McClung, Vernon Frederick (Flying Officer)
Killed in Action 1945-June-18


Birth Date: 1922-May-09
Born:
Parents: Son of Frederick W. and Jessie G. McClung, of Stoney Creek, Ontario.
Spouse:
Home: Stoney Creek, Ontario
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
442 Sqn- Squadron
Un Dieu, Une Reine, Un Coeur One God, one queen, one heart
Base
Rank
Flying Officer
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
J/37017
Crew or Other Personnel
Mustang KH694
Mustang serial: KH694
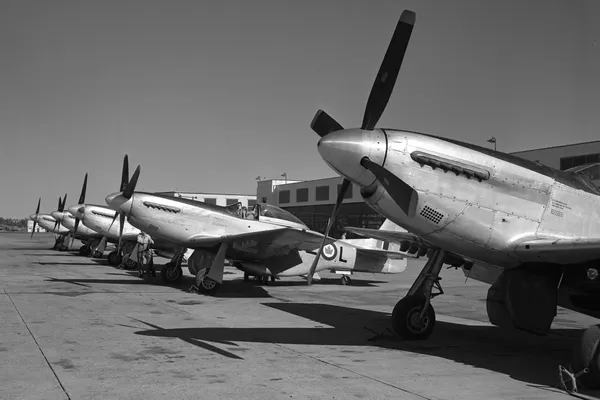

North American Mustang Mk. IV, RCAF (Serial No. 9253), coded BA-S,
No. 424 Squadron, Hamilton, Ontario
Chris Charland noted that the Mustang in the forefront is former USAF P-51D (Serial No. 44-74502A).
The North American Aviation P-51 Mustang is an American long-range, single-seat fighter and fighter-bomber used during World War II and the Korean War, among other conflicts. The Mustang was designed in April 1940 by a team headed by James Kindelberger of North American Aviation (NAA) in response to a requirement of the British Purchasing Commission. The Purchasing Commission approached North American Aviation to build Curtiss P-40 fighters under license for the Royal Air Force (RAF). Rather than build an old design from another company, North American Aviation proposed the design and production of a more modern fighter. The prototype NA-73X airframe was rolled out on 9 September 1940, 102 days after the contract was signed, and first flew on 26 October
The Mustang was designed to use the Allison V-1710 engine, which had limited high-altitude performance in its earlier variants. The aircraft was first flown operationally by the RAF as a tactical-reconnaissance aircraft and fighter-bomber (Mustang Mk I). Replacing the Allison with a Rolls-Royce Merlin resulted in the P-51B/C (Mustang Mk III) model, and transformed the aircraft's performance at altitudes above 15,000 ft (4,600 m) (without sacrificing range), allowing it to compete with the Luftwaffe's fighters. The definitive version, the P-51D, was powered by the Packard V-1650-7, a license-built version of the two-speed, two-stage-supercharged Merlin 66, and was armed with six .50 caliber (12.7 mm) AN/M2 Browning machine guns.
Canada had five squadrons equipped with Mustangs during the Second World War. RCAF Nos. 400, 414 and 430 Squadrons flew Mustang Mk. Is (1942"“1944) and Nos. 441 and 442 Squadrons flew Mustang Mk. IIIs and Mk. IVAs in 1945. Wikipedia and Harold Skaarup web page
Unit Desciption
442 Sqn Un Dieu, Une Reine, Un Coeur ("Caribou")
History of the Squadron before and during World War II (Aircraft: Spitfire VB, IXB, IXE, Mustang III)

[ Note that during WWII the squadron did not have a badge nor a motto. These were awarded later.]
No 442 (F) Squadron was formed in Rockcliffe, ON  as No. 14 (F) Squadron RCAF on January 2, 1942. It originally flew Curtiss Kittyhawks with the RCAF Western Air Command due to the threat to Canada's west coast after the Pearl Harbor attack. The squadron moved to Alaska and participated on strafing and bombing missions against then-Japanese held Kiska during the Aleutian Islands Campaign. The squadron was the fifth of six home squadrons transferred overseas without its aircraft, and was re-designated No. 442 (F) Squadron RCAF at Digby, Lincolnshire, UK.
as No. 14 (F) Squadron RCAF on January 2, 1942. It originally flew Curtiss Kittyhawks with the RCAF Western Air Command due to the threat to Canada's west coast after the Pearl Harbor attack. The squadron moved to Alaska and participated on strafing and bombing missions against then-Japanese held Kiska during the Aleutian Islands Campaign. The squadron was the fifth of six home squadrons transferred overseas without its aircraft, and was re-designated No. 442 (F) Squadron RCAF at Digby, Lincolnshire, UK. on February 8 1944. It flew Spitfire aircraft in offensive and defensive operations in the preparation for D-Day, and afterwards gave close support to the ground troops. They moved with the ground troops through France, the Low Countries, and Germany. In March 1945 the squadron was re-equipped with Mustang aircraft, to provide fighter cover for long-range bomber groups. The squadron was disbanded at Molesworth, Huntingdonshire, UK
on February 8 1944. It flew Spitfire aircraft in offensive and defensive operations in the preparation for D-Day, and afterwards gave close support to the ground troops. They moved with the ground troops through France, the Low Countries, and Germany. In March 1945 the squadron was re-equipped with Mustang aircraft, to provide fighter cover for long-range bomber groups. The squadron was disbanded at Molesworth, Huntingdonshire, UK  on August 7, 1945.
on August 7, 1945.
