts always seems to work in peculiar ways & what seemed to us like a very small explosion from petrol tanks from the comparatively close vicinity of the control tower shook everything up as far away as Leeming & threw people out of bed a few miles away. The bodies were all recovered finally in pieces & so we packed up for the night to get some sleep. As a slight aftermath, when I got to my billet all the parcels & groceries which I had sitting on a shelf in my room had been blown off on to the floor including my nice birthday cake; candles & all which I hadn't eaten yet; the one Mrs. Mac sent me." Note: This is the event that Squadron Leader Dawson believes was the reason he received an MBE.
Despite the loss of Halifax BIII LW164 and her crew, the operation ahead: 602 aircraft - 316 Halifaxes, 258 Lancasters, 28 Mosquitoes - of 1, 4, 6 and 8 Groups. 11 aircraft - 6 Lancasters, 4 Halifaxes, I Mosquito - lost.
This raid was split into 2 parts, with a 3-hour interval. The first force - of 226 aircraft - was directed against the important railway yards at Kornwestheim, a town lo the north of Stuttgart, and the second was against the north-western Stuttgart suburb of Zuffenhausen, where the target is believed to have been the Hirth aero-engine factory. The target area was mostly cloud-covered for both raids and the bombing, on sky-markers, was scattered.
There are some interesting local reports. Bombs fell in many parts of Stuttgart's northern and western suburbs. The important Bosch works, in the suburb of Feuer-bach, was hit. The attack on Kornwestheim was the worst suffered by that town during the war; the Kornwestheim local report shows that the local people felt they had been bombed by mistake and that the main target was in Stuttgart. 14 high, explosive bombs fell in the industrial area of the town and in the railway yards. Fires burned for up to 12 hours. 123 people were killed in Stuttgart and 41 in Kornwest-. heim. A large number of bombs fell outside Stuttgart, particularly in the east around a decoy fire site which was also firing dummy target-indicator rockets into the air. The village of Weilimdorf, situated not far away, complained bitterly about its damage and casualties!
Our local expert, Heinz Bardua, also tells the story of the newly promoted Flak Leutnant at his battery position at Vaihingen, situated just south of the decoy fire site. With bombs falling all around his position, the Leutnant thought that the raid was directed against the Flak positions. He ignored regulations about conservation of ammunition and shot his entire stock at the radar echoes of the attacking bombers, 2 Lancasters and a Halifax crashed in the immediate vicinity, much to the relief of the officer, who had feared a court martial because of his prodigious use of ammunition.
This was the last large R.A.F. raid on Stuttgart. Herr Bardua says that the city had endured 53 major raids, most of them by the R.A.F., during which 32,549 blocks of flats or houses were destroyed (67 per cent of the total). After the war, 49 million cubic metres of rubble had to be cleared. 4,562 people died in the air raids, among them 770 prisoners of war or foreign workers. Stuttgart's experience was not as severe as other German cities. Its location, spread out in a series of deep valleys, had consistently frustrated the Pathfinders and the shelters dug into the sides of the surrounding hills had saved many lives
Halifax serial: LW164
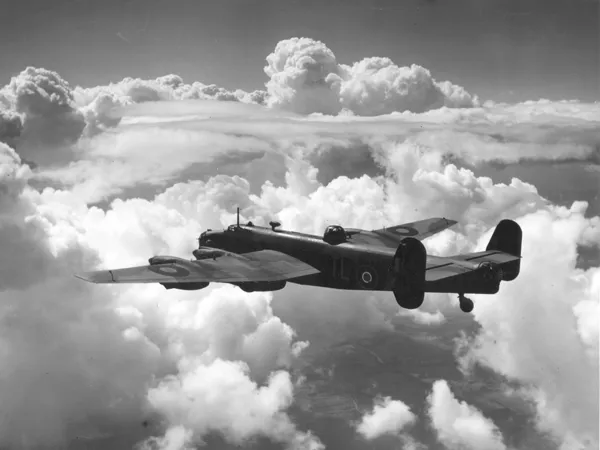

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces. Wikipedia
Unit Desciption
424 (B) Sqn Castigandos Castigamus ("Tiger")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington III, X, Halifax III, Lancaster I, III)

424 Squadron was the sixth RCAF bomber squadron to be formed overseas in WWII, at Topcliffe, Yorkshire, UK ![]() on October 15, 1942, originally as part of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. It remained at Topcliffe when it was transferred to the newly-formed 6 (RCAF) Group on January 1, 1943. It moved to Leeming, Yorkshire
on October 15, 1942, originally as part of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. It remained at Topcliffe when it was transferred to the newly-formed 6 (RCAF) Group on January 1, 1943. It moved to Leeming, Yorkshire ![]() , and then Dalton, Yorkshire
, and then Dalton, Yorkshire ![]() , flying Vickers Wellington Mk III and X aircraft before being dispatched on June 22, 1943 to No 331 (RCAF) Wing of No 205 Group in Tunisia (Kairouan/Zina
, flying Vickers Wellington Mk III and X aircraft before being dispatched on June 22, 1943 to No 331 (RCAF) Wing of No 205 Group in Tunisia (Kairouan/Zina ![]() and Hani East
and Hani East ![]() airfields), from where it flew in support of the invasions of Sicily and Italy. It returned by sea to Skipton-on-Swale, Yorkshire
airfields), from where it flew in support of the invasions of Sicily and Italy. It returned by sea to Skipton-on-Swale, Yorkshire ![]() in October/November 1943. It re-equipped with Handley Page Halifax Mk III aircraft, which it flew until January 1945, when it re-equipped with Avro Lancaster I and III aircraft. After the termination of hostilities in Europe, the squadron was transferred to No 1 Group, and was employed in operation DODGE, the repatriation of British and Canadian troops from Italy. It was disbanded at Skipton on October 15, 1945, 3 years to the day since its formation.
