Ross, Robert Alexander (Captain)
Killed in Flying Accident 1976-October-05
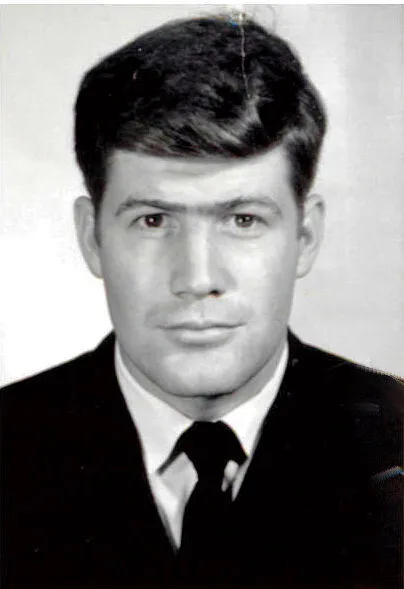


Birth Date: 1947
Born:
Parents: Son of Robert Davis Ross of Thorold, Ontario.
Spouse: Husband of Marilyn Louise (nee Brooks) Ross and father of Alicia and Caren of Dartmouth, Nova Scotia.
Home:
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
406 Sqn- Squadron
We Kill By Night
Base
Rank
Captain
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
247218
Unit Desciption
406 Sqn We Kill By Night ("Lynx")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Blenheim I & IV, Beaufighter IIF & VIF, Mosquito XII & XXX)

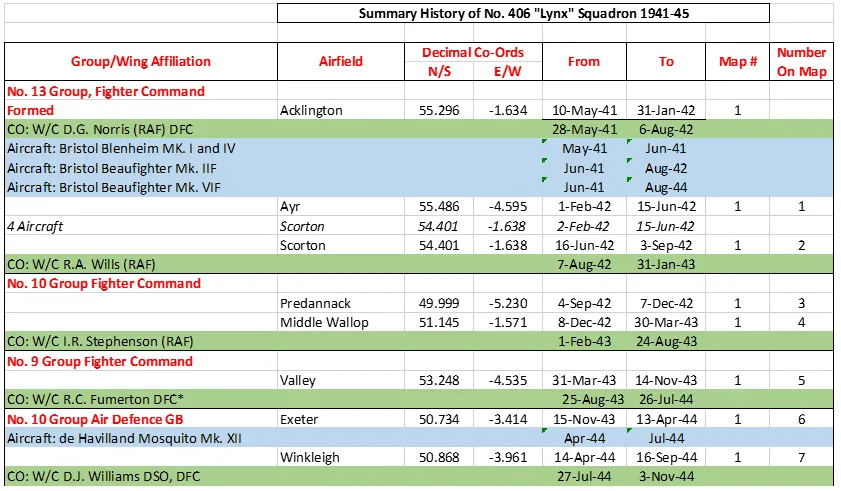
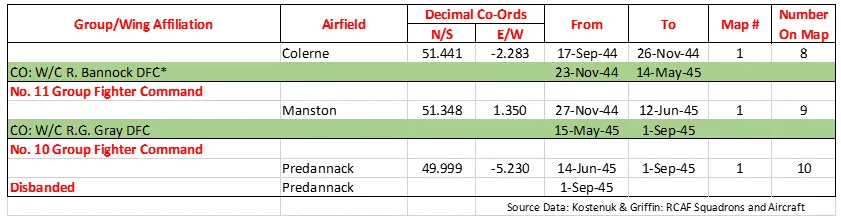
The Squadron was formed at Acklington, Northumberland, UK ![]() on May 10, 1941 as the RCAF's 5th squadron formed overseas, as a night-fighter unit. It flew Blenheim, Beaufighter and Mosquito aircraft in the night air defence of Great Britain role, before being re-designated as an Intruder squadron in November 1944. It was listed as the top scoring RAF/RCAF Intruder unit for the period November 27 1944 until the end of WWII. The squadron was disbanded at Predannack, Cornwall, UK
on May 10, 1941 as the RCAF's 5th squadron formed overseas, as a night-fighter unit. It flew Blenheim, Beaufighter and Mosquito aircraft in the night air defence of Great Britain role, before being re-designated as an Intruder squadron in November 1944. It was listed as the top scoring RAF/RCAF Intruder unit for the period November 27 1944 until the end of WWII. The squadron was disbanded at Predannack, Cornwall, UK ![]() on Sep 1, 1945.
on Sep 1, 1945.
