Dunaway, George Mason (Pilot Officer)
Killed in Action 1941-November-21
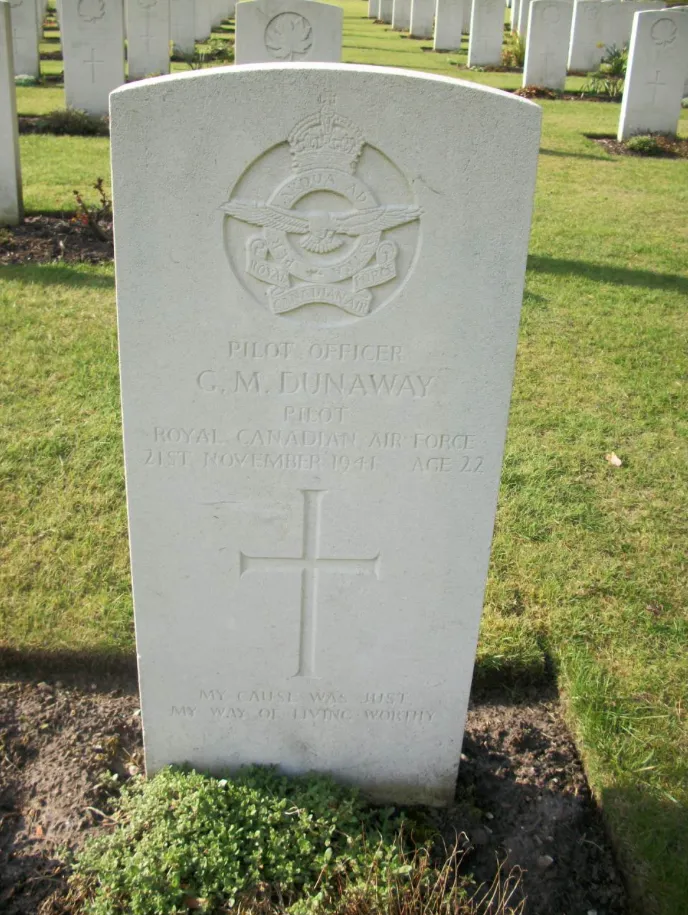


Birth Date: 1919-January-03
Born: Tulsa Oklahoma USA
Parents: Son of George Mason Dunaway and Dana Mary Dunaway, of Siloam Springs, Arkansas, U.S.A.
Spouse:
Home: Fayetville, Arkansas, USA
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RCAF
Unit
414 Sqn- Squadron
Totis Viribus With All our Might
Base
RAF Croyden
Rank
Pilot Officer
Position
Pilot
Service Numbers
J/5796
Crew or Other Personnel
Tomahawk AH902
Tomahawk serial: AH902
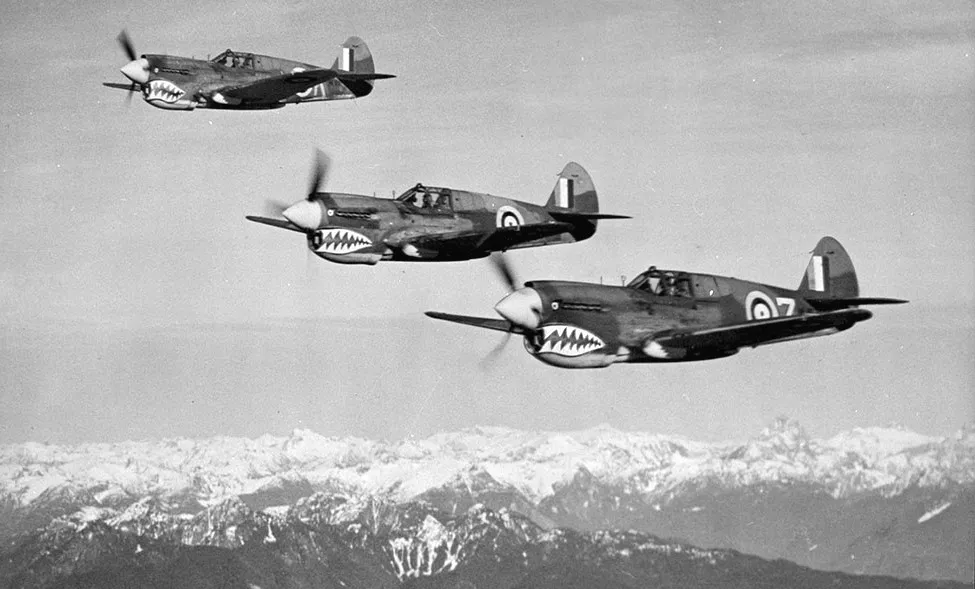

RCAF Curtiss P-40 Kittyhawks in formation over the West Coast, 11 Nov 1942
The Curtiss P-40 (known as the Warhawk in the USA) is single-engined, single-seat, all-metal fighter and ground-attack aircraft that first flew in 1938. Â The British Commonwealth air forces including the RCAF, and the Soviet air forces used the name Tomahawk for models equivalent to the P-40B and P-40C, and the name Kittyhawk for models equivalent to the P-40D and all later variants. Â The P-40 was in frontline service until the end of the Second World War. Â It was the third most-produced American fighter of the war after the P-51 and P-47, with 13,738 being built in Buffalo, New York. Â Based on war-time victory claims, over 200 Allied fighter pilots from 7 different nations (Australia, Canada, England, New Zealand, South Africa, the Soviet Union and the United States) became aces flying the P-40. Â A total of 13 RCAF units operated the Kittyhawk in the North West European or Alaskan theatres.
