Mansfield, Richard Gerard
Killed in Action 1944-11-24
Service
RCAF
Unit
419 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Moosa Aswayita Beware of Moose
Base
Middleton St George
Rank
Flying Officer
Position
Flying Officer
Service Numbers
J/85770
Home
 Ottawa, Ontario
Ottawa, Ontario
Flying Officer Mansfield RCAF awarded DFC whilst with 419 Squadron. Gazetted 9 January 1945
CITATIONPilot Officer Mansfield has participated in many attacks on various enemy targets and has displayed a fine fighting spirit and great keenness. On a recent occasion he captained an aircraft detailed to attack Duisburg. During the operation the aircraft was hit by fire from the ground defences and the mid-upper gunner was badly wounded. Nevertheless, Pilot Officer Mansfield completed a successful attack and flew the aircraft to an airfield near the English coast where he effected a landing so that his wounded crew member could be taken off for medical attention. Pilot Officer Mansfield then took off again and flew the aircraft to base. This officer is a most able and inspiring captain whose example has been well reflected in the high standard of efficiency of his crew. (London Gazette)
Lancaster Mk.X KB785
Operational 1944-November-24 to 1944-November-24
419 (B) Sqn (RCAF) Middleton St. George
419 Moose Squadron (Moosa Aswayita). At 18:12 KB785 was returning from an assigned cross country detail, they "came up" on R/T. Where instructions from Officer in charge of Night Flying told the crew to proceed on a Bombing Detail. These instruction were acknowledged at 1814 hours.At 18:25 Bradbury Bombing Range called their base saying they had seen a great flash in the air, after which the sound of an approaching aircraft's motors were no longer heard.
An investigation lead by two Engineers and headed by an Investigating Officer, gave conflicting evidence on the cause of the events surrounding the aircraft's loss. It then fell on to Air Commodore R. E. McBurney to consider the evidence of the 16 witnesses to the accident, which he proceed to do. In his opinion the witnesses provided greater help in solving what had happened. And he therefore accepted or put forth the cause of the fire being due to the fuel jettison system which was inadvertently selected instead of cold air. And the Air Commodore advised that all Groups to render the fuel jettison system inoperative until modified or a satisfactory system replaces it.
