Lockheed CT-133 Silver Star Shooting Star T-33 T-33A CT-33

The Canadair CT-133 Silver Star (company model number CL-30) is the Canadian license-built version of the Lockheed T-33 jet trainer aircraft, in service from the 1950s to 2005.
The Canadair CT-133 was the result of a 1951 contract to build T-33 Shooting Star trainers for the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF). The powerplant is a Rolls-Royce Nene 10 turbojet instead of the Allison J33 used by Lockheed in the production of the original T-33. A project designation of CL-30 was given by Canadair and the name was changed to Silver Star. The appearance of the CT-133 is very distinctive due to the large fuel tanks usually carried on each wingtip. A total of 656 CT-133 aircraft were built by Canadair.
The CT-133 entered service in the RCAF as its primary training aircraft for fighter/interceptors. The designation of the Silver Star in the Canadian Forces was CT-133.
The CT-133's service life in the RCAF (and later the Canadian Forces) was extremely long. One of the more unusual roles it played was as an aerobatic demonstration aircraft, the RCAF's Red Knight. Although the aircraft stopped being used as a trainer in 1976, there were still over 50 aircraft in Canadian Forces inventory in 1995. The youngest of these airframes was then 37 years old and had exceeded its expected life by a factor of 2.5. During this period, the Canadair T-33 was employed in communication, target towing, and enemy simulation. Wikipedia
 Wikipedia Canadair CT-133 Silver Star
Wikipedia Canadair CT-133 Silver Star
CASPIR Aircraft Groups:
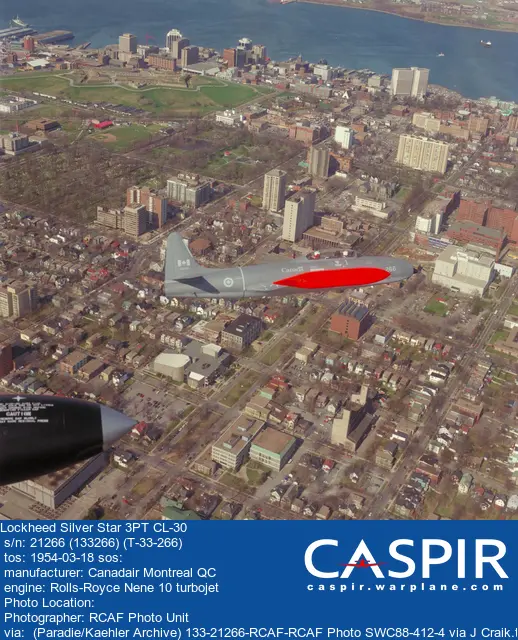
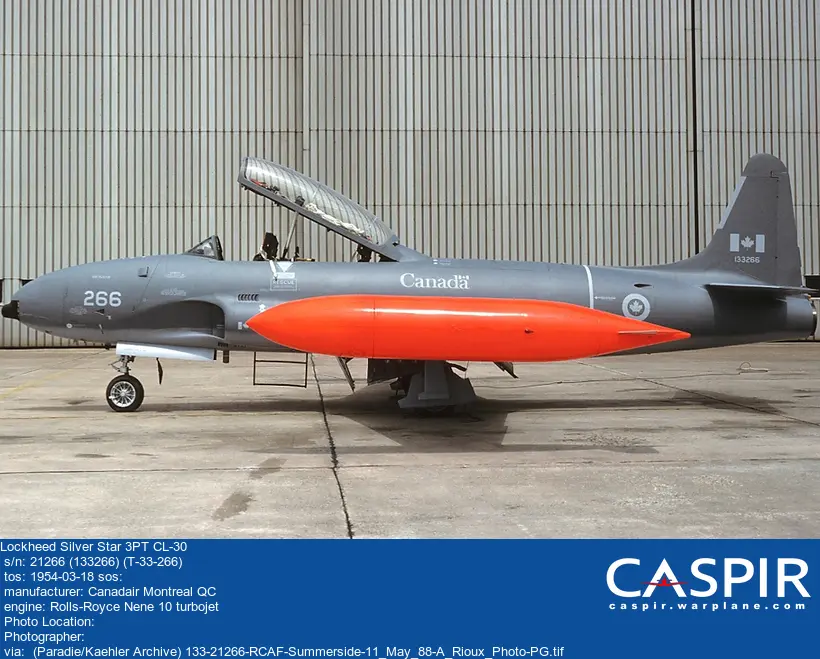
RCAF On Strength (689), RCAF 400 Squadron (3), Canadian Aircraft Losses (54), RCN On Strength (1)Silver Star 3PT 21266
Served with VU33/409 Squadron at CFB Comox 1982-1983. Delmar Target Tow gear installed. With 434 (CS) Squadron CFB Greenwood. Cat A crash 27 July 1994 nw of Halifax NS. Capt. H.W. Munro killed.