in October/November 1943. It re-equipped with Handley Page Halifax Mk III aircraft, which it flew until January 1945, when it re-equipped with Avro Lancaster I and III aircraft. After the termination of hostilities in Europe, the squadron was transferred to No 1 Group, and was employed in operation DODGE, the repatriation of British and Canadian troops from Italy. It was disbanded at Skipton on October 15, 1945, 3 years to the day since its formation.
In the course of hostilities, the squadron flew 3257 sorties for the loss of 52 aircraft. 8776 tons of bombs were dropped. Crew members were awarded 1 DSO, 49 DFC's and 1 Bar to DFC, 1 CGM, 11 DFM's and 1 MiD. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943-45, Baltic 1944-45, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1943-44, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1944, German Ports 1943-45, Nornamdy 1944, Rhine, Bisacy 1943-44, Sicily 1943, Italy 1943, Salerno.Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 424 Squadron 1942-45
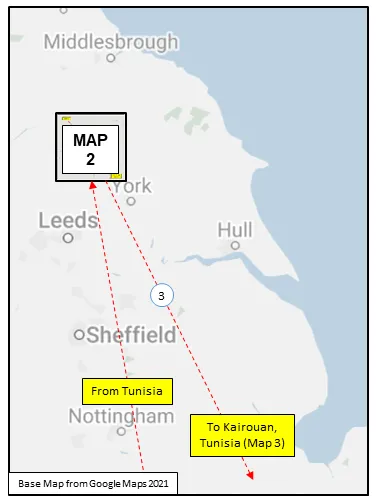
MAP 1: 424 Squadron Movements 1942-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
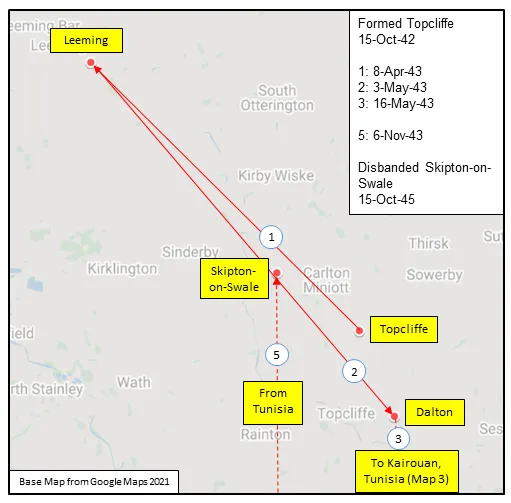
MAP 2: 424 Squadron Movements 1942-45 (detail of Map 1)
|
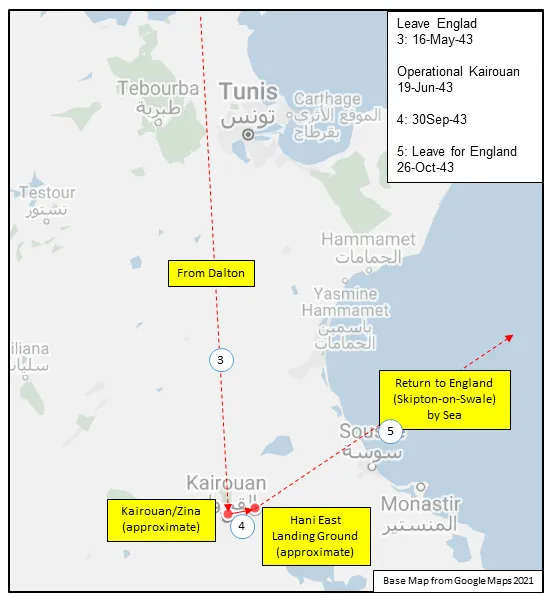
MAP 3: 424 Squadron Movements in North Africa 1943
|
424 Squadron History Summary 1942-45
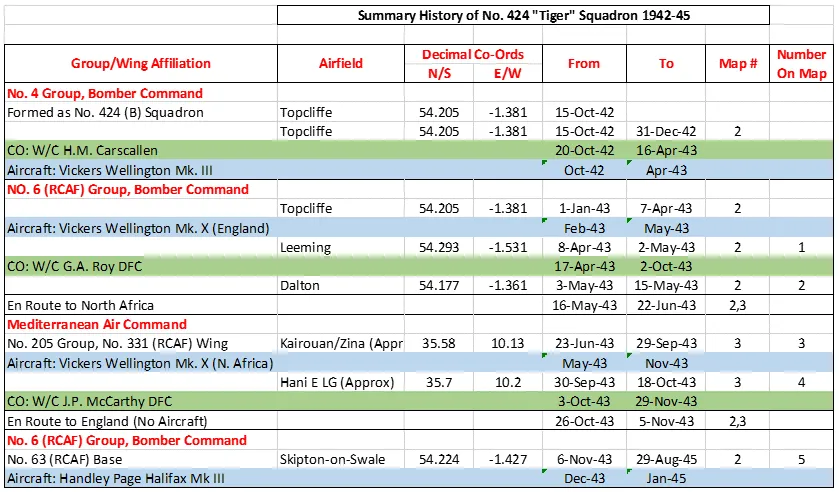
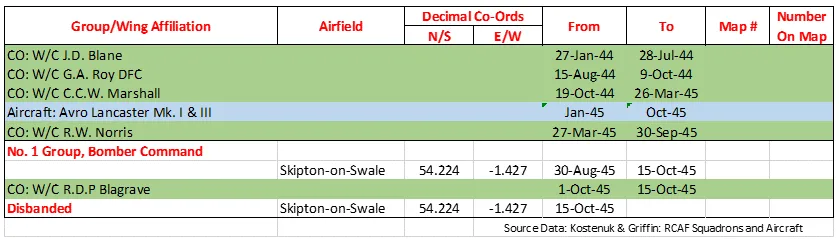
424 Squadron History Summary 1942-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard II, Mustang IV, Silver Star 3, Expeditor, Otter, Griffon, Hercules)
The squadron was re-formed at Mount Hope, Hamilton, Ontario ![]() on 15 April 1946, as a light bomber unit. It was redesignated as an auxiliary fighter unit on 1 April 1947. It flew North American Harvard II and Mustang IV aircraft in a fighter role, as well as Canadair Silver Star aircraft until 1 September 1957 when it was then reassigned as a light transport and emergency rescue role and re-equipped with Beechcraft Expeditor and de Havilland Otter aircraft. On 21 October 1961 the unit received its Squadron Standard for 25 years’ service as No. 119 and 424 Squadron. A reduction of the Auxiliary Force resulted in the squadron being disbanded on 1 April 1964. On 8 July 1968, with unification of the Canadian Forces, the squadron was reactivated as 424 Communications and Transport Squadron, operating from CFB Trenton, Ontario
