MacPherson, Norman (Warrant Officer 2)
Killed in Action 1942-September-01


Birth Date: 1920
Born:
Parents: Son of Evan and Hannah Mary Macpherson; husband of Isabella Elizabeth Melvin Nelson Macpherson.
Spouse: Husband of Isabella Elizabeth Melvin Nelson Macpherson.
Home: Winnipeg, Manitoba
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
410 Sqn- Squadron
Noctivaga Wandering by Night
Base
Rank
Warrant Officer 2
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
R/71487
Home
Beaufighter serial: T3221

Bristol Beaufighter, coded PN-B.
The Bristol Type 156 Beaufighter (often referred to simply as the "Beau") was a multi-role aircraft developed during the Second World War in the UK. It was originally conceived as a heavy fighter variant of the Bristol Beaufort bomber. Upon its entry to service, the Beaufighter proved to be well suited to the night fighter role, for which the RAF initially deployed the type during the height of the Battle of Britain, in part due to its large size allowing it to accommodate both heavy armaments and early airborne interception radar without major performance penalties.
As its wartime service continued, the Beaufighter was used in many different roles; receiving the nicknames Rockbeau for its use as a rocket-armed ground attack aircraft, and Torbeau in its role as a torpedo bomber against Axis shipping, in which it came to replace the Beaufort which had preceded it. In later operations, it served mainly as a maritime strike/ground attack aircraft, RAF Coastal Command having operated the largest number of Beaufighters amongst all other commands at one point.
The Beaufighter saw extensive service during the war with the RAF (59 squadrons), Fleet Air Arm (15 squadrons), RAAF (seven squadrons), RCAF (four squadrons), USAAF (four squadrons), RNZAF (two squadrons), SAAF (two squadrons) and the Free Polish Air Force (one squadron). In addition, variants of the Beaufighter were also manufactured in Australia by the Department of Aircraft Production (DAP), often called the DAP Beaufighter. n the fall of 1940, Luftwaffe bombers, unable to escape Allied fighters by day, started flying night missions, where they would encounter much less opposition. Immediately, the Allies prepared their response: the improvement of interception radars used in ground controls, the use of twin-engine Bristol Beaufighters as night-fighter aircraft, and the development of the Mk. IV airborne interception radar. Faster than a Junkers Ju 88, the Beaufighter displayed impressive firepower. Three RCAF squadrons were involved in night fighter operations, Nos. 406, 409 and 410, created in the spring and summer of 1941. Harold Skaarup web page with revisions
Unit Desciption
410 Sqn Noctivaga ("Cougar")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Defiant IF, Beaufighter IIF, Mosquito NF II, FB VI, NF XIII,)

The Squadron was formed at Ayr, Scotland ![]() on June 30, 1941 as the RCAF's third Night Fighter squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. It was the ninth RCAF squadron formed overseas. The squadron flew Boulton Paul Defiant, Bristol Beaufighter and later de Havilland Mosquito aircraft in the night air defence of Britain, and then Europe. It was based at a number of locations in the UK before moving to Europe in September 1944, where it remained until the end of hostilities. It was disbanded at Gilze-Rijen, the Netherlands
on June 30, 1941 as the RCAF's third Night Fighter squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. It was the ninth RCAF squadron formed overseas. The squadron flew Boulton Paul Defiant, Bristol Beaufighter and later de Havilland Mosquito aircraft in the night air defence of Britain, and then Europe. It was based at a number of locations in the UK before moving to Europe in September 1944, where it remained until the end of hostilities. It was disbanded at Gilze-Rijen, the Netherlands ![]() , on June 9, 1945.
, on June 9, 1945.
