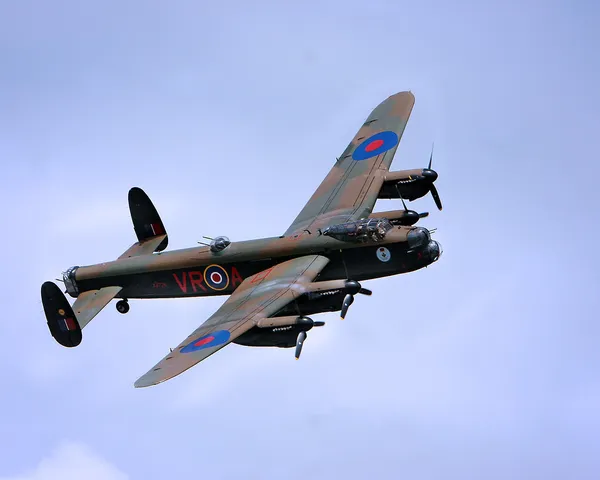
Avro Type 683 Lancaster
| General Characteristics |
| Crew: |
7 (typical) |
| Length: |
69 ft 6 in (21.18 m) |
| Wingspan: |
102 ft 0 in (31.09 m) |
| Height: |
20 ft 6 in (6.25 m) |
| Wing area: |
1,300 sq ft (120 m2) |
| Aerofoil: |
Root: NACA 23018. Tip: NACA 23012 |
| Empty weight: |
36,900 lb (16,738 kg) |
| Max takeoff weight: |
72,000 lb (32,657 kg) |
| Fuel capacity: |
2,154 imp gal (9,792 L) |
|
|
| Powerplants: |
Lancaster Mk.I, III, VI, VII & X:
- 4 x Rolls-Royce, Packard or Ford UK built Merlin XX, 22, 24, 28, 85 or 224 liquid-cooled
V-12 piston engines
with power output between 1,280 hp (954 kW) and 1,635 hp (1,219 kW) each
Lancaster Mk.II:
- 4 x Bristol Hercules Mk.VI or XVI air-cooled 14-cylinder radial piston engines with power
output of 1,615 hp
(1,204 kW) each
|
|
|
|
Propellers: |
Lancaster Mk.I, III, VI, VII & X:
- 3-bladed de Havilland, Hamilton Standard or Nash Kelvinator Hydromatic constant-speed fully
feathering metal
bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m) diameter
Lancaster Mk.II:
- Rotol electric constant-speed fully feathering wooden bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m)
diameter
|
| Performance: |
|
Maximum speed: |
- Lancaster Mk.I, II, III, VII & X: 287 mph (461 km/h)
- Lancaster Mk.VI: 315 mph (507 km/h)
- Cruising speed: 207 mph (333 km/h)
- Range: 2,530 mi (4,073 km)
- Service ceiling: 23,500 ft (7,162 m)
|
| Armament: |
|
Standard:
|
- Two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in:
- Nash and Thompson FN5 nose and
- FN50/150 mid-upper turrets,
- four 0.303-inch Browning Mark II machine guns in Nash and Thompson FN20/120/121 rear turret
|
|
|
|
Alternative/additional: |
- Nash and Thompson FN64 ventral turret with two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns
- Glenn Martin 250CE electrically operated mid-upper turret with two 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2
machine
guns (Lancaster Mk.VII and late production Lancaster Mk. X only)
- Nash and Thompson FN82 rear turret with two 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine guns
(Lancaster Mk.VII &late production Lancaster Mk.I only)
- Rose Brothers Type R rear turret with two 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine guns
(late production Lancaster Mk.I & III only)
- Ventral 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mk.II machine gun in a free mount (Lancaster Type 464 only)
- Ventral 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine gun in a free mount
- ARI 5559 A.G.L.T. 'Village Inn' Mk.I: Radar guided gun laying system (incorporating Infrared IFF
