McGrath, John Felix (Flight Lieutenant)
Killed in Action 1942-July-21


Birth Date: 1918
Born:
Parents: Son of Felix and Runa McGrath, of North Battleford, Saskatchewan.
Spouse:
Home: Moose Jaw, Saskatchewan
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
400 Sqn- Squadron
Percussuri Vigiles On the watch to strike
Base
Rank
Flight Lieutenant
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
J/3517
Mustang serial: AG540
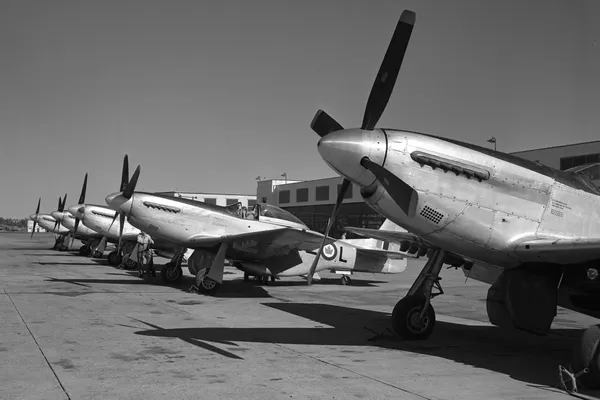

North American Mustang Mk. IV, RCAF (Serial No. 9253), coded BA-S,
No. 424 Squadron, Hamilton, Ontario
Chris Charland noted that the Mustang in the forefront is former USAF P-51D (Serial No. 44-74502A).
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James Kindelberger of North American Aviation (NAA) in response to a requirement of the British Purchasing Commission. The Purchasing Commission approached North American Aviation to build Curtiss P-40 fighters under license for the Royal Air Force (RAF). Rather than build an old design from another company, North American Aviation proposed the design and production of a more modern fighter. The prototype NA-73X airframe was rolled out on 9 September 1940, 102 days after the contract was signed, and first flew on 26 October
The Mustang was designed to use the Allison V-1710 engine, which had limited high-altitude performance in its earlier variants. The aircraft was first flown operationally by the RAF as a tactical-reconnaissance aircraft and fighter-bomber (Mustang Mk I). Replacing the Allison with a Rolls-Royce Merlin resulted in the P-51B/C (Mustang Mk III) model, and transformed the aircraft's performance at altitudes above 15,000 ft (4,600 m) (without sacrificing range), allowing it to compete with the Luftwaffe's fighters. The definitive version, the P-51D, was powered by the Packard V-1650-7, a license-built version of the two-speed, two-stage-supercharged Merlin 66, and was armed with six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) AN/M2 Browning machine guns.
Canada had five squadrons equipped with Mustangs during the Second World War. RCAF Nos. 400, 414 and 430 Squadrons flew Mustang Mk. Is (1942"“1944) and Nos. 441 and 442 Squadrons flew Mustang Mk. IIIs and Mk. IVAs in 1945. Wikipedia and Harold Skaarup web page
Unit Desciption
400 Sqn Percussuri Vigiles ("City of Toronto")
History of the Squadron before and during World War II (Aircraft:Lysander III, Tomahawk I, IIA, IIB, Mustang I, Mosquito PR Mk. XVI, Spitfire PR Mk. XII)

The squadron started life as No. 10 (Army Co-Operation) Squadron (Auxiliary) at Toronto in October 1932. In November 1937 the unit was renumbered No 110. On the outbreak of WWII, the squadron was mobilized and moved to Rockcliffe, ON, to train on Westland Lysander aircraft, having previously flown de Havilland DH-60 Moth, Fleet Fawn, Avro 621 Tutor, Avro 626, and de Havilland DH-82 Tiger Moth. The squadron arrived in England in February 1940. The squadron did not see action and with the fall of France, it remained in England, and was later renumbered as No. 400 (Army Cooperation) Squadron at Odiham, Hampshire, UK ![]() on March 1, 1941.
on March 1, 1941.
