Harper, Willard James (Flight Lieutenant)
Killed in Action 1944-05-14


Birth Date: 1910-June-24
Born:
Home: Rossland, British Columbia
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
418 Sqn- Squadron
Piyautailili Defend even unto death: Inuktitut
Base
Rank
Flight Lieutenant
Position
Flight Lieutenant
Service Numbers
C/5584
Target
 Luxeuil France
Luxeuil France
de Havilland Mosquito
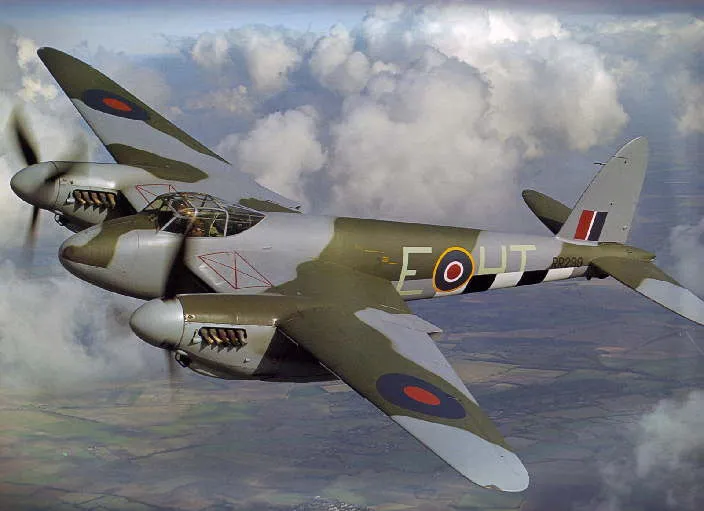

The de Havilland DH.98 Mosquito was a British twin-engine shoulder-winged multi-role combat aircraft, introduced during the Second World War. It was one of few operational front-line aircraft of the era whose frame was constructed almost entirely of wood. Nicknamed The Wooden Wonder, it was affectionately as the "Mossie" to its crews. The total number of DH98 Mosquito aircraft built was 7,781, the type serving with the main Allied air forces, including both the United States and Russia.
When Mosquito production began in 1941 it was the fastest propeller driven operational aircraft in the world. The first variant was an unarmed, high-speed, high-altitude photo-reconnaissance aircraft. Originally conceived as an unarmed fast bomber, the Mosquito's use evolved during the war into many roles including low to medium-altitude daytime tactical bomber, high-altitude night bomber, pathfinder, day or night fighter, fighter-bomber, intruder, and maritime strike aircraft. It was also used by the British Overseas Airways Corporation (BOAC) as a fast transport to carry small high-value cargoes to, and from, neutral countries, through enemy-controlled airspace. The crew of two, pilot and navigator, sat side by side, but a single passenger could ride in the aircraft's bomb bay when necessary.
The Mosquito FB Mk. VI was often flown in special raids, such as Operation Jericho, an attack on Amiens Prison in early 1944, and precision attacks against military intelligence, security and police facilities (such as Gestapo headquarters). On the 10th anniversary of the Nazi' seizure of power in 1943, a morning Mosquito attack knocked out the main Berlin broadcasting station while Hermann Goering was speaking, putting his speech off the air. Goering later said: "It makes me furious when I see the Mosquito. I turn green and yellow with envy. There is nothing the British do not have. They have the geniuses and we have the nincompoops."
The Mosquito flew with the RCAF and other air forces in the European, Mediterranean and Italian theatres. After the end of the Second World War Spartan Air Services flew 10 ex-RAF Mosquitoes, mostly B.35's plus one of only six PR.35's built, for high-altitude photographic survey work in Canada. There are approximately 30 non-flying Mosquitos around the world with five airworthy examples, four in the United States, and one in Canada. Harold Skaarup web page and Wikipedia
 BAE Systems (formerly De Havilland)
BAE Systems (formerly De Havilland)
418 Sqn Piyautailili ("City of Edmonton")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Boston III, Mosquito II, FB Mk VI)