on 15 April 1946, as a light bomber unit. It was redesignated as an auxiliary fighter unit on 1 April 1947. It flew North American Harvard II and Mustang IV aircraft in a fighter role, as well as Canadair Silver Star aircraft until 1 September 1957 when it was then reassigned as a light transport and emergency rescue role and re-equipped with Beechcraft Expeditor and de Havilland Otter aircraft. On 21 October 1961 the unit received its Squadron Standard for 25 years’ service as No. 119 and 424 Squadron. A reduction of the Auxiliary Force resulted in the squadron being disbanded on 1 April 1964. On 8 July 1968, with unification of the Canadian Forces, the squadron was reactivated as 424 Communications and Transport Squadron, operating from CFB Trenton, Ontario ![]() . The squadron has flown more than 14 different types of aircraft during its history.
. The squadron has flown more than 14 different types of aircraft during its history.
424 (Tiger) Squadron is now a Transport and Rescue Squadron based at 8 Wing Trenton. To fulfil its roles, 424 Squadron operates the CH-146 Griffon helicopter and the CC-130H Hercules. 424 Squadron and 435 Transport and Rescue Squadron provide primary search and rescue response for the Trenton Search and Rescue Region (SRR), the largest in Canada. The Trenton SRR extends from Quebec to the British Columbia/Alberta border, and from the Canada/United States border to the North Pole. The Squadron crews one aircraft of each type on standby response posture in order to respond to distress cases as tasked by Joint Rescue Coordination Centre Trenton.
In addition to providing SAR response through a para-rescue capability, the CC-130H Hercules allows the squadron to conduct its transport role in Canada and around the world. The CH-146 Griffon enables rescues and medical evacuations from locations on land and over water. Both aircraft carry Search and Rescue Technicians onboard in order to provide urgent care to those in need. The members of 424 Squadron provide SAR response to incidents under the federal SAR mandate; all aircraft incidents and all marine incidents in waters under federal jurisdiction. They also support humanitarian missions and other SAR organizations when able. Wikipedia and www.canada.ca/en/air-force/corporate/squadrons/424-squadron.html






