Tattersfield, Anthony William
Killed in Action 1944-01-14


Birth Date: 1923
Born:
Son of Harold Walter and Florence Amy Tattersfield
Home:
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RAFVR
Unit
408 (B) Sqn- Squadron
For Freedom
Base
Linton-on-Ouse, Yorkshire
Rank
Sergeant
Position
Sergeant
Service Numbers
1217551
Target
 Brunswick Germany
Brunswick Germany
First Burial
 Hanover War Cemetery, Germany
Hanover War Cemetery, Germany
408 Goose Squadron (For Freedom) RAF Linton-on-Ouse. Lancaster BII aircraft LL 699 EQ-C was shot down by a night fighter while engaged in an operation against targets in Brunswick, Germany. The Lancaster crashed near Hellendorf and Negenborn at Wedemark, Niedersachsen, Germany
Sergeant AW Tattersfield (RAFVR) was killed in action
Lancaster LL699
Avro Lancaster
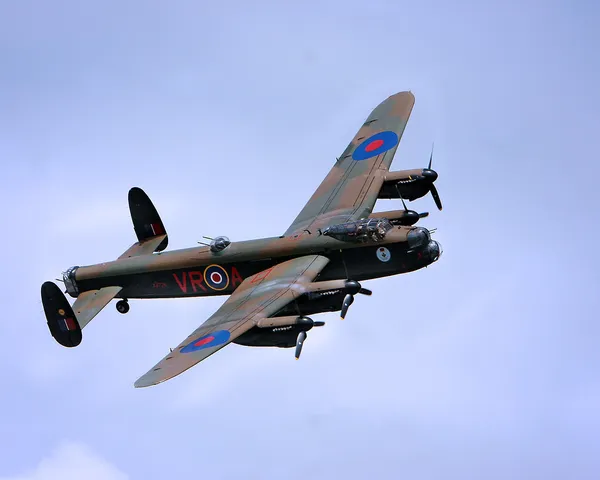

Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same wartime era.
The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use". Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one version, Bristol Hercules engines. It first saw service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942 and as the strategic bombing offensive over Europe gathered momentum, it was the main aircraft for the night-time bombing campaigns that followed. As increasing numbers of the type were produced, it became the principal heavy bomber used by the RAF, the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and squadrons from other Commonwealth and European countries serving within the RAF, overshadowing the Halifax and Stirling. Wikipedia
408 (B) Sqn For Freedom ("Goose")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Hampden I, Halifax II & V, Lancaster II, Halifax III & VII, Lancaster X)

The squadron was the second Canadian bomber squadron to be formed in WWII. It was formed at Lindholme, Yorkshire, UK in June of 1941 as part of Bomber Command No 5 Group, flying Handley Page Hampden Mk I bombers from Syerston, Nottinghamshire, Balderton, Newark and North Luffenham, Rutland. Its squadron code letters were EQ. In September 1942 the squadron was moved to No 4 Group, re-equipping with Halifax Mk II aircraft and flying from Leeming, Yorkshire. On January 1, 1943, by this time equipped with Lancaster Mk II bombers, the squadron joined No. 6 Group (RCAF) and flew from Linton-on-Ouse, Yorkshire from August 27 1943 to the end of WWII. In September 1944 it converted to Halifax Mk III and VII aircraft and flew these for the remainder of hostilities. It was slated to be part of the "Tiger Force" to attack Japan and had re-equipped with Lancaster Mk X aircraft, but the Japanese surrender ended all plans for the Tiger Force and the squadron was disbanded in September 1945 at Greenwood, Nova Scotia .