recognition system) fitted to FN121 rear turret with four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II
machine guns
|
|
|
| Bomb loads: |
Typical:
- 14,000 lb (6,350 kg) consisting of varying combinations of 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 4,000 lb HC,
8,000 lb HC, 250 lb, 500 lb, 1,000 lb bombs, or various sizes of incendiary bombs installed in Small
Bomb
Containers or Cluster Projectiles
- 1 x 12,000lb (5,443 kg) HC bomb
- 6 x 1,850 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines
Specialized:
- 1 x 5,500 lb (2,494 kg) Capital Ship Bomb
- 12 x 500 lb (226 kg) JW 'Johnny Walker' Oscillating Mine
- 1 x 9,250 lb (4,195 kg) Vickers-Armstrongs Type 464 'Upkeep' revolving depth charge
- 1 x 12,000lb (5,443 kg) MC Vickers-Armstrongs 'Tallboy' deep penetration bomb
- 1 x 22,000 lb (9,979 kg) MC Vickers-Armstrongs 'Grand Slam' deep penetration bomb
|
|
|
|
| Communication and navigation equipment:
|
- TR9F: HF R/T radio transceiver
- TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver
- TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver
- T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter
- R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver
- ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system
- ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system
- TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of radar navigation beacons,
Eureka beacons & IFF
- ARI 5525/5597 GEE-H Mk.I/II: Radio navigation/target finding system
- AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system
- ARI 5148/5514/5582 Oboe Mk.I & II: Radar bomb aiming system
- AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter
- SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter
- Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system
|
|
|
|
| Radio Countermeasures: |
- ARI 5000/5025/5640 IFF Mk.II & III: Friend or Foe radar identification system
- ARI 5171/5625/5672/5769 Mandrel: Freya and Wurzburg radar jamming system
- ARI 5538/5557 Boozer Mk.I & II: Passive radar warning receiver
- ARI 5122/5281 Monica Mk.I, III & V ('Lulu'): Active tail warning radar
- Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S
- Monica-Fishpond ('Fishcake'): Hybrid tail warning radar
- Tinsel/Special Tinsel: Night fighter radio control jamming system
- TR3549 Airborne Cigar (ABC): Night fighter radio control jamming system
- ARI 5549 Carpet II: Wurzburg radar jamming system
|
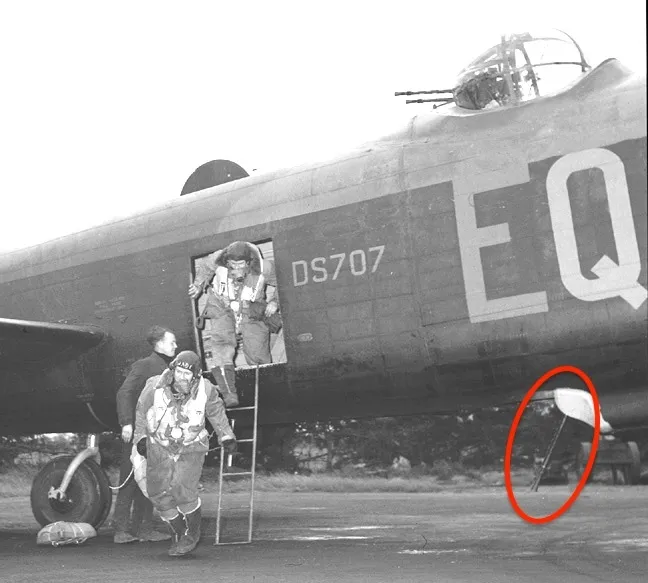
Ventral Turrets
Orginal Ventral Turret. Discontinued
early.