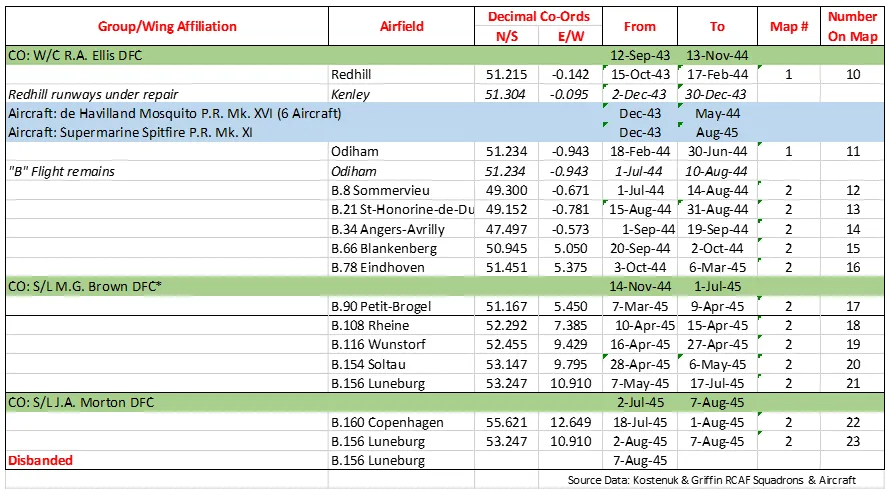
From then until 3 December 1942 the squadron was affiliated to No. 39 (Army Co-operation) Wing (RCAF), then it moved to Fighter Command (No 10 Group) at Dunsfold, Surrey. In December 1942 and January 1943 a section of aircraft flew in No 19 Group of Coastal Command providing fighter cover over the Bay of Biscay from airfields at Portreath and Trebelzue, Cornwall. The squadron rejoined 10 Group and then rapidly returned in January 1943 to No 39 Army Co-operation Wing, by now designated as a Fighter Reconnaissance (FR) Squadron. It then formed part of the 2nd Tactical Air Force, based successively at Woodchurch, Kent, Redhill, Surrey and Odiham, Hampshire. With squadron code letters SP, the squadron flew Curtiss Tomahawks, North American Mustangs and Supermarine Spitfires on photo-reconnaissance work, collecting intelligence information to help to plan the D-Day invasion, and later on the effects of bombing of V-1 launch sites. From December 1943 to May 1944 the squadron aircraft included 6 Mosquito PR Mk XVI. Shortly after D-day the Squadron moved to airfields in France, and provided tactical photographic reconnaissance for the British Second Army. As the armies moved forwards, the squadron followed, flying from bases in France, Belgium, The Netherlands and Germany. The squadron was finally disbanded at Luneburg, Germany ![]() in August 1945.
in August 1945.