In the course of operations, the squadron flew 4954 sorties for the loss of16 pilots, of whom 1 was killed, 9 presumed dead and 4 POWs. They accounted for 56 enemy aircraft confirmed destroyed, 5 probables and 25 damaged. In ground attacks they were credited with 909 motor vehicles, 125 locomotives and 194 trains. The squadron had 1 ace: Flight Lieutenant D.C. Gordon, DFC. The squadron amassed 1 DSO, 3 Bars to DFC, 10 DFCs, 1 Croix de Guerre (France). Battle Honours were: Fortress Europe 1944, France and Germany 1944-45, Normandy 1944, Arnhem, Rhine, Aleutians 1943. Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Maps for Movements of 442 Squadron 1944-45
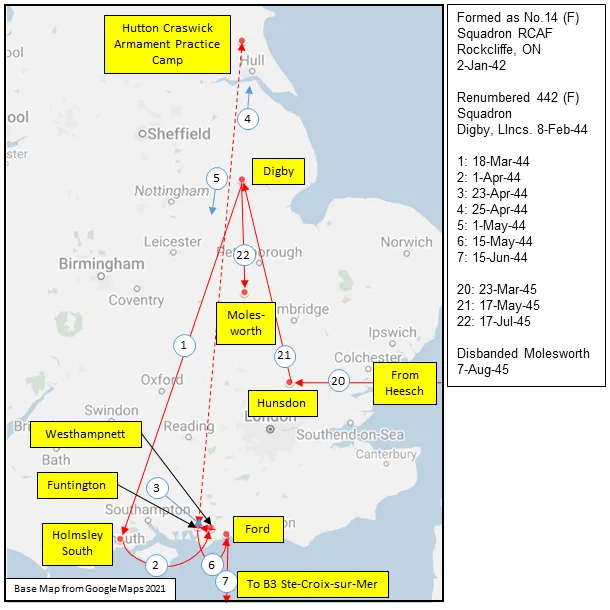
MAP 1: 442 Squadron Movements 1944-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
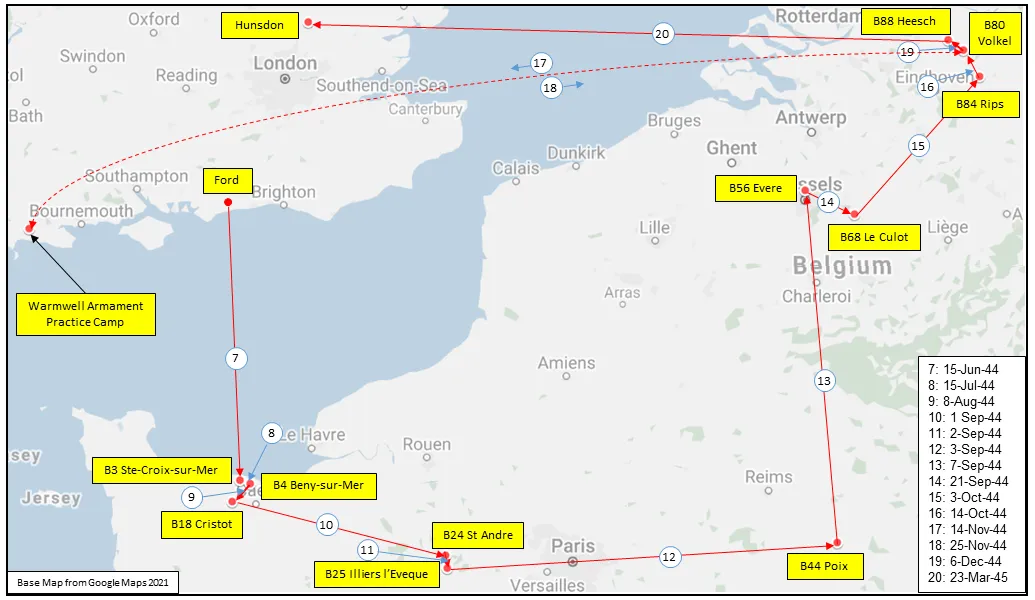
MAP 2: 442 Squadron Movements 1944-45
|
442 Squadron History Summary 1944-45
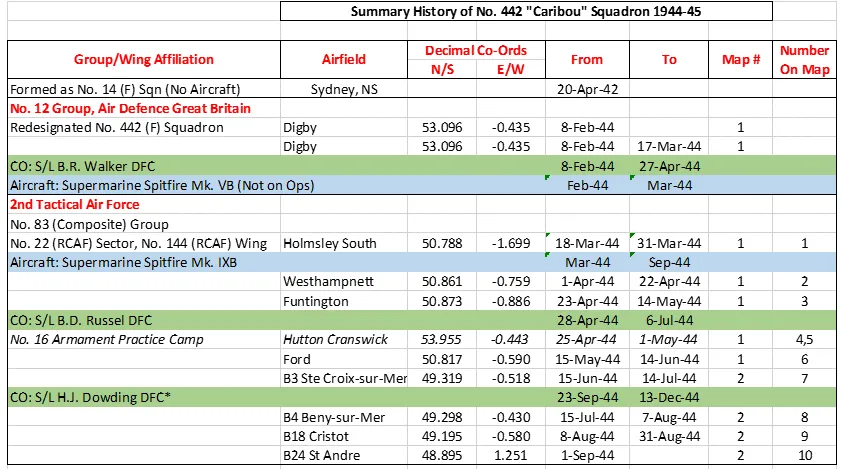
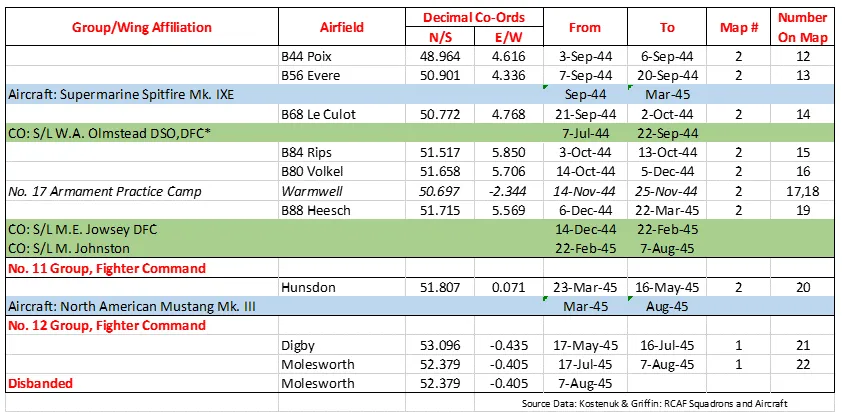
442 Squadron History Summary 1944-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard, Vampire III, Mustang IV, Sabre 5, Expeditor, Otter, Cormorant)

The squadron was re-formed at Vancouver, British Columbia  on 15 April 1946. It was redesignated 442 "City of Vancouver" (F) Squadron on 3 September 1952. It flew de Havilland Vampire, North American Mustang and Canadair Sabre aircraft in a fighter role until October 1958 when it was reassigned to a light transport and emergency rescue role and re-equipped with Beech Expeditor and de Havilland Otter aircraft. It was redesignated 442 Squadron. A reduction of the Auxiliary Force resulted in the squadron being disbanded on 1 April 1964.
on 15 April 1946. It was redesignated 442 "City of Vancouver" (F) Squadron on 3 September 1952. It flew de Havilland Vampire, North American Mustang and Canadair Sabre aircraft in a fighter role until October 1958 when it was reassigned to a light transport and emergency rescue role and re-equipped with Beech Expeditor and de Havilland Otter aircraft. It was redesignated 442 Squadron. A reduction of the Auxiliary Force resulted in the squadron being disbanded on 1 April 1964.
