Handley Page Halifax
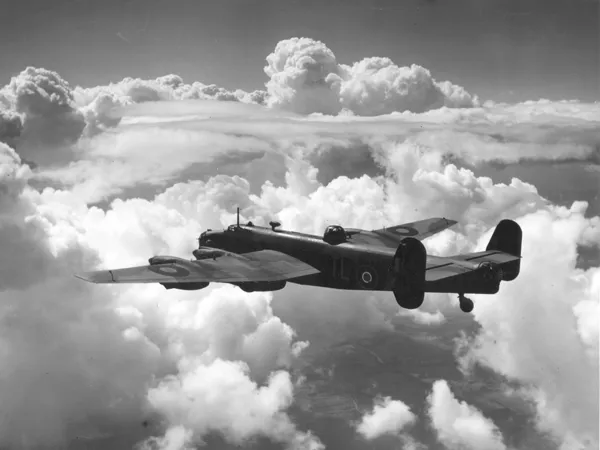

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces. Wikipedia
 National Air Force Museum of Canada
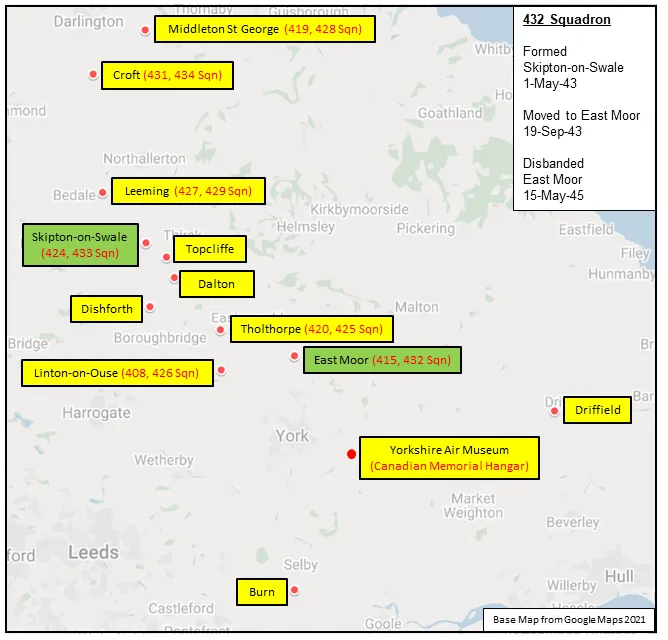
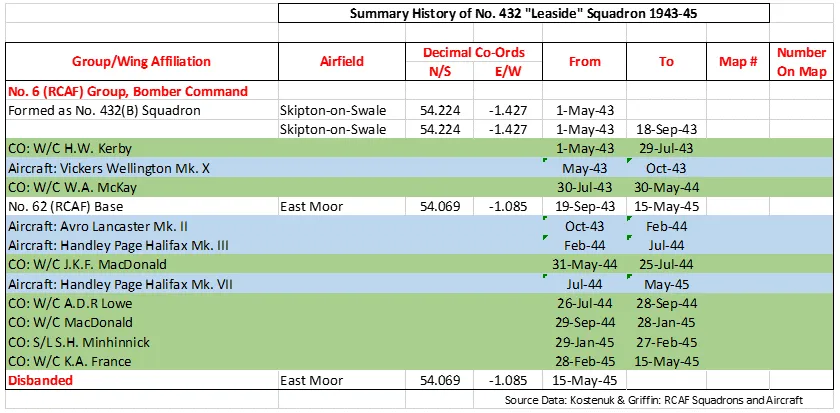
National Air Force Museum of Canada
CASPIR Aircraft Groups:
RCAF On Strength (5), RCAF 6 Group (1596), RCAF 400 Squadron (1443), Canadian Aircraft Losses (1562), Canadian Museum(2)Halifax B/A.Mk.III LW597
 C
C
1944-02-26 Failed to Return Failed to return from attack on Augsburg, shot down by a night fighter. 5 crew were killed and 2 POW. 2019-08-20




 Augsburg Germany
Augsburg Germany

 Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII
Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page Wikipedia Halifax Bomber
Wikipedia Halifax Bomber