McGovern, H T
Prisoner of War 1945-01-29


Birth Date: unkown date
Born:
Home:
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
408 (B) Sqn- Squadron
For Freedom
Base
Linton-on Ouse
Rank
Flying Officer
Position
Flying Officer
Service Numbers
J/26214
Target
 Stuttgart Germany
Stuttgart Germany

Halifax B.Mk.VII NP746
Bombing Stuttgart Germany 1945-January-29 to 1945-January-29
(B) Sqn (RCAF) Linton-on-Ouse
602 aircraft - 316 Halifaxes, 258 Lancasters, 28 Mosquitoes - of 1, 4, 6 and 8 Groups. I I aircraft - 6 Lancasters, 4 Halifaxes, 1 Mosquito - lost.
This raid was split into 2 parts, with a 3-hour interval. The first force - of 226 aircraft - was directed against the important railway yards at Kornwestheim, a town to the north of Stuttgart, and the second was against the north-western Stuttgart suburb of Zuffenhausen, where the target is believed to have been the Hirth aero¬engine factory. The target area was mostly cloud-covered for both raids and the bombing, on sky-markers, was scattered.
Bombs fell in many parts of Stuttgart's northern and western suburbs. The important Bosch works, in the suburb of Feuer¬bach, was hit. The attack on Kornwestheim was the worst suffered by that town during the war; the Kornwestheim local report shows that the local people felt they had been bombed by mistake and that the main target was in Stuttgart. 14 highs explosive bombs fell in the industrial area of the town and in the railway yards. Fires burned for up to 12 hours. 123 people were killed in Stuttgart and 41 in Kornwest¬heim. A large number of bombs fell outside Stuttgart, particularly in the east arourid a decoy fire site which was also firing dummy target-indicator rockets into the .air. The village of Weilimdorf, situated not far away, complained bitterly about its damage and casualties!
Local expert, Heinz Bardua, also tells the story of the newly promoted Flak Leutnant at his battery position at Vaihingen, situated just south of the decoy fire site. With bombs falling all around his position, the Leutnant thought that the raid was directed against the Flak positions. He ignored regulations about conservation of ammunition and shot his entire stock at the radar echoes of the attacking bombers, 2 Lancasters and a Halifax crashed in the immediate vicinity, much to the relief of the officer, who had feared a court martial because of his prodigious use of ammunition.
This was the last large R.A.F. raid on Stuttgart. Herr Bardua says that the city had endured 53 major raids, most of them by the R.A.F., during which 32,549 blocks of flats or houses were destroyed (67·8 per cent of the total). After the war, 4·9 million cubic metres of rubble had to be cleared. 4,562 people died in the air raids, among them 770 prisoners of war or foreign workers. Stuttgart's experience was .not as severe as other German cities. Its location, spread out in a series of deep valleys, had consistently frustrated the Pathfinders and the shelters dug into the sides of the surrounding hills had saved many lives.