The squadron was re-formed as '442 Communications and Rescue Squadron' on 8 July 1968, from '121 Composite Unit' (authorized 1 January 1959). The squadron is based at Comox, British Columbia  , flying the CH-149 Cormorant Helicopters. The primary role of 442 Transport and Rescue Squadron is the provision of aviation resources in support of the Joint Rescue Coordination Center (JRCC) Victoria. This region consists of approximately 920,000 square kilometers of mainly mountainous terrain of Yukon and British Columbia and 560,000 square kilometers of the Pacific Ocean extending to approximately 600 nautical miles offshore, including over 27,000 kilometers of rugged British Columbia coastline. The rugged and often inaccessible terrain, severe weather, and large expanses of sparsely populated areas make the Victoria SRR the most demanding region in the country.
, flying the CH-149 Cormorant Helicopters. The primary role of 442 Transport and Rescue Squadron is the provision of aviation resources in support of the Joint Rescue Coordination Center (JRCC) Victoria. This region consists of approximately 920,000 square kilometers of mainly mountainous terrain of Yukon and British Columbia and 560,000 square kilometers of the Pacific Ocean extending to approximately 600 nautical miles offshore, including over 27,000 kilometers of rugged British Columbia coastline. The rugged and often inaccessible terrain, severe weather, and large expanses of sparsely populated areas make the Victoria SRR the most demanding region in the country.
While approximately 80 of the Squadron's personnel strength of 200 are aircrew trades, including pilots, navigators, flight engineers, and Search and Rescue Technicians (SAR Techs), the majority are maintenance personnel, charged with keeping the aircraft at peak operational readiness. On occasions when major search operations dictate the establishment of a forward operating base somewhere else in the province, 442's maintenance personnel will deploy with the aircrew, providing servicing and repairs to aircraft on site.