Small, Lorne Chalmers
Killed in Flying Accident 1942-06-25


Birth Date: 1919-April-24
Born:
Son of Adolphus Robert and Mary Ellen Small, of Stratford; husband of Carey Alona Small, of Stratford.
Home: Stratford, Ontario
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
12 EFTS- Elementary Flying Training School
Base
Goderich, Ontario, Canada
Rank
Flight Sergeant
Position
Flight Sergeant
Service Numbers
R/90190
Home
 Stratford, Ontario
Stratford, Ontario
First Burial
 Avondale Cemetery, Stratford, Ontario
Avondale Cemetery, Stratford, Ontario
This incident involved multiple aircraft:
- Moth, Tiger I Serial: 1279
All the above aircraft in the above list are referenced in this report.
de Havilland DH 82 Tiger Moth
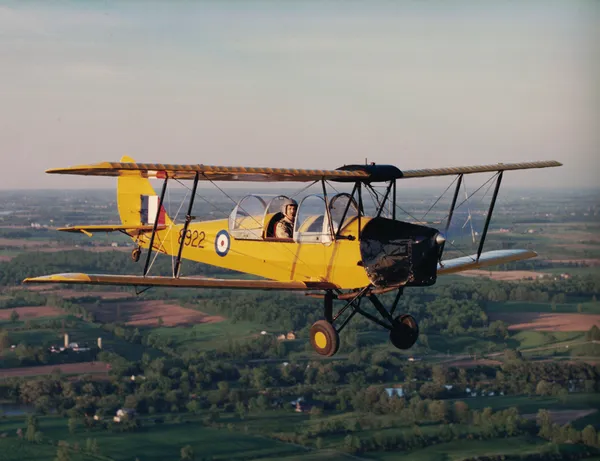

The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and many other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ab-initio training, the Second World War saw RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers.
The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was succeeded and replaced by the de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civil operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civil applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft in several countries. It is still occasionally used as a primary training aircraft, particularly for those pilots wanting to gain experience before moving on to other tailwheel aircraft.
Overseas manufacturing of the type commenced in 1937, the first such overseas builder being de Havilland Canada at its facility in Downsview, Ontario. In addition to an initial batch of 25 Tiger Moths that were built for the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), the Canadian firm began building fuselages which were exported to the UK for completion. Canadian-built Tiger Moths featured modifications to better suit the local climate, along with a reinforced tail wheel, hand-operated brakes (built by Bendix Corporation), shorter undercarriage radius rods and the legs of the main landing gear legs being raked forwards as a safeguard against tipping forwards during braking. In addition the cockpit had a large sliding canopy fitted along with exhaust-based heating; various alternative undercarriage arrangements were also offered. By the end of Canadian production, de Havilland Canada had manufactured a total of 1,548 of all versions.Wikipedia
 Wikipedia de Havilland Tiger Moth
Wikipedia de Havilland Tiger Moth
 YouTube de Havilland DH.82A Tiger Moth
YouTube de Havilland DH.82A Tiger Moth
12 EFTS (12 Elementary Flying Training School)
An Elementary Flying Training School (EFTS) gave a trainee 50 hours of basic flying instruction on a simple trainer like the De Havilland Tiger Moth, Fleet Finch, or Fairchild Cornell over 8 weeks.Elementary schools were operated by civilian flying clubs under contract to the RCAF and most of the instructors were civilians. For example, No. 12 EFTS Goderich was run by the Kitchener-Waterloo Flying Club and the County of Huron Flying Club.The next step for a pilot was the Service Flying Training School.

Information on RCAF Station Goderich can be found here

Information on RCAF Station Goderich Relief Field can be found here

Notable students from 12 ETFS
Flight Lieutenant Hornell, David Ernest VC and Flight Officer and Dambuster Joe McCarthy Project 44 BCATPMoth, Tiger 1279
Moth, Tiger I 1279
Ordered by USAAF as PT-24 42-1143; then to Lend-Lease as RAF FH630. Serving with No. 12 Elementary Flying Training School at Goderich, Ontario at time of crash.1942-04-08 Taken on Strength 2019-08-20
1942-June-25 Accident: 12 Elementary Flying Training School Loc: Hawksville Names: Joly | Small
1942-08-04 Struck off Strength Struck off, after Category A crash on 25 June 1942 2019-08-20
 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page 12 EFTS Course Photos
12 EFTS Course Photos