In mid-May 1940, Canadian and US officers watched comparative tests of a XP-40 and a Spitfire, at RCAF Station Uplands, Ottawa, Ontario. Â While the Spitfire was considered to have performed better, it was not available for use in Canada and the P-40 was ordered to meet home air defense requirements. Â In all, eight Home War Establishment Squadrons were equipped with the Kittyhawk: 72 Kittyhawk Mk. I, 12 Kittyhawk Mk. Ia, 15 Kittyhawk Mk. III and 35 Kittyhawk Mk. IV aircraft, for a total of 134 aircraft. Â These aircraft were mostly diverted from RAF Lend-Lease orders for service in Canada. Â The Kittyhawks were obtained in lieu of 144 Bell P-39 Airacobras originally allocated to Canada but reassigned to the RAF. Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Unit Desciption
414 Sqn Totis Viribus ("Sarnia Imperials")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Lysander III, Tomahawk I & II, Mustang I, Spitfire X)

Note that during WWII the squadron had no crest nor motto. These were awarded later. The squadron was unofficially known as the “Sarnia Imperialsâ€.
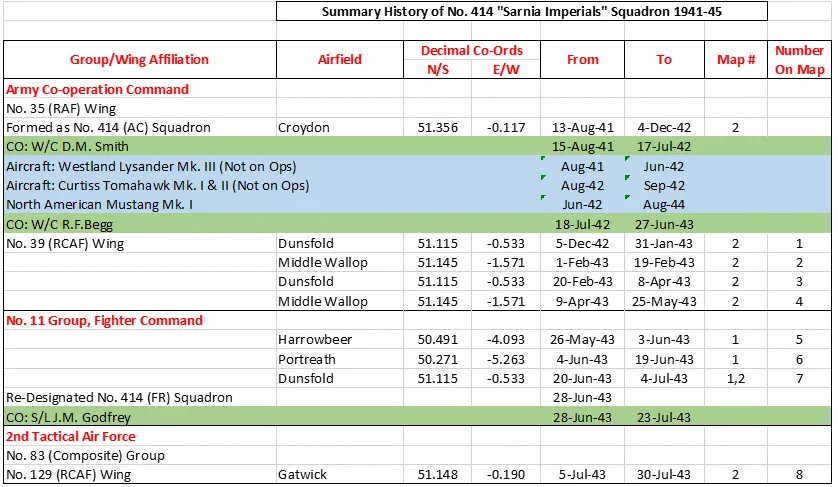
No. 414 Squadron was formed as the RCAF's 12th squadron formed overseas in WWII, at Croydon, Surrey, UK  . It was the second Army Co-operation unit to be formed in this group, and was initiated on 13 August 1941. In the early days, it flew Westland Lysander Mk. III aircraft before flying Curtiss Tomahawk Mks. I and II (both non-operationally). It saw no action in the AC role since no army units were active in Europe. On 28 June 1943 the unit was re-designated a Fighter Reconnaissance unit at Dunsfold, Surrey. Thereafter, the squadron joined the 2nd Tactical Air Force. By now it was flying North American Mustang Mk. I aircraft. The duties were to provide intelligence, such as photographic reconnaissance before and after D-Day, and tactical reconnaissance once the invasion had taken hold. The squadron was issued with Supermarine Spitfire aircraft and moved to France in August 1944, and thereafter followed the Allied armies in their progress through France, the Low Countries and Germany, providing reconnaissance for them. The squadron was disbanded at Luneburg, Germany
. It was the second Army Co-operation unit to be formed in this group, and was initiated on 13 August 1941. In the early days, it flew Westland Lysander Mk. III aircraft before flying Curtiss Tomahawk Mks. I and II (both non-operationally). It saw no action in the AC role since no army units were active in Europe. On 28 June 1943 the unit was re-designated a Fighter Reconnaissance unit at Dunsfold, Surrey. Thereafter, the squadron joined the 2nd Tactical Air Force. By now it was flying North American Mustang Mk. I aircraft. The duties were to provide intelligence, such as photographic reconnaissance before and after D-Day, and tactical reconnaissance once the invasion had taken hold. The squadron was issued with Supermarine Spitfire aircraft and moved to France in August 1944, and thereafter followed the Allied armies in their progress through France, the Low Countries and Germany, providing reconnaissance for them. The squadron was disbanded at Luneburg, Germany  on August 7, 1945.