KB785 came down 250 yards South East of Sedgefield Railway Station, killing all crew members. The crew's loss was felt deeply by the whole squadron as it was nearing the completion of the crews tour. (419 Squadron Website)
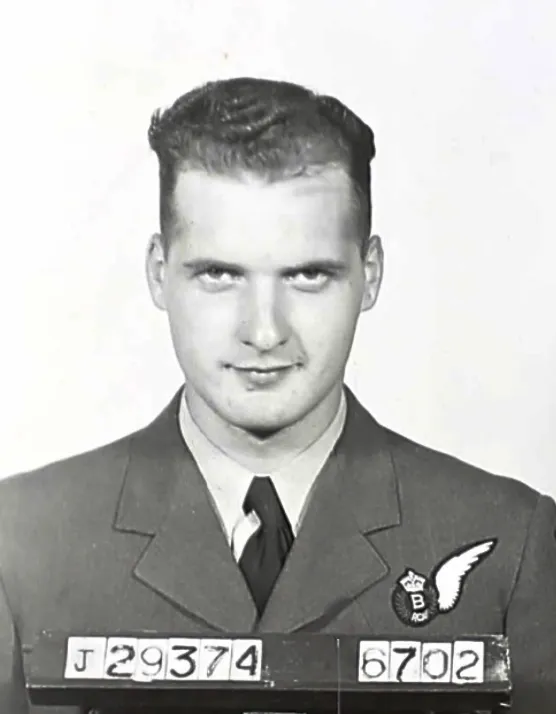
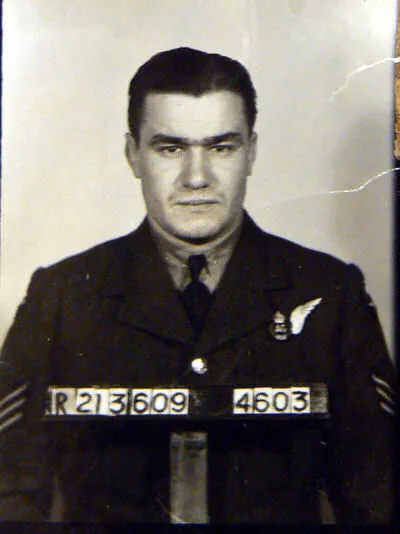
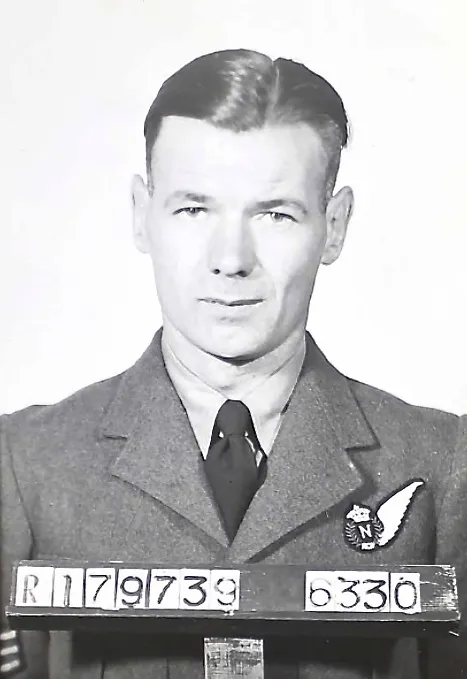
Flying Officer A.C. Hirst, Flying Officer R.G. Mansfield, Pilot Officer G.H. Warren-Darley, Flight Sergeant(s) L.W. Toth, D.A. Gunn, J.J. Murphy, and Pilot Officer D.G. Newland (RAF) were all killed
On 19 June 1994 a special plaque was dedicated and a maple tree was planted as a memorial to the crew of KB 785 The plaque was sited on the church wall adjoining the village memorial. This took place in the village of Sedgefield and the service was conducted at the St Edmund's Parish Church. The Roll of Honour on the plaque reads: On 24th November 1944, the crew of a Lancaster Bomber of number 419 Moose Squadron, Royal Canadian Air Force, Middleton St George, paid the SUPREME SACRIFICE. This plaque is dedicated to those who lost their lives Pilot Officer Richard Mansfield DFC Ottawa, Canada; Flight Sergeant Douglas Ginn Toronto, Canada; Flight Sergeant George Warren-Dailey Toronto, Canada; Flying Officer Allan Hirst Vancouver, Canada; Flight Sergeant John Murphy Detroit, USA; Flight Sergeant Leslie Toth Kipling, Canada; Sergeant Derrick Newland London, England. LEST WE FORGET. Detail provided by David E. Thompson, Middlesborough, England.
Lancaster KB785
Avro Lancaster
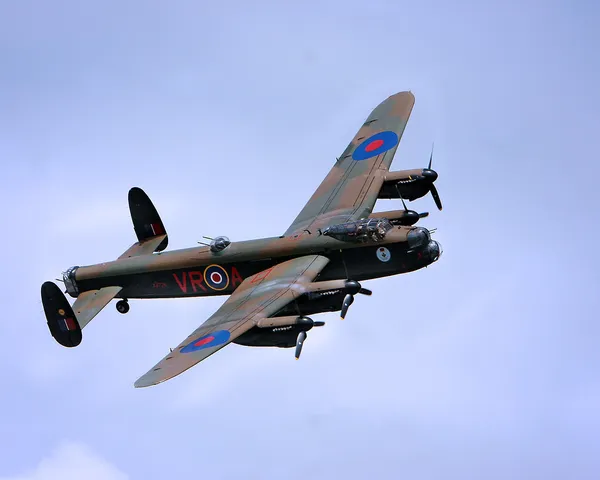

Canadian Warplane Heritage Museum
The Avro Lancaster is a British Second World War heavy bomber. It was designed and manufactured by Avro as a contemporary of the Handley Page Halifax, both bombers having been developed to the same specification, as well as the Short Stirling, all three aircraft being four-engined heavy bombers adopted by the Royal Air Force (RAF) during the same wartime era.