In the course of the war, the squadron flew around 3000 sorties, for the loss of 12 pilots killed or missing. They destroyed numbers of enemy aircraft and attacked numerous trains and locomotives. They were awarded 10 DFC's, 1 Bar to DFC, 1 BEM, 3 MiD's. Battle Honours include Fortress Europe 1941–44, Dieppe, France and Germany 1944–45, Normandy 1944, Arnhem, Rhine, Biscay 1942–43 Kostenuk and Griffin
Maps for Movements of 400 Squadron 1940-45
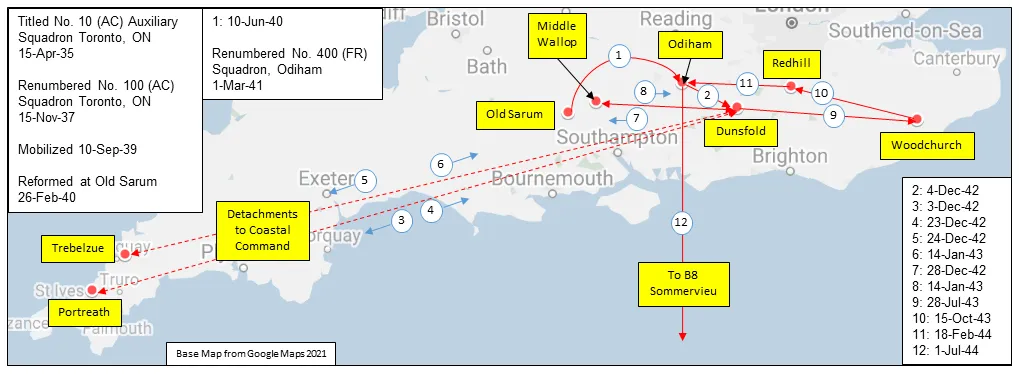
MAP 1: 400 Squadron Movements in Britain 1940-44, (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
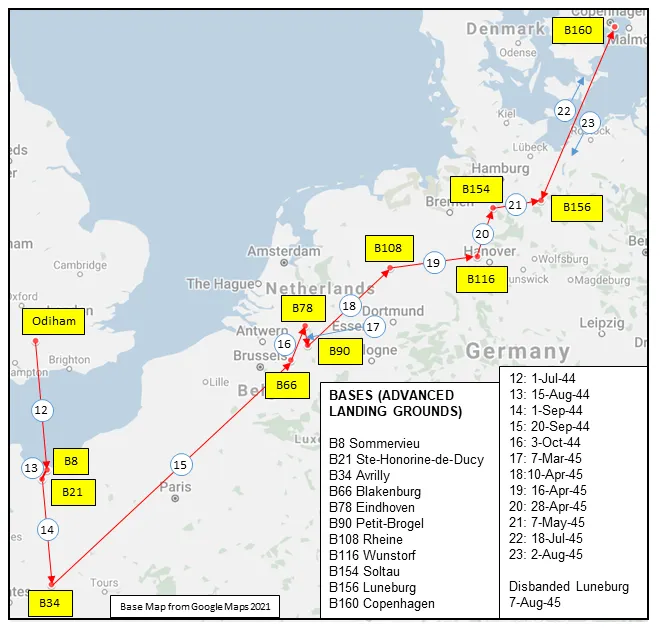
MAP 2: 400 Squadron Movements in Europe 1944-45
|
400 Sqn History Summary 1939-45
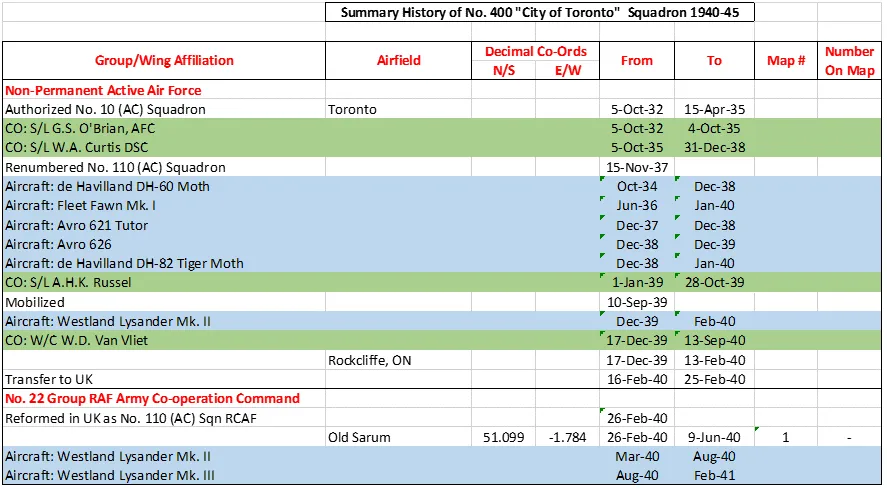
400 Sqn History Summary 1939-45 Page 2
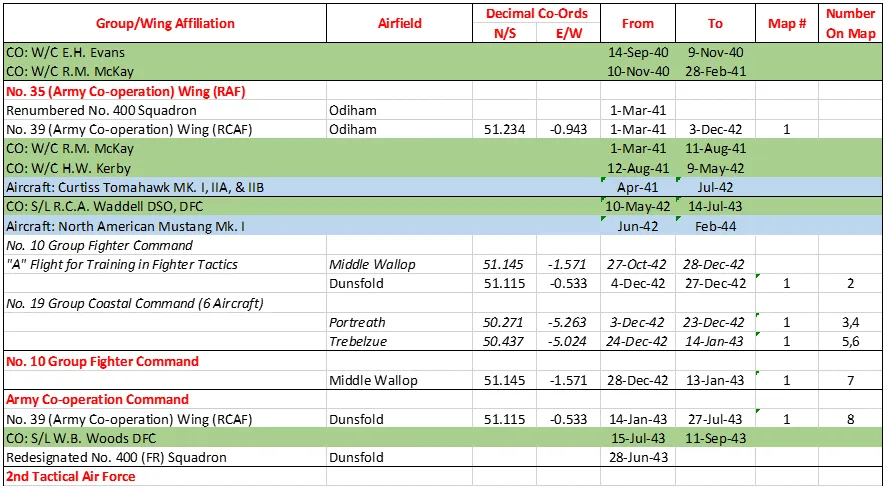
400 Sqn History Summary 1939-45 Page 3
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard III, Vampire III, Sabre V, Expeditor, Otter, Kiowa, Griffin)
No. 400 Squadron reformed at RCAF Station Downsview, ONtario ![]() on 15 April 1946 as an Auxiliary Fighter-Bomber Squadron, and later as an Auxiliary Fighter Squadron, operating North American Harvard Mk IIB. At the start of the Cold War the squadron flew de Havilland Vampire Mk IIIs and then Canadair Sabre Mk.V aircraft. It was re-named No. 400 "City of Toronto" (Fighter) Squadron on 6 November 1952, and then re-designated No. 400 “City of Toronto†Sqn (Aux) on 1 October 1958, when it was reassigned to a light transport and emergency rescue function and was equipped with Beechcraft Expeditor (1958) and de Havilland Otter (1960) aircraft. These aircraft were flown throughout the 1960s and 1970s.