on August 7, 1945.
In the course of WWII the squadron flew over 6,000 sorties for the loss of 23 pilots, 19 of whom were killed or missing, the remaining 4 being POWs. They claimed 29 enemy aircraft destroyed, 1 probable and 11 damaged. On ground attack, they accounted for 76 locomotives and other miscellaneous targets. The squadron produced one ace, Flight Lieutenant D.I. Hall DFC. Awards gained were 2 Bars to DFC, 16 DFCs and 3 MiD. Battle Honours were:Defence of Britain 1942-43, Fortress Europe 1942-44, Dieppe, France and Germany 1944-45: Normandy 1944, Arnhem Rhine, Biscay 1943Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
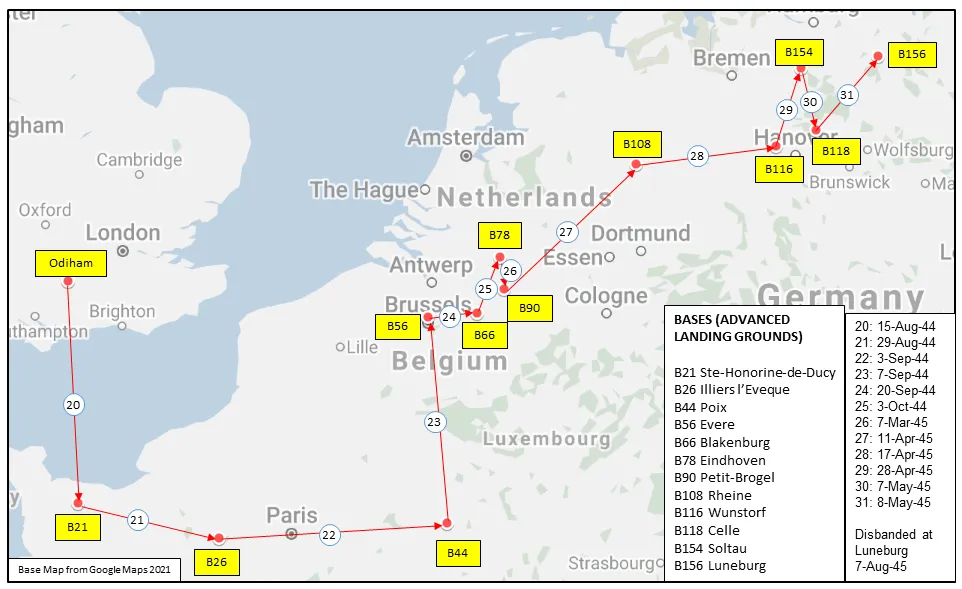
Maps for Movements of 414 Squadron 1941-45
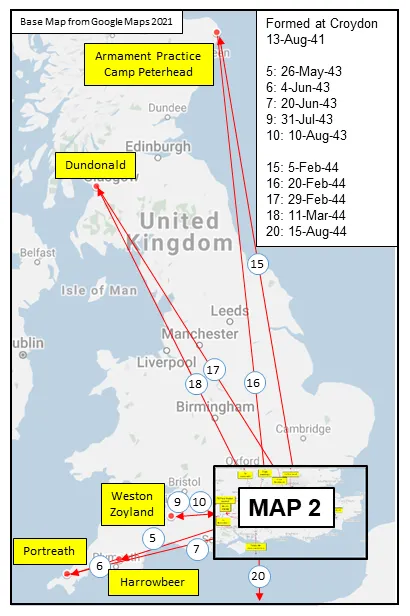
MAP 1: 414 Squadron Movements in Britain 1941-44 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