The Lancaster has its origins in the twin-engine Avro Manchester which had been developed during the late 1930s in response to the Air Ministry Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use". Originally developed as an evolution of the Manchester (which had proved troublesome in service and was retired in 1942), the Lancaster was designed by Roy Chadwick and powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlins and in one version, Bristol Hercules engines. It first saw service with RAF Bomber Command in 1942 and as the strategic bombing offensive over Europe gathered momentum, it was the main aircraft for the night-time bombing campaigns that followed. As increasing numbers of the type were produced, it became the principal heavy bomber used by the RAF, the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) and squadrons from other Commonwealth and European countries serving within the RAF, overshadowing the Halifax and Stirling. Wikipedia
419 (B) Sqn Moosa Aswayita ("Moose")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington IC, III, Halifax II, Lancaster X)

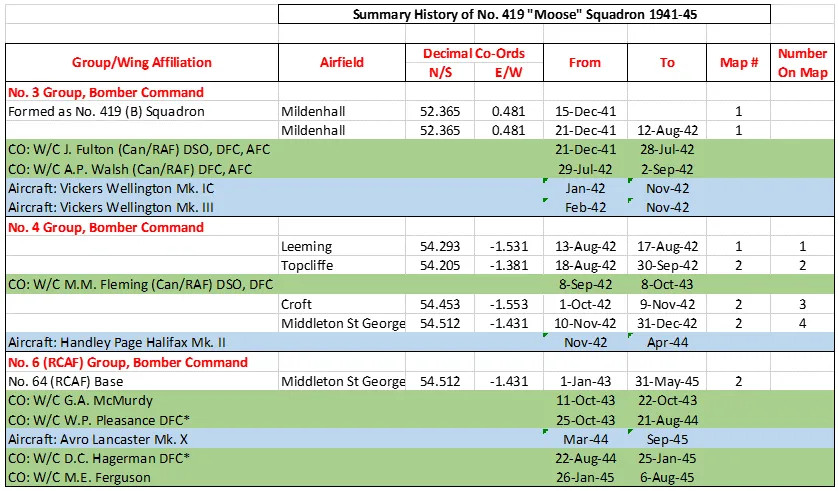
419 (Bomber) Squadron formed at RAF Mildenhall, Suffolk, UK in 1941 as part of No 3 Group of Bomber Command. It got its name from its first commanding officer, Wing Commander John "Moose" Fulton, DSO, DFC, AFC. The squadron operated Vickers Wellington, then Handley Page Halifax and finally Avro Lancaster bombers through the course of WWII, with the squadron code letters VR. It was the third RCAF bomber unit to be formed in England. It started operations in January 1942, converting almost immediately from Wellington Mk ICs to Wellington Mk IIIs and then moving north to Leeming, Yorkshire, as part of 4 Group Bomber Command in August 1942. After short stays at Topcliffe and Croft , it moved to Middleton St. George, County Durham in November 1942, from which it flew until the end of hostilities. Here in November 1942 it was re-equipped with Halifax Mk IIs, which it flew for the next 18 months on the night offensive against Germany. In January 1943 it joined the newly formed 6 (RCAF) Group of Bomber Command.