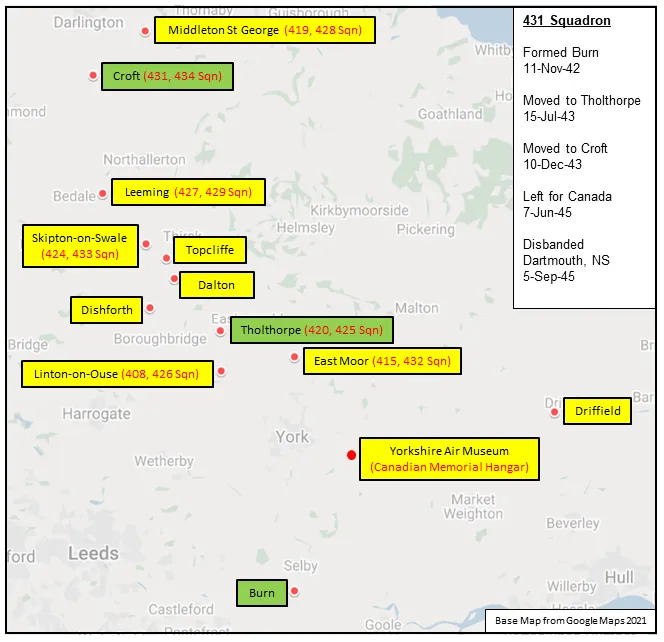
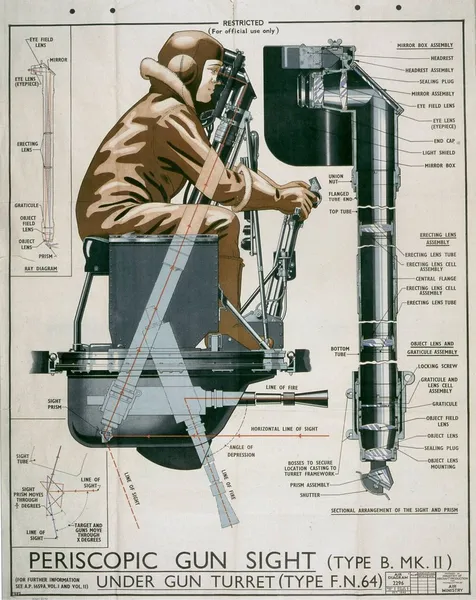
As originally designed the Lancaster was provided with ventral defence in the form of a Nash and Thompson
FN64 turret, which was fitted to some early production aircraft. However, in common with all other periscope sighted
ventral turrets, the narrow viewing angle made it almost impossible for gunners to acquire and track targets,
and the few turrets which were installed were soon removed from service.
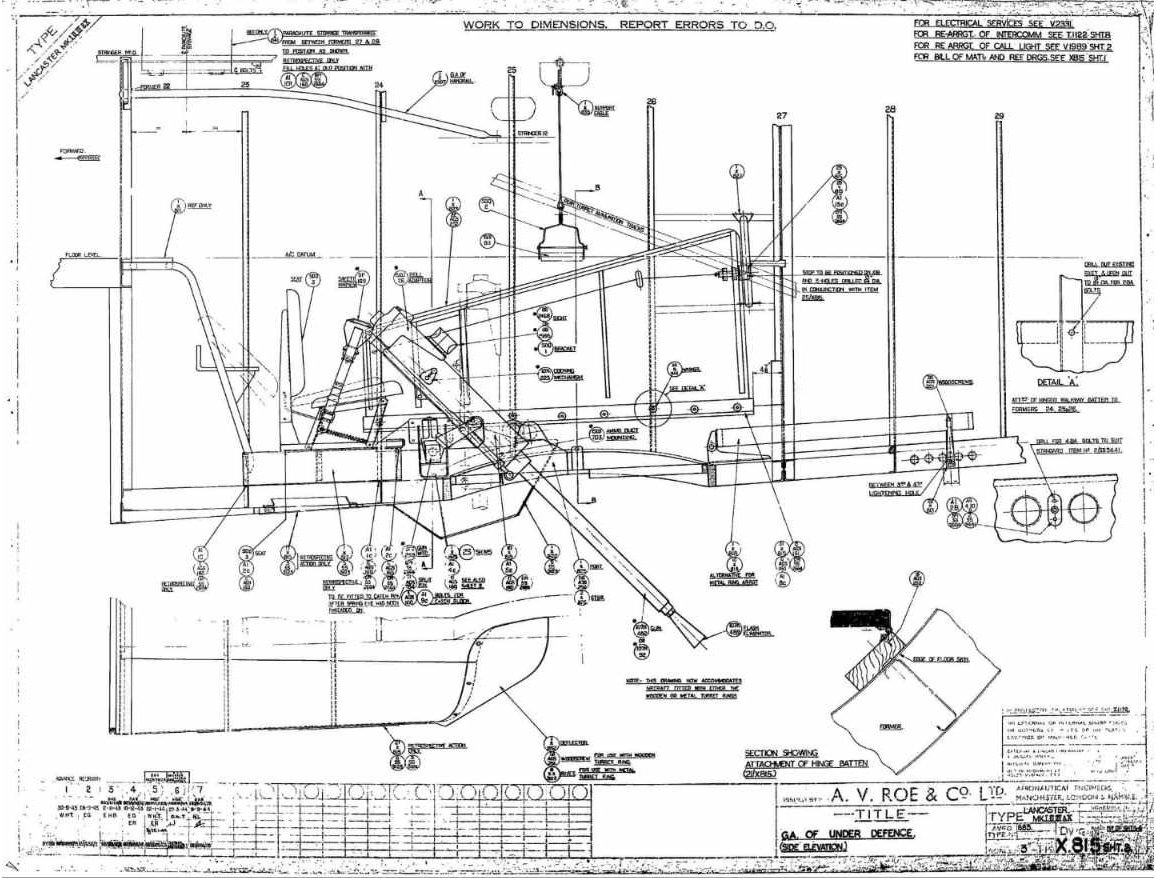
Note: 50 cal gun pointing at 45°
Original Drawings. Right click for larger view.
The ventral .50 inch (50 calib) was approved as Lanc Mod.925 during February 1944, and was one of a number of
unsuccessful
measures taken to counter night fighter attacks from below.
The growth of the Luftwaffe night fighter force was followed by an increase in the in the number of attacks from
below, exacerbated from August 1943 onward by the introduction of aircraft equipped with Schrage Musik upward firing
20mm cannon. A number of responses were considered by Bomber Command including a free mounted ventral .50 calibre
Browning machine gun, which was approved on the Lancaster as Modification 925 during February 1944.
The modification was very basic, consisting of little more than an enlarged bicycle seat for the gunner and a simple
free mounted gun with open sights which fired through the ventral turret/H2S aperture. On aircraft with bulged bomb
doors the mounting (often unpainted) was incorporated into the fairing at the rear of the doors.
Non-H2S fitted aircraft were sporadically equipped with the gun from February 1944 onward, although a clear plan for
installation appears to have been lacking.
The quantity of aircraft which actually had the gun installed is unknown and photos of the mounting with a Browning
actually installed are very rare.
Serious problems quickly became apparent, as noted in the following V Group monthly newsletter for
April 1944:- "With the gunner strapped in his seat it is difficult to follow the gun round on the beam;
it is difficult for the gunner to get his head down behind the sight as it tends to push the oxygen mask upwards on
the gunners face; and also considerable vibration is experienced on the sight when the gun is fired."
These problems, plus the gradually more widespread introduction of H2S saw the gun fall out of use quite quickly,
although it does appear to have been retained on some aircraft until war's end (most notably in 3 Group).
The quantity of aircraft which actually had the gun installed is unknown and photos of the mounting with a Browning
actually installed are very rare.