,source: The Bomber Command War Diaries, Martin Middlebrook and Chris Everitt
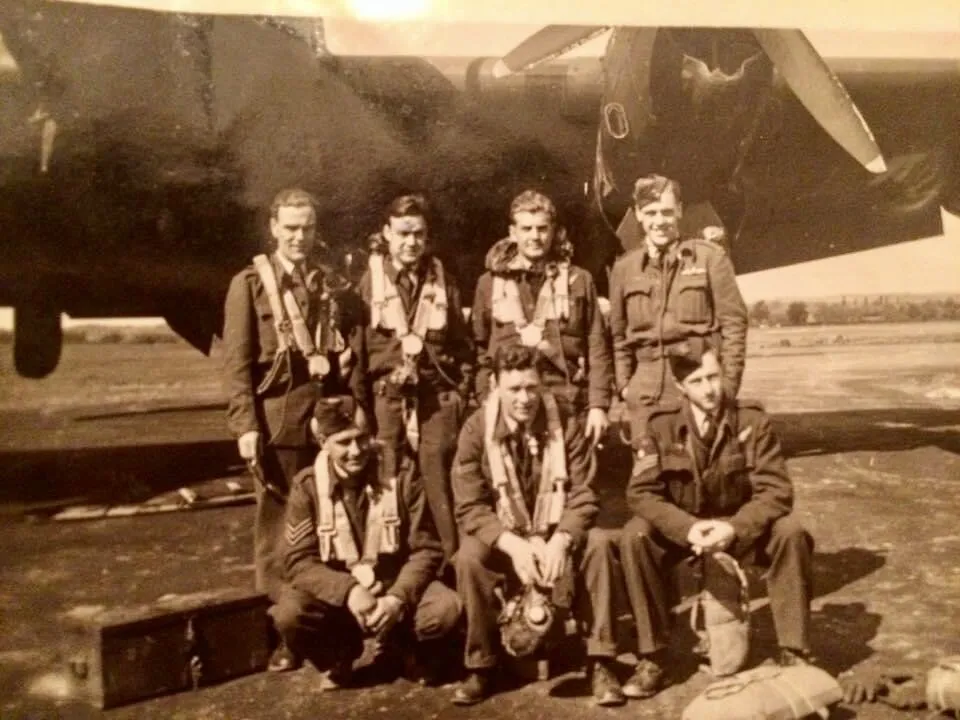
Halifax NP746 Took off from Linton-on-Ouse at 19:43 in Halifax Mk VII (Sqn code: EQ-E Bomber Command) to bomb Stuttgart.
Shot down (means not listed) and crashed. FO. McGovern, was the only survivor and, according to his family, became a Prisoner of War for three months..
Killed:Pilot Officer Leslie John Collinson RCAF C/95228 KIA Durnbach War Cemetery Ref: 3. G. 23.Flying Officer Thomas Bruce Little RCAF J/40372 KIA Durnbach War Cemetery Ref: 3. G. 20.Pilot Officer Philip Myerson RAF KIA Durnbach War Cemetery [Ref : 3. G. 21.]Pilot Officer Thomas Phillip QUINN (J/93944) Air Gunner Halifax NP746 IBCC [RCAF] 1945-01-29 408 Sqdn AIR27 Germany Durnbach War Cemetery Ref: 3. G. 25.Pilot Officer Robert Lloyd Siewert RCAF J/93945KIA Durnbach War Cemetery Ref: 3. G. 24.Flying Officer Richard Macmillan Wallis RCAF J/28593 pilot KIA Durnbach War Cemetery Ref: 3. G. 22.
Halifax NP746
Handley Page Halifax
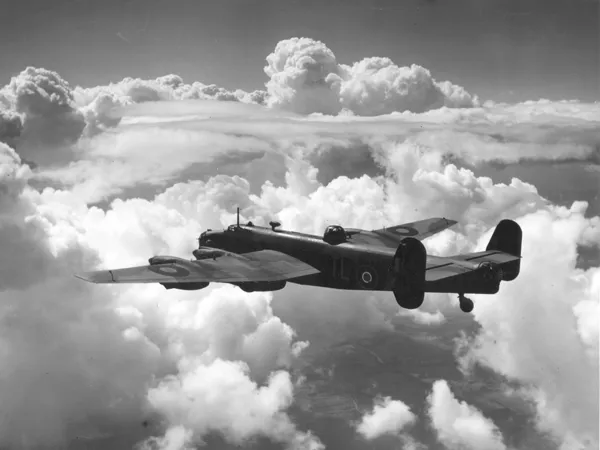

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces.Wikipedia
 National Air Force Museum of Canada
National Air Force Museum of Canada
408 (B) Sqn For Freedom ("Goose")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Hampden I, Halifax II & V, Lancaster II, Halifax III & VII, Lancaster X)

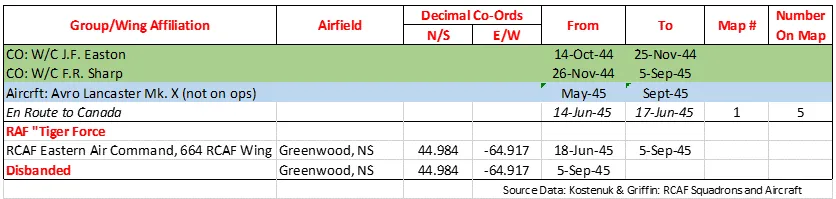
The squadron was the second Canadian bomber squadron to be formed in WWII. It was formed at Lindholme, Yorkshire, UK in June of 1941 as part of Bomber Command No 5 Group, flying Handley Page Hampden Mk I bombers from Syerston, Nottinghamshire, Balderton, Newark and North Luffenham, Rutland. Its squadron code letters were EQ. In September 1942 the squadron was moved to No 4 Group, re-equipping with Halifax Mk II aircraft and flying from Leeming, Yorkshire. On January 1, 1943, by this time equipped with Lancaster Mk II bombers, the squadron joined No. 6 Group (RCAF) and flew from Linton-on-Ouse, Yorkshire from August 27 1943 to the end of WWII. In September 1944 it converted to Halifax Mk III and VII aircraft and flew these for the remainder of hostilities. It was slated to be part of the "Tiger Force" to attack Japan and had re-equipped with Lancaster Mk X aircraft, but the Japanese surrender ended all plans for the Tiger Force and the squadron was disbanded in September 1945 at Greenwood, Nova Scotia .