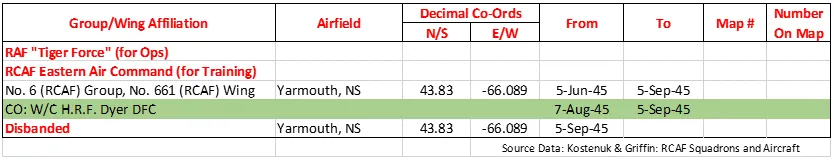
In April 1944 the squadron began to convert to the Avro Lancaster Mk X, which was produced in Canada and flown across the Atlantic. The squadron remained continuously on the offensive until 25 April 1945, when it flew its last sortie. Squadron personnel flew a total of 4,325 operational sorties during the war from Mannheim to Nuremberg, Milan to Berlin and Munich to Hanover, inflicting heavy damage on the enemy. On completion of the war in Germany, the squadron was earmarked to become part of the proposed "Tiger Force" to continue the war against Japan. However, the Japanese surrender in August 1945 led to the disbandment of the squadron in at Yarmouth, Nova Scotia September 1945.
As a result of its wartime record, 419 Squadron became one of the most decorated units under the RCAF during the war. Over a span of roughly three-and-a-quarter years it logged 400 operational missions (342 bombing missions, 53 mining excursions, 3 leaflet raids and 1 "spoof") involving 4,325 sorties. A total of one hundred and twenty nine aircraft were lost on these operations. Members of the squadron accumulated 1 VC, 4 DSO's, 1 MC, 150 DFC's, 3 bars to DFC, 1 CGM, 35 DFM's: the VC was awarded posthumously to Flight Sergeant Andrew Mynarski for his attempts to help a fellow crew member escape from their burning aircraft. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1942-44, Baltic 1942-44, Fortress Europe 1942-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1942-44, Ruhr 1942-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1942-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1942; 1944. Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
 Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum)
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum)
Maps for Movements of 419 Squadron 1941-45