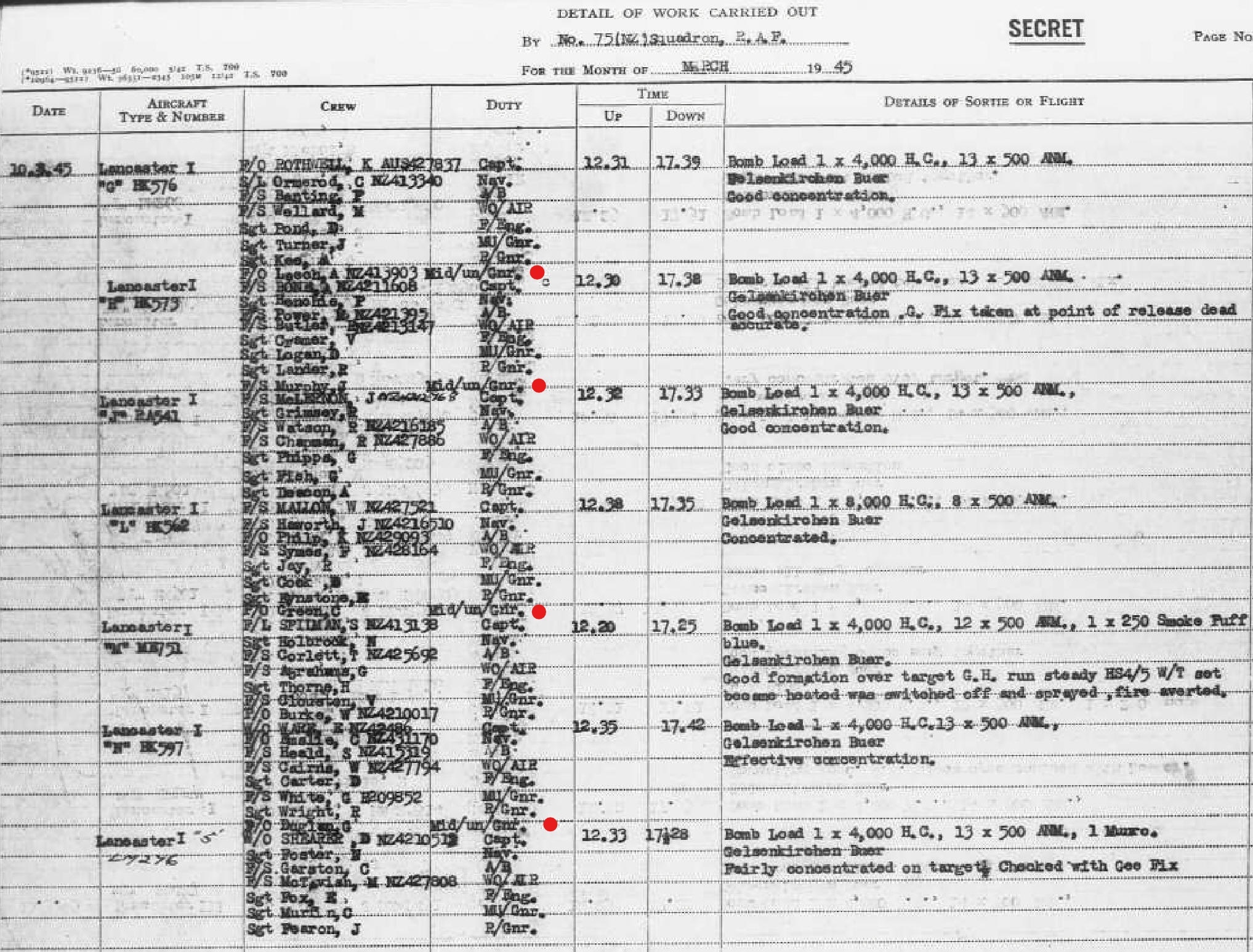
75 Squadron ORB March 1945
Notice on these aircraft the extra position in the eight person crew of Mid-Under-Gunner.