Altogether, the squadron logged 4610 operational sorties with 25,500 operational hours, in the course of which 11,430 tons of bombs were dropped. 146 aircraft were lost in the course of these operations. Awards included 161 DFC's and 6 bars to DFC, 32 DFM's, 1 MBE and 10 MiD's. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1941-43, Baltic 1941-43, Fortress Europe 1941-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1941-44, Ruhr 1941-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1941-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1942-43. Wikipedia, Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 408 Squadron 1941-45
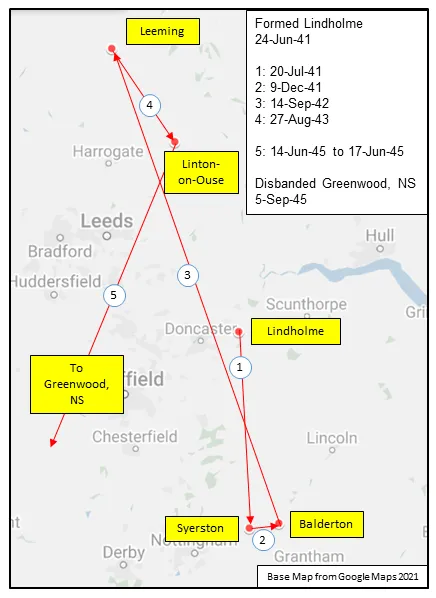 MAP 1: 408 Squadron Movements 1941-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab) | 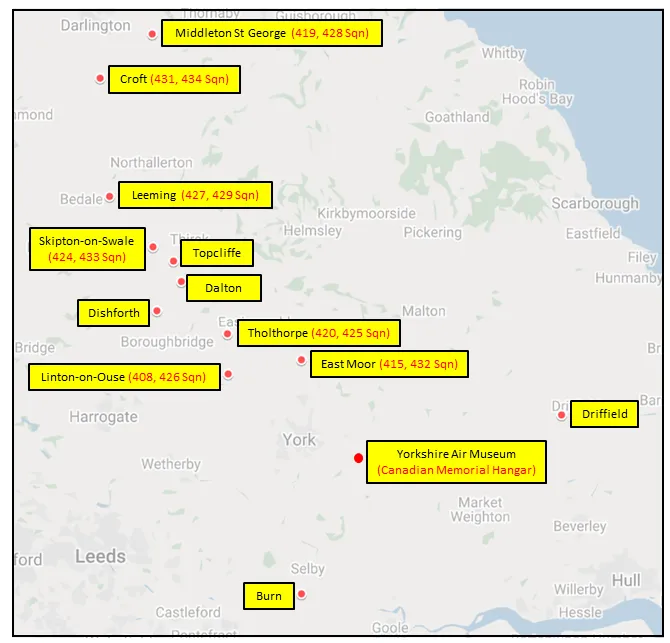 MAP 2: 6 Group Bomber Bases in Durham and Yorkshire 1943-45 |
408 Squadron History Summary
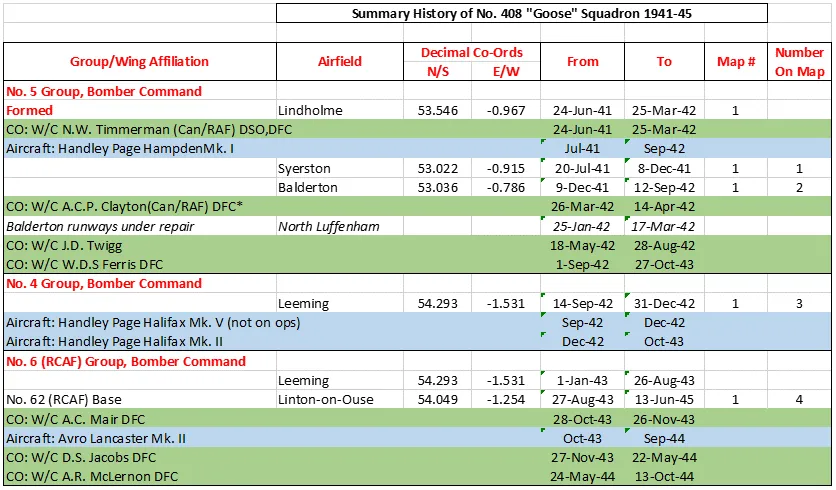
408 Squadron History Summary Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Lancaster X, Canso A, Norseman VI, Otter, Dakota III & IV, Boxcar, Silver Star, Hercules, Griffon, Chinook)
On 10 January 1949, the squadron was reformed as 408 (Photographic) Squadron at RCAF Station Rockcliffe, Ontario . Equipped with eight Lancaster Mark X photographic aircraft equipped with SHORAN, a short-range navigational device. It was tasked with the mapping of Canada, specifically the far North. It also flew Canso, Norseman, Otter and Dakota aircraft on this mission, for photography and to maintain the SHORAN stations. Once the task was complete, the squadron was re-designated 408 (Reconnaissance) Squadron and flew Lancasters on Arctic surveillance patrols. In 1964, equipped with the Fairchild C-119G Flying Boxcar, it was again re-designated 408 (Transport Support and Aerial Reconnaissance) Squadron and moved to Rivers, Manitoba. In 1964, the squadron formed a flight of Canadair CT-133 Silver Star aircraft. In 1965, the Boxcars were replaced by CC-130 Hercules aircraft.