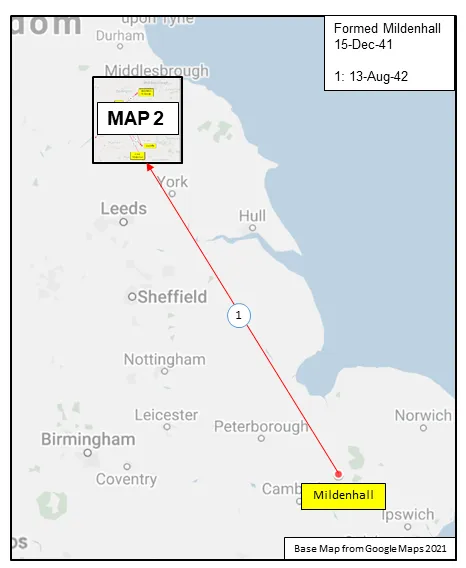 MAP 1: 419 Squadron Movements Dec 1941-Aug-42 (right-click on image to display enlarged new tab) | 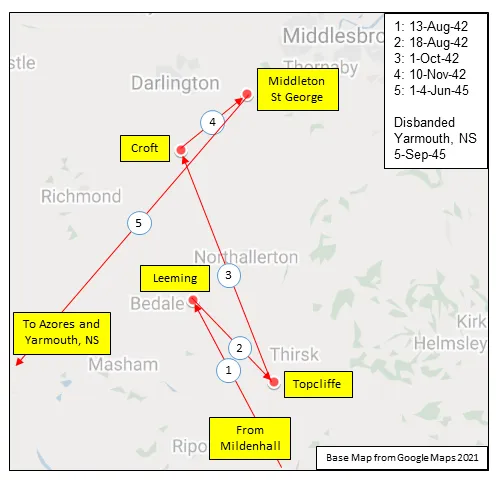 MAP 2: 419 Squadron Movements Aug 1942-Jun 1945 | 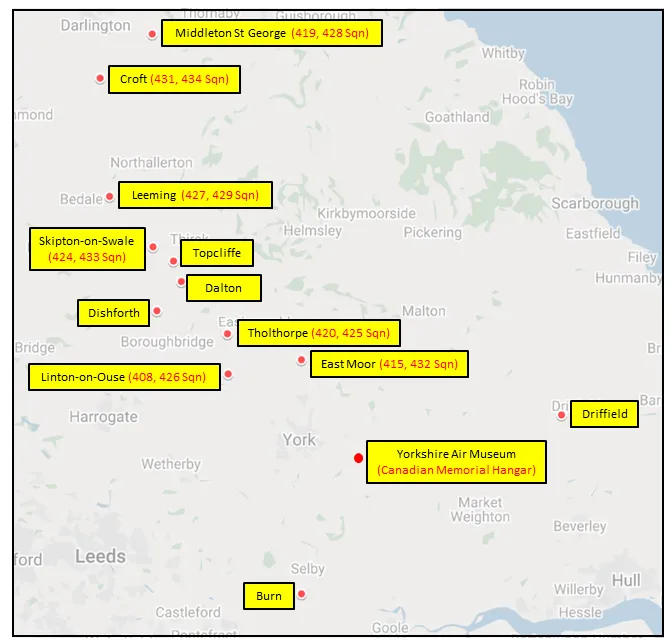 MAP 3: 6 Group Bomber Bases 1943-1945 |
419 Squadron History Summary 1941-45
419 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Canuck, Silver Star, Freedom Fighter, Hornet)
The squadron was reactivated on 15 March 1954 at North Bay, Ontario , as an all-weather fighter squadron flying the CF-100 Canuck. It moved to the NATO Air Division base at Baden-Soellingen, Germany shortly after being formed. The squadron remained there until its disbandment in December 1962.
The squadron was again re-formed in December 1970, when it relocated to Cold Lake, Alberta as No. 1 Canadian Forces Flight Training School. It initially flew the T-33 Silver Star but then transitioned to the Canadair CF-5 Freedom Fighter. The squadron was on full active duty in November 1975 but disbanded again 20 years later when the CF-5’s were retired in June 1995.
The squadron was again reactivated as 419 Tactical Fighter (Training) Squadron on 23 July 2000. The squadron has since conducted Phase IV of the NATO Flying Training Canada (NFTC) program for the air forces of Canada, Austria, Denmark, Italy, Hungary, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, the United Arab Emirates and the United Kingdom. This program trains basic jet pilots to become fighter pilots and prepares them for training on CF-188 class aircraft through instruction in Air-to-Air and Air-to-Ground combat tactics over a six month period.



 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial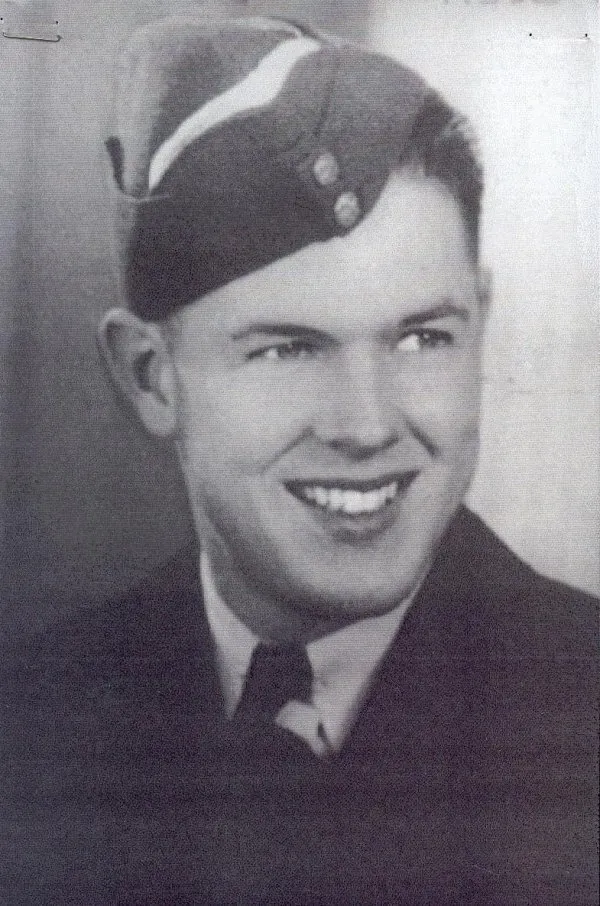






 Lancaster Bomber
Lancaster Bomber Wikipedia
Wikipedia Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page