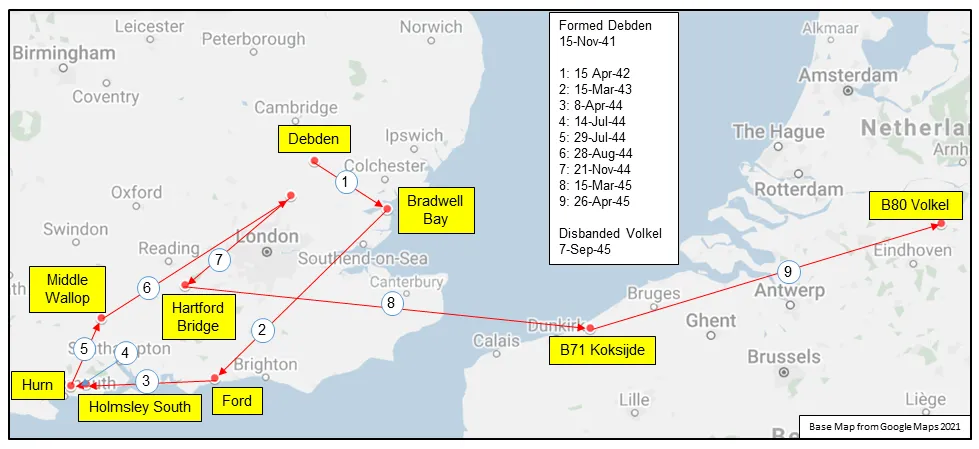
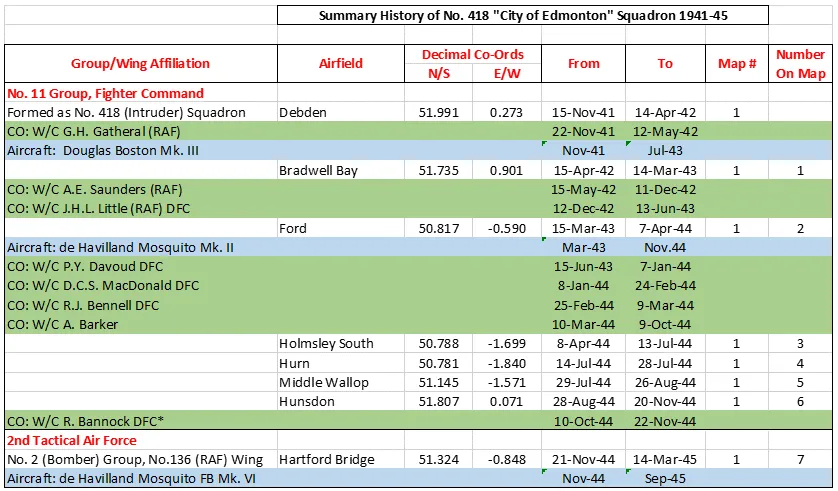
[Note that the squadron crest and motto were not given to the squadron until after WWII. During WWII the squadron had neither crest nor motto.] The squadron was formed at Debden, Essex, UK in November 1941as the RCAF's only Intruder Squadron. As such, it was attached to 11 Group of Fighter Command (later renamed Air Defence of Great Britain), conducting day and night intruder operations. These involved a variety of targets, strategic attacks and intruder attacks on airfields. Originally the squadron flew Douglas Boston Mk. III, with the squadron code letters being TH. They flew from a number of airfields in the south of England from 1942 to 1944, namely Debden, Bradwell Bay, Ford, Holmsley South, Hurn, Middle Wallop and Hunsdon. In March 1943 the squadron re-equipped with de Havilland Mosquito Mks. II and F.B. VI aircraft., with a marked increase in their successes in destroying enemy aircraft. The squadron claimed its hundredth victory in May 1944. After D-Day the squadron was involved in the campaign against V-1 and V-2 weapons.
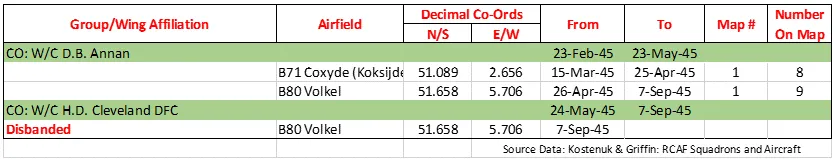
On November 21, 1944 the squadron was transferred from Fighter Command to the 2nd Tactical Air Force in No. 136 (RAF) Wing and operated from Hartford Bridge, Hampshire, UK. before moving to Base 71 at Coxyde, Belgium, and then finally moving to Base 80 at Volkel, the Netherlands . The squadron was disbanded there on September 7th 1945.
The squadron was the most high-scoring unit of the RCAF in WWII. It claimed 178 aircraft and 79 and a half V-1 Flying Bombs. There were a number of aces, among them Wing Commander R. Bannock, DFC and Bar, Squadron Leader R. Gray, DFC, Flying Officer S.P. Reid DFC, Squadron Leader H.D. Cleveland DFC, Flight Lieutenant C.M. Jasper DFC, Flight Lieutenant J. Evans, Flight Lieutenant S.H.R. Cotterill DFC, Flight Lieutenant D.E. Forsyth, Squadron Leader J.B. Kerr, Flight Lieutenant H.E. Miller and Flight Lieutenant P.S. Leggatt. The squadron won 3 DSO's, 42 DFC's, 9 Bars to DFC's, 1 Second Bar to DFC, 5 DFM's, 1 DFC(USA) and 1 Air Medal (USA). Overall, 3492 sorties were flown, 402 of which were on anti-V-1 patrols. 11,248 hours were flown operationally for the loss of 59 aircraft. The squadron was credited with destroying 178 aircraft, 17 locomotives destroyed and 59 damaged, with other destruction of rolling stock and motor vehicles. Battle Honours were: Defence of Britain 1944, Fortress Europe 1942-44, Dieppe, France and Germany 1944-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine. Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Map for Movements of 418 Squadron 1941-45
418 Squadron History Summary 1941-45
418 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard II, Mitchell, Expeditor, Silver Star, Otter, Twin Otter, Kingfisher)

The squadron re-formed at Edmonton, Alberta on 15 April 1946, flying North American B-5 Mitchell aircraft in a light bomber role. It moved to RCAF Station Namao, Alberta in 1955. In March 1958 it was reassigned to a light transport and emergency rescue role and was re-equipped with Beechcraft Expeditor and de Havilland Otter aircraft. Its duties ranged from aid to the civil power to aerial resupply. On 27 May 1967 it received a Squadron Standard for 25 years’ service. On 1 February 1968 the squadron was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces as No. 418 “City of Edmonton†Air Reserve Squadron, and acquired de Havilland Twin Otter aircraft The squadron was disbanded in 1994, its aircraft being transferred to No 440 Transport Squadron.
418 Squadron was re-formed on March 13, 2019, The unit is based at 19 Wing Comox, British Columbia as 418 Search and Rescue Operational Training Squadron, training aircrew and maintenance personnel on the CC-295 Kingfisher, using simulators and aircraft, when the aircraft are delivered.
 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com
 Mosquito
Mosquito Wikipedia Mosquito
Wikipedia Mosquito Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page USAAF F-8 Mosquito Serial Numbers
USAAF F-8 Mosquito Serial Numbers Mosquitos shipped to Taiwanese Airforce
Mosquitos shipped to Taiwanese Airforce