on 15 April 1946 as an Auxiliary Fighter-Bomber Squadron, and later as an Auxiliary Fighter Squadron, operating North American Harvard Mk IIB. At the start of the Cold War the squadron flew de Havilland Vampire Mk IIIs and then Canadair Sabre Mk.V aircraft. It was re-named No. 400 "City of Toronto" (Fighter) Squadron on 6 November 1952, and then re-designated No. 400 “City of Toronto†Sqn (Aux) on 1 October 1958, when it was reassigned to a light transport and emergency rescue function and was equipped with Beechcraft Expeditor (1958) and de Havilland Otter (1960) aircraft. These aircraft were flown throughout the 1960s and 1970s.
Unification of the Canadian Forces brought about another name change, this time to 400 "City of Toronto" Air Reserve Squadron on 1 February 1968. In 1980, the conversion to helicopters began with the CH-136 Kiowa. The squadron received its current name in the 1980s, becoming 400 Tactical Helicopter and Training Squadron. The squadron moved to CFB Borden, Ontario ![]() in 1996 after the closure of CFB Downsview, and is now equipped with the CH-146 Griffon.
in 1996 after the closure of CFB Downsview, and is now equipped with the CH-146 Griffon.
During peacetime, the squadron fulfills 1 Wing commitments by providing operational and training support to the 4th Canadian Division, the defence of Canadian sovereignty, support to national taskings, and support to peacekeeping operations. Its secondary duties are to support search and rescue operations of the Royal Canadian Air Force.