Overall, the squadron claimed 64 enemy aircraft destroyed, 7 probables and 47 damaged. Also claimed were 88 locomotives and many other vehicles. Squadron operational losses were 11 aircraft, 20 aircrew killed or missing and 2 POWs. The squadron personnel were awarded 3 DSOs, 1 second Bar to DFC, 1 Bar to DFC, 14 DFCs, 2 DFMs and 4 Mentioned in Dispatches. Battle Honours were: Defence of Britain 1941-45, English Channel and North Sea 1944, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45: Biscay Ports 1944, Normandy 1944, Rhine: Biscay 1944.Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Maps for Movements of 406 Squadron 1941-45
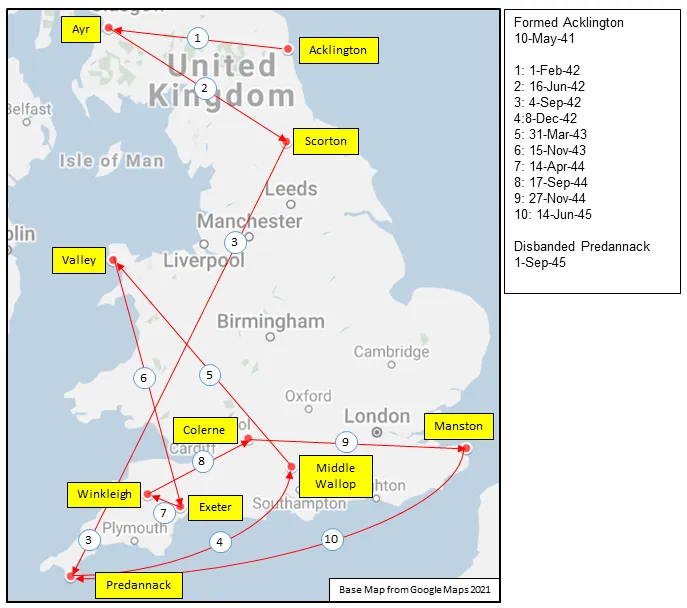
406 Sqn History Summary 1941-45
406 Sqn History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard II, Mitchell III, Silver Star, Expeditor, Otter, Sea King, Tracker, Cyclone)
The unit was re-formed as a reserve unit, 406 Tactical Bomber Squadron (Auxiliary) on 1 April 1947 at RCAF Station Saskatoon ![]() . It flew B-25 Mitchell III light bombers, and also Harvard and T-33 Silver Star aircraft for army co-operation duties. It was re-designated 406 (Light Bomber) Squadron on 1 April 1949 and adopted the title City of Saskatoon in September 1952. In March 1958 under the name 406 Squadron, it was re-equipped with C-45 Expeditor and later CSR-123 Otter aircraft, and assigned to a light transport and emergency rescue role. The squadron was disbanded again on 1 April 1964 as a result of the reduction of the Auxiliary Force.
. It flew B-25 Mitchell III light bombers, and also Harvard and T-33 Silver Star aircraft for army co-operation duties. It was re-designated 406 (Light Bomber) Squadron on 1 April 1949 and adopted the title City of Saskatoon in September 1952. In March 1958 under the name 406 Squadron, it was re-equipped with C-45 Expeditor and later CSR-123 Otter aircraft, and assigned to a light transport and emergency rescue role. The squadron was disbanded again on 1 April 1964 as a result of the reduction of the Auxiliary Force.
The squadron was re-formed for a third time at CFB Shearwater, Nova Scotia ![]() on 12 July 1972 as the 406 Maritime Operational Training Squadron, operating the CH-124 Sea King helicopter and the CP-121 Tracker ASW aircraft. In mid-1981, the operational Tracker squadron, 880 Maritime Reconnaissance Squadron, was transferred CFB Summerside, which left 406 Squadron only responsible for Sea King training. At the present time, the squadron trains pilots, Air Combat Systems Officers (ACSOs), and Airborne Electronic Sensor Operators (AES Ops) on the CH-148 Cyclone aircraft and flight operations relevant to the Maritime Helicopter (MH) role. In addition, the Squadron’s Technical Training Flight conducts a wide range of avionics and aviation courses for Cyclone technicians, as well as specialty maintenance courses. On an annual basis, between 200 and 300 students graduate from 406 Squadron. The squadron’s partner squadrons 423 Squadron in Shearwater, N.S., and 443 Squadron in Patricia Bay, B.C., employ 406 Squadron Cyclone graduates as integral members of helicopter air detachments aboard Her Majesty’s Canadian ships.
on 12 July 1972 as the 406 Maritime Operational Training Squadron, operating the CH-124 Sea King helicopter and the CP-121 Tracker ASW aircraft. In mid-1981, the operational Tracker squadron, 880 Maritime Reconnaissance Squadron, was transferred CFB Summerside, which left 406 Squadron only responsible for Sea King training. At the present time, the squadron trains pilots, Air Combat Systems Officers (ACSOs), and Airborne Electronic Sensor Operators (AES Ops) on the CH-148 Cyclone aircraft and flight operations relevant to the Maritime Helicopter (MH) role. In addition, the Squadron’s Technical Training Flight conducts a wide range of avionics and aviation courses for Cyclone technicians, as well as specialty maintenance courses. On an annual basis, between 200 and 300 students graduate from 406 Squadron. The squadron’s partner squadrons 423 Squadron in Shearwater, N.S., and 443 Squadron in Patricia Bay, B.C., employ 406 Squadron Cyclone graduates as integral members of helicopter air detachments aboard Her Majesty’s Canadian ships.