On January 1, 1971, 408 Squadron was once again re-activated at Namao in Edmonton, Alberta , as a tactical helicopter squadron (THS) and equipped with CH-135 Twin Huey and CH-136 Kiowa helicopters. Its primary tasking is to provide tactical aviation to the army. The mission includes air mobile assault, air ambulance, air observation, reconnaissance insertions, troop movement, airborne command and control platform and dropping paratroopers. In September 1996, the squadron was re-equipped with CH-146 Griffon helicopters. Personnel from 408 Squadron deployed to Afghanistan nearly continually from 2006 until 2011. Initially forming a Tactical Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (TUAV) detachment using the CU-161 Sperwer. From 2008, 408 members were deployed to Kandahar airfield operating the CH-146 Griffon and CH-147D helicopters as part of the Joint Task Force Afghanistan Air Wing. The primary role of the JTF-A Air Wing was to provide transportation, reconnaissance, armed escort, and fire support to the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF). In July of 2018, 408 THS deployed to Mali as part of Task Force Mali on Operation Presence. In Mali, 408 THS operated the CH-146 Griffon in the armed escort role, providing support to MEDEVAC and utility missions. 408 THS completed its tour in Mali in January of 2019, having participated in 7 medical evacuation missions. It is now co-located with 1 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group at the 3rd Canadian Division Support Base, Edmonton, Alberta.
link,general,https://www.forfreedom.ca,408 “Goose†Squadron Association
 Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)
Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)




 Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII
Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page Wikipedia Halifax Bomber
Wikipedia Halifax Bomber