Altogether, the squadron logged 4610 operational sorties with 25,500 operational hours, in the course of which 11,430 tons of bombs were dropped. 146 aircraft were lost in the course of these operations. Awards included 161 DFC's and 6 bars to DFC, 32 DFM's, 1 MBE and 10 MiD's. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1941-43, Baltic 1941-43, Fortress Europe 1941-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1941-44, Ruhr 1941-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1941-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1942-43. Wikipedia, Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 408 Squadron 1941-45
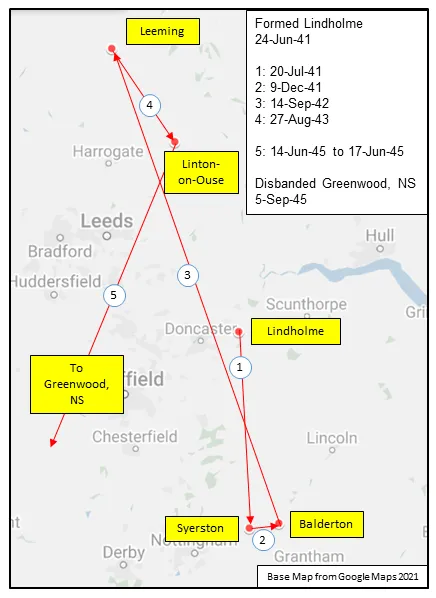 MAP 1: 408 Squadron Movements 1941-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab) | 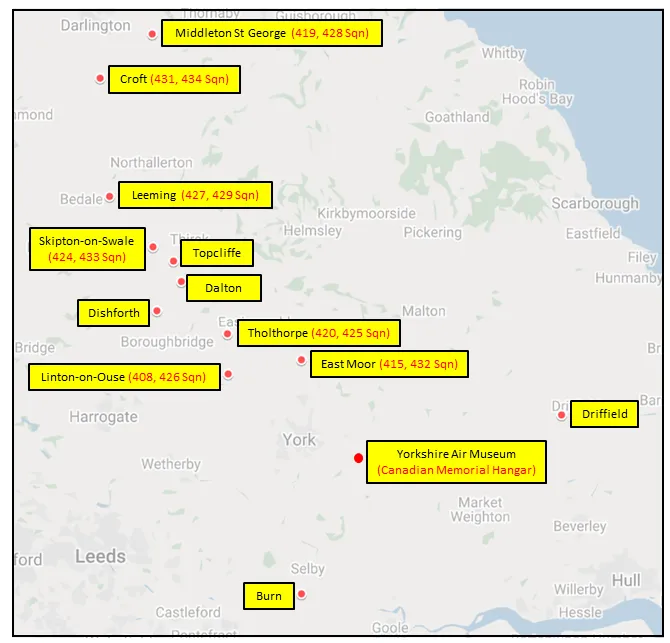 MAP 2: 6 Group Bomber Bases in Durham and Yorkshire 1943-45 |
408 Squadron History Summary
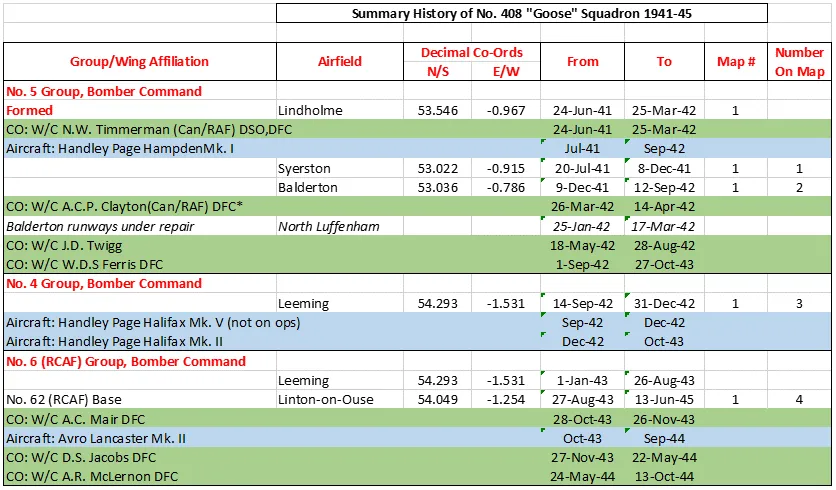
408 Squadron History Summary Page 2
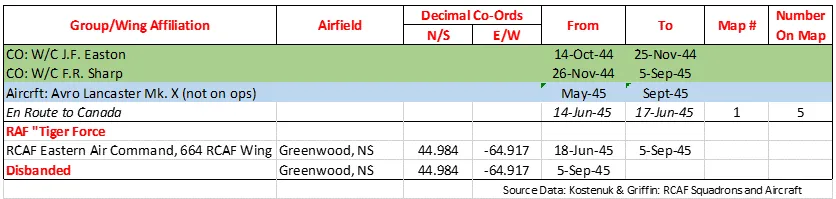
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Lancaster X, Canso A, Norseman VI, Otter, Dakota III & IV, Boxcar, Silver Star, Hercules, Griffon, Chinook)
On 10 January 1949, the squadron was reformed as 408 (Photographic) Squadron at RCAF Station Rockcliffe, Ontario . Equipped with eight Lancaster Mark X photographic aircraft equipped with SHORAN, a short-range navigational device. It was tasked with the mapping of Canada, specifically the far North. It also flew Canso, Norseman, Otter and Dakota aircraft on this mission, for photography and to maintain the SHORAN stations. Once the task was complete, the squadron was re-designated 408 (Reconnaissance) Squadron and flew Lancasters on Arctic surveillance patrols. In 1964, equipped with the Fairchild C-119G Flying Boxcar, it was again re-designated 408 (Transport Support and Aerial Reconnaissance) Squadron and moved to Rivers, Manitoba. In 1964, the squadron formed a flight of Canadair CT-133 Silver Star aircraft. In 1965, the Boxcars were replaced by CC-130 Hercules aircraft.
