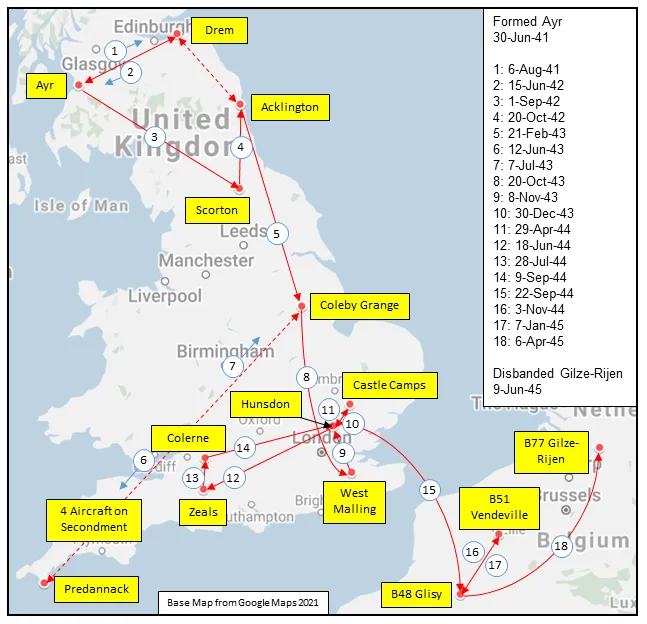
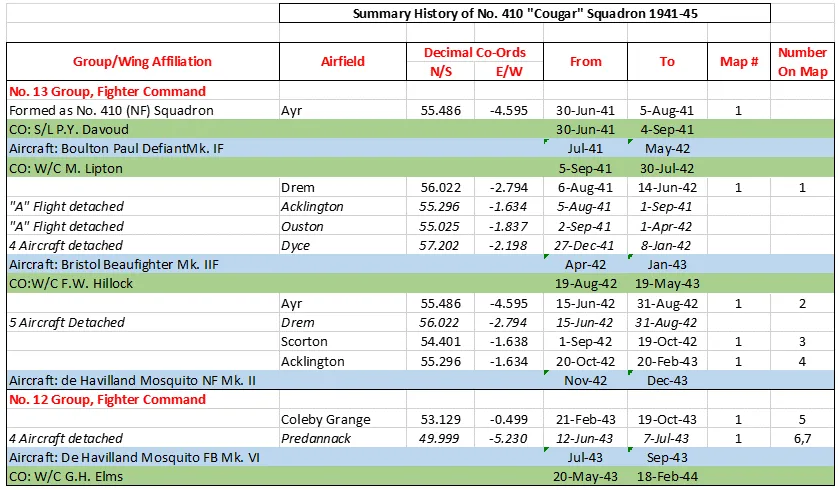
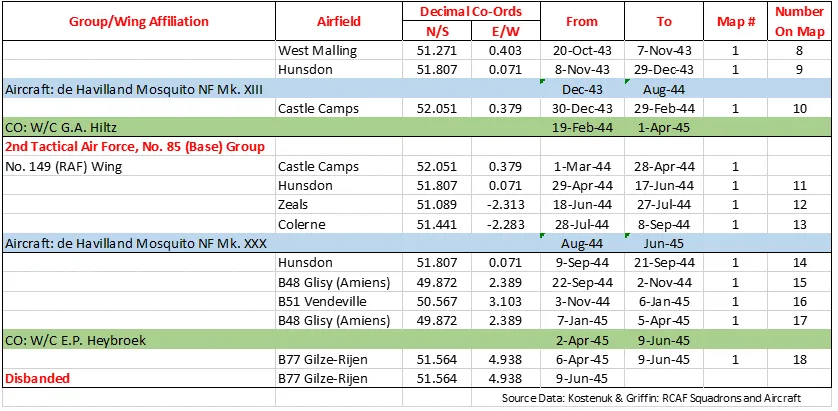
Boulton Paul Defiant

Boulton Paul P.82 Defiant, RAF (Serial No. L7026), coded PS*V, c1941.
The Boulton Paul Defiant is a British interceptor aircraft that served with the Royal Air Force (RAF) during World War II. The Defiant was designed and built by Boulton Paul Aircraft as a "turret fighter", without any fixed forward-firing guns, also found in the Blackburn Roc of the Royal Navy.
In combat, the Defiant was found to be reasonably effective at destroying bombers but was vulnerable to the Luftwaffe's more manoeuvrable, single-seat Messerschmitt Bf 109 fighters. The lack of forward-firing armament proved to be a great weakness in daylight combat and its potential was realised only when it was converted to a night fighter. It eventually equipped thirteen squadrons in this role, compared to just two squadrons as a day-fighter. In mid-1942 it was replaced by better performing night-fighters, the Bristol Beaufighter and de Havilland Mosquito.
The Defiant continued to find use in gunnery training, target towing, electronic countermeasures and air-sea rescue. Among RAF pilots it had the nickname "Daffy". Wikipedia
CASPIR Aircraft Groups:
Canadian Aircraft Losses (21)Defiant MK. I N3503
Served with No. 410 (NF) Squadron, RCAF, in 1941/42. Crashed into Aberlady Bay, East Loyhian on 11 April 1942, during a training flight. Sgt. R.G. Smith and Sgt. A.G. MacKinnon killed.




 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)
Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist) Winnipeg, Manitoba
Winnipeg, Manitoba Defiant Fighter
Defiant Fighter Wikipedia Defiant Fighter
Wikipedia Defiant Fighter Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page