In the course of the conflict, the squadron flew 2972 sorties and accounted for 75 enemy aircraft confirmed destroyed, with 2 probables and 9 damaged. Operational casualties were 17 aircraft and 32 aircrew, of whom 10 were killed, 20 presumed killed and 2 POW. The squadron had 10 aces (shot down 5 or more enemy aircraft), of whom 4 were pilots and the others navigators: kills were credited to both crew members (Flight Lieutenant R.D. Schultz DFC&Bar; Flying Officer D.G. Tonque, RAF DFC&Bar (Nav.); Lieutenant A.A. Harrington (USAAF) DSO,DFC; Flight Lieutenant C.E. Edinger DFC; Flying Officer J.S. Christie (RAF) DFC (Nav.); Flying Officer C.L. Vaessen DFC (Nav.); Flight Lieutenant G.P.A. Bodard DFC (Nav.); Squadron Leader J.D. Somerville DSO, DFC; Flying Officer G.D. Robinson DFC (Nav.); Flight Lieutenant V.A. Williams DFC (Nav.). The squadron won 1 DSO, 1 MBE, 2 Bars to DFC, 19 DFCs, 1 BEM and 17 Mentioned in Dispatches. Battle Honours were: Defence of Great Britain 1941-44, Fortress Europe 1943, France and Germany 1944-45 Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1943.Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Maps for Movements of 410 Squadron 1941-45
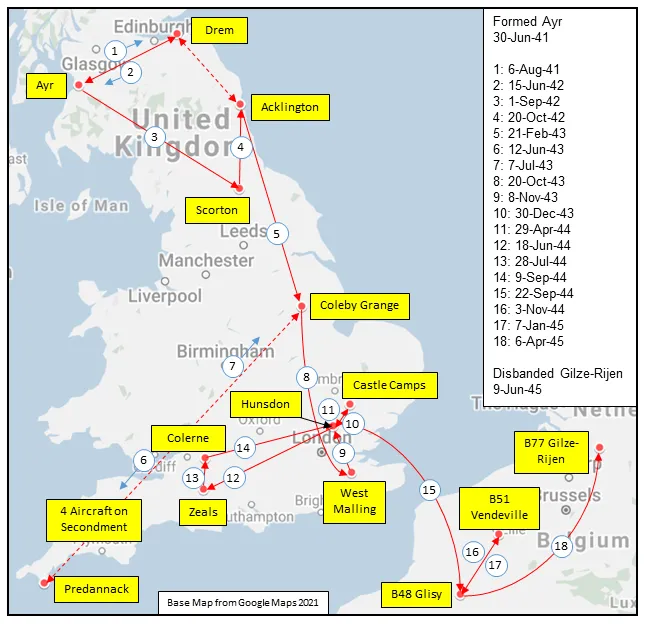
410 Squadron History Summary 1941-45
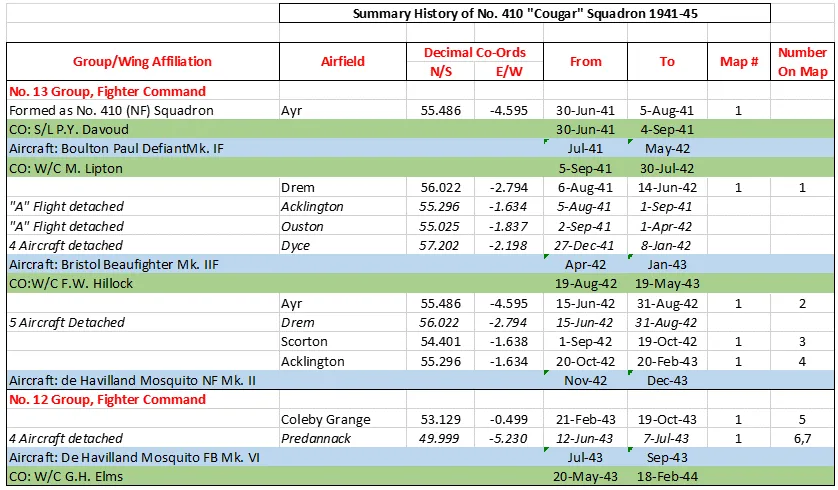
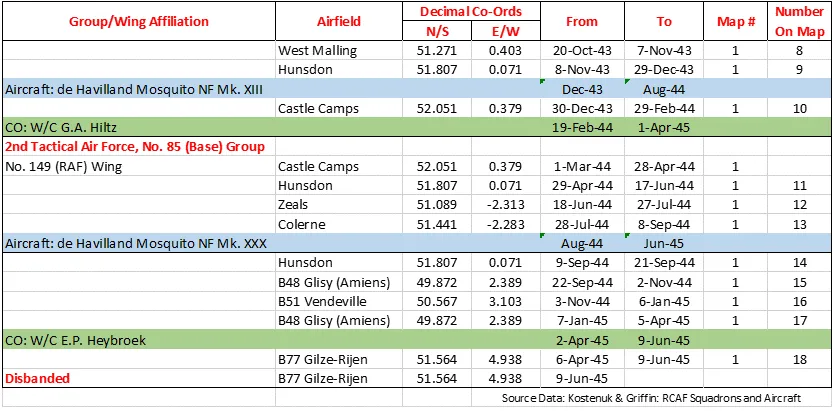
410 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Vampire III, Sabre 2, CF-100, Voodoo, Hornet)
The squadron was re-formed in a Fighter role at St Hubert (Montreal), Quebec ![]() on 1 December 1948. It was the first post-war Regular Force fighter unit, the first to fly Vampire and Sabre aircraft, and the first to join No. 1 (Fighter) Wing of No. 1 Air Division Europe. In 1956, it was decided to replace one Sabre squadron in each of the Air Division’s four wings with an all-weather fighter unit. When No. 445 AW(F) Squadron arrived from Canada, No. 410 was deactivated at Marville, France
on 1 December 1948. It was the first post-war Regular Force fighter unit, the first to fly Vampire and Sabre aircraft, and the first to join No. 1 (Fighter) Wing of No. 1 Air Division Europe. In 1956, it was decided to replace one Sabre squadron in each of the Air Division’s four wings with an all-weather fighter unit. When No. 445 AW(F) Squadron arrived from Canada, No. 410 was deactivated at Marville, France ![]() on 1 October 1956 and reactivated as All-Weather (Fighter) at Uplands (Ottawa), Ontario
on 1 October 1956 and reactivated as All-Weather (Fighter) at Uplands (Ottawa), Ontario ![]() on 1 November. The squadron flew CF-100 and CF-101 aircraft on North American air defence until being disbanded on 1 April 1964.