On January 1, 1971, 408 Squadron was once again re-activated at Namao in Edmonton, Alberta , as a tactical helicopter squadron (THS) and equipped with CH-135 Twin Huey and CH-136 Kiowa helicopters. Its primary tasking is to provide tactical aviation to the army. The mission includes air mobile assault, air ambulance, air observation, reconnaissance insertions, troop movement, airborne command and control platform and dropping paratroopers. In September 1996, the squadron was re-equipped with CH-146 Griffon helicopters. Personnel from 408 Squadron deployed to Afghanistan nearly continually from 2006 until 2011. Initially forming a Tactical Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (TUAV) detachment using the CU-161 Sperwer. From 2008, 408 members were deployed to Kandahar airfield operating the CH-146 Griffon and CH-147D helicopters as part of the Joint Task Force Afghanistan Air Wing. The primary role of the JTF-A Air Wing was to provide transportation, reconnaissance, armed escort, and fire support to the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF). In July of 2018, 408 THS deployed to Mali as part of Task Force Mali on Operation Presence. In Mali, 408 THS operated the CH-146 Griffon in the armed escort role, providing support to MEDEVAC and utility missions. 408 THS completed its tour in Mali in January of 2019, having participated in 7 medical evacuation missions. It is now co-located with 1 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group at the 3rd Canadian Division Support Base, Edmonton, Alberta.
link,general,https://www.forfreedom.ca,408 “Goose†Squadron Association
 Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)
Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)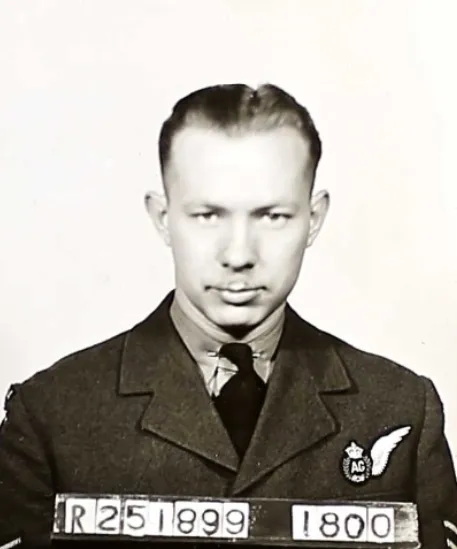




 Lancaster Bomber
Lancaster Bomber Wikipedia
Wikipedia Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page