On 1943-10-08, Squadron Leader A. Ross Dawson, an Engineering Officer with 427 Sqn at Skipton-on-Swale, wrote in his diary:
"Well we were on tonight for a change after a two week stand-down [due to poor weather]. I thought I'd make an effort to make a good showing on my first real op on my own. The boys co-operated fine and we got a record 16 kites up each with 1882 gals of petrol, 6500 lbs of bombs, 1-2000 lb., 5 cans of 4-30 lb. incendiaries & 8 cans of 90- 4lb. as well as 14 bundles of "window" incendiaries, the metallic strips they shower down when over target to throw out & jam the jerry radio-location beams. It looked pretty good at take-off & although we had 2 go u/s [unserviceable] just before take-off we managed to shift the crews around to stand-by kites & so we got them all away.
I was feeling pretty good about this but soon things began to happen. First the weather closed in & it turned very cold with a sheet-like rain. Then one after another we got the news that seven aircraft were coming back on early returns never having reached the target. This was awful for my first "do" but it seemed that 3 of the seven were due to very bad icing conditions, 2 were due to maintenance faults for which I had to take the blame. One was due to the pilot getting lost and getting too low down over the Ruhr where he got badly shot up with flak while the seventh never got back at all. He crashed down near Eastmoor somewhere & burned up. All crew were killed so I don't suppose we'll ever find out what happened. With Squadron Leader Ganderton I drove around & met each pilot and flight engineer as they got out of their kites, found out their story & made out my report to the station engineering officer. I was nearly 11:00 o'clock when they all got back & since the weather was duff I was getting a little apprehensive about how many of the rest would get back.
At 12:00 o'clock I went down to flying control to watch as the rest of the kites came in. It was very exciting hearing them talk them in one by one by radio and watching them land. We had two near accidents, one when he was swung & ground looped just after landing & the other when a few hung-up incendiaries fell out of a kite on the runway and went up with a terrific roar & bright flames. However, no one was hurt & we kept counting them one by one as they got down safely until there was only 4 more of ours to come in. We waited and waited but they didn't come & we finally had to give them up for lost. About 1:00am I went up to interrogation to find out from each pilot & flight engineer how the kite had functioned & what damage had been sustained. Finally after about an hour I went to the operations room to see if they had any word of our missing aircraft (& they hadn't). I finally got back to the Mess at 3:30am, had fried potatoes and sausages & went to bed.
Sat Oct 23, 1943: "Things were pretty grim here this morning with everyone worried about our big losses. 4 of ours & 2 from 429 making 6 out of 28 aircraft. Also my six early returns didn't make me feel any too happy. Fortunately we were stood down tonight. The target was Kassel last night & 42 were lost altogether. Mostly due to icing I imagine. Our K-Kitty which had several flak holes in it wasn't too bad although it needed and engine change. . . ."