1954-03-18 Taken on Strength . No Record Card. From 2005 Numerical register. 2022-08-04
1994-07-27 Accident Category A 2022-03-14








 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Find-A-Grave.com
Find-A-Grave.com Heatherdale Memorial Gardens, Canada
Heatherdale Memorial Gardens, Canada Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page
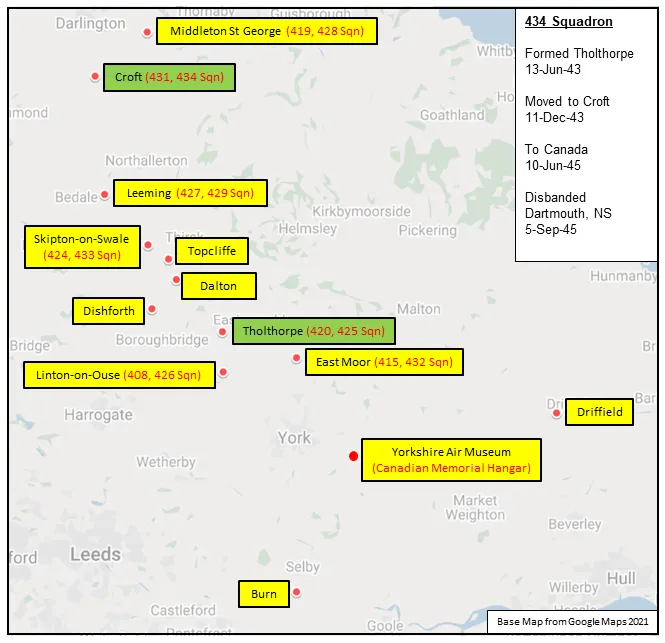
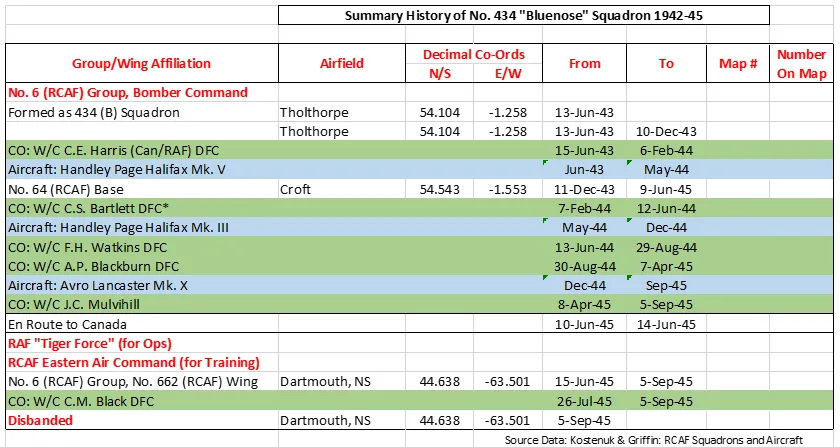
 Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)