on 1 November. The squadron flew CF-100 and CF-101 aircraft on North American air defence until being disbanded on 1 April 1964.
In 1968, No.3 (Operating Training Unit) at CFB Bagotville, Quebec ![]() , which was tasked with training pilots and navigators for the three operational RCAF Voodoo squadrons, was renamed No. 410 Squadron. It moved to Cold Lake, Alberta
, which was tasked with training pilots and navigators for the three operational RCAF Voodoo squadrons, was renamed No. 410 Squadron. It moved to Cold Lake, Alberta ![]() in 1982, changing aircraft to become the training unit for Canada's new CF-18 Hornet aircraft. The squadron’s mission is: To Train World Class Fighter Pilots to Meet Canada's Needs.
in 1982, changing aircraft to become the training unit for Canada's new CF-18 Hornet aircraft. The squadron’s mission is: To Train World Class Fighter Pilots to Meet Canada's Needs.
The squadron runs two ab initio Fighter Pilot Courses (FPC) each year, training up to 20 fighter pilots. Each course comprises seven intense months of academics, simulator flights and flying missions. Graduates are taken from 419 Tactical Fighter (Training) Squadron (also known as NATO Flying Training in Canada (NFTC) Phase IV) and then provided with the tools to develop a solid foundation in both air-to-air and air-to-ground fighter combat.The squadron is also responsible for training and recertifying approximately five former CF-18 Hornet pilots annually. These are pilots who are returning to the CF-18 cockpit after a ground or exchange tour. Furthermore, 410 Squadron also trains newly arrived foreign exchange officers who will be joining one of Canada's two operational fighter squadrons.
A lesser-known sub-unit of 410 Squadron is FOTEF. FOTEF - the Fighter Operational Test & Evaluation Flight - is responsible for the operational testing and evaluation to meet the needs of the Fighter Force (FF). Their efforts have been and continue to be integral to the operational effectiveness of all aspects of core and CF-18 capabilities. Some the new systems being evaluated are Night Vision Imaging Systems (NVIS), Multi-function Information Distribution Systems (MIDS), the Advanced Multi-role Infra-Red Sensor, the evaluation of new mission planning software and the Advanced Distributed Combat Training System (the civilian contracted simulator system). Working closely with a variety of key units across the Air Force including the Aerospace Engineering & Test Establishment (AETE), FOTEF has enabled the seamless integration of newly modernized CF-18 ECP-583 R2 aircraft into the FF.