Brown, Kenneth Alfred
Killed in Action 1943-10-22


Birth Date: 1923
Born:
Home: The Lee, Buckinghamshire, England
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RAFVR
Unit
427 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Ferte Manus Certas Strike sure
Base
RAF Leeming
Rank
Sergeant
Position
Sergeant
Service Numbers
1803924
Target
 Kassel Germany
Kassel Germany
First Burial
 Lee (St John The Baptist) Churchyard
Lee (St John The Baptist) Churchyard
Sergeant KA Brown (RAFVR) was killed in action
Halifax B/Met.Mk.V DK182
Bombing 1943-October-21 to 1943-October-22
427 (B) BG (RCAF) Skipton on Swale
Battle of the Ruhr
Halifax DK182
Handley Page Halifax
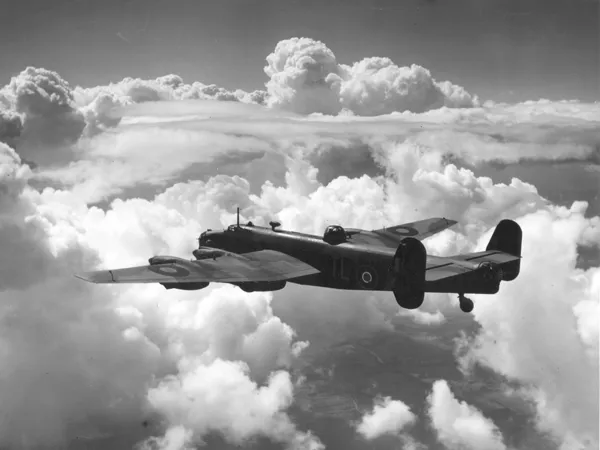

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces.Wikipedia
 National Air Force Museum of Canada
National Air Force Museum of Canada
427 (B) Sqn Ferte Manus Certas ("Lion")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington III, X, Halifax III, V, Lancaster I, III)

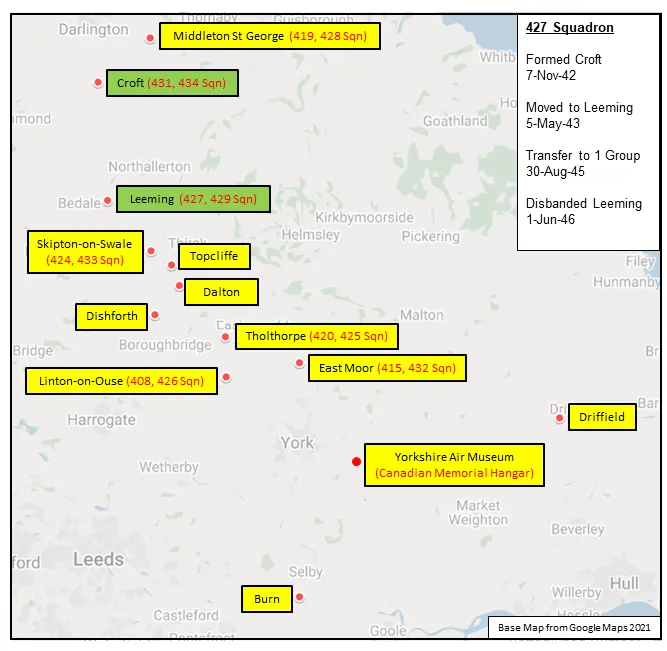
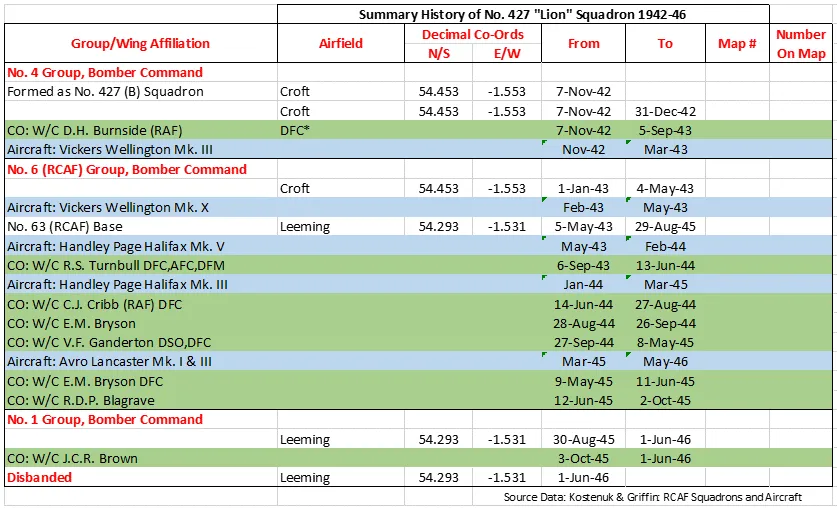
427 Squadron was the RCAF's 25th squadron and eighth bomber squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. It was formed at Croft, Yorkshire, England on 7 November 1942 as part of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. With squadron code letters ZL it flew Wellington Mk III aircraft. On 1 January 1943 it joined No 6 (RCAF) Group, remaining at Croft until May of 1943, when it moved to Leeming, Yorkshire , where it remained for the rest of the war in Europe. Its duties were to take part in strategic and tactical bomber operations. It briefly re-equipped with Vickers Wellington Mk X before acquiring Handley Page Halifax Mk V aircraft in May 1943. In January 1944 it re-equipped again with the improved Halifax Mk III. Finally it was equipped with Avro Lancaster Mks I and III in March 1945. After the termination of hostilities in Europe, the squadron remained in England and transferred to No 1 Group. It participated in operation EXODUS, the repatriation of POW's and operation DODGE, bringing back British troops from Italy. The squadron disbanded at Leeming on 1 June 1946.
In the course of WWII the squadron flew approximately 3300 operational sorties in the course of which either 88 (Moyes) or 90 (Kostenuk) aircraft were lost and approximately 10,300 tons of bombs were dropped. The squadron earned 4 DSO's, 147 DFC'c and 6 Bars to DFC, 1 AFC, 2 CGM's, 16 DFM's and 8 MiD. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943-45, Baltic 1944-45, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1943-44, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1943-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1944. Wikipedia, Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 427 Squadron 1942-46
427 Squadron History Summary 1942-46
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Sabre 2, 5, 6, Starfighter, Kiowa, Twin Huey, Griffon)
The squadron was reactivated on 1 August 1952 as a fighter squadron in the Air Defence Command, based in St Hubert, Quebec and equipped with Canadair F-86 Sabre Mk 2s. The Squadron moved on to Sabre Mks. 5 and 6 while working out of St Hubert before deploying to Zweibrücken, Germany and becoming a part of 3 Wing, in March-April 1953. The Squadron continued in this role, operating out of Germany, for another decade, participating in many multi-national NATO exchanges and exercises with destinations including; Rabat, Morocco, Decimomannu, Sardinia and France. The squadron moved to Grostenquin, France in June 1962, but was inactive pending its conversion to the CF-104 Starfighter. On 15 December 1962, the Squadron was deactivated as a Fighter squadron and reactivated on the 17th as a Strike/Attack squadron, becoming the first Canadian squadron to be equipped with the Starfighter. This change in aircraft necessitated changes in training and tactics. In 1969 the squadron moved from Zweibrücken to Baden-Soellingen , and with that, a change from 3 Wing to 4 Wing.
The Squadron disbanded again on 1 July 1970 and was re-established on 1 January 1971 as a Tactical Helicopter Squadron with 10 Tactical Air Group of Mobile Command, later simply called ‘Air Command.’ The first helicopter used after this transition was the CH-136 Kiowa light observer helicopter and, simultaneously, the CH-135 Twin Huey utility helicopters. The Squadron participated in many operations, including: Norway, Egypt, Sinai and Central America. After switching to a fleet of only CH-135 Twin Hueys in 1992, the squadron deployed to Somalia in 1993 and to Haiti on Operations. In July 1997 the Squadron received the BELL CH-146 Griffon Helicopter fleet to replace the Twin Huey. By 1999, the Griffon’s had participated in operations in Canada and in Honduras. The early 2000’s saw rotations going to Bosnia.
On 1 February 2006, 427 Squadron became part of Canadian Special Operations Forces Command (CANSOFCOM), as a Special Operations Aviation Squadron (SOAS), with the responsibility of providing air capability to various units with the Canadian Special Forces Command, where it remains today, located at Canadian Forces Base Petawawa, Ontario . In recent years, 427 SOAS participated in Exercise FLINTLOCK, an annual regional exercise among African, Western and United States counterterrorism forces, in multiple countries in West Africa. It also deployed to the Middle-East as part of Operation IMPACT, the Canadian Armed Forces mission to build the military capabilities of Iraq, Jordan and Lebanon, and set the conditions for their long-term success. 
 Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)
Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist) Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII
Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page Wikipedia Halifax Bomber
Wikipedia Halifax Bomber