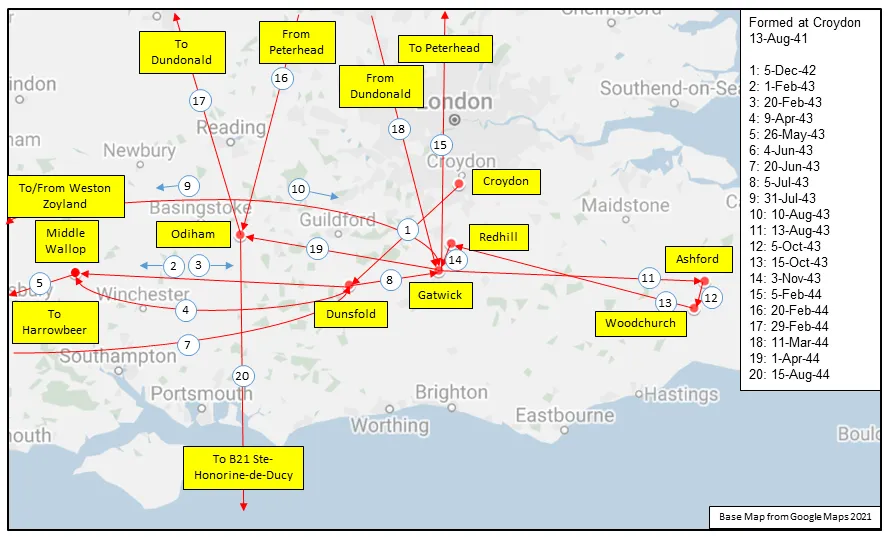
MAP 2: 414 Squadron Movements Detail of Map 1
|
414 Squadron History Summary 1941-45
414 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
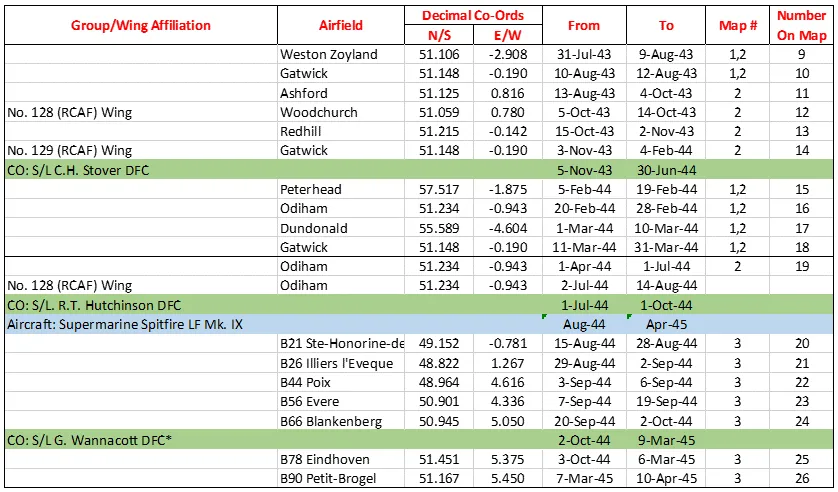
414 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 3
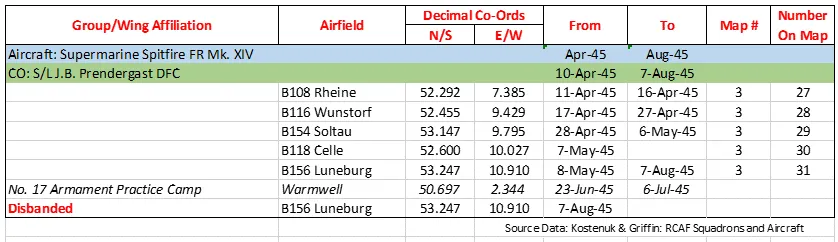
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Dakota IIIP & IVP, Sabre 4, 5, 6, Canuck, Voodoo, Silver Star)

Unofficially, No. 14 (Photographic) Squadron at Rockcliffe (Ottawa), Ontario  was formed on 12 June 1944, and it was officially renumbered No. 414 on 1 April 1947. The squadron flew Douglas Dakota IIP and IVP aircraft on vertical photographic duty, to photograph 323,754 square miles (838,520 km2) of Canada's North. When this task was completed the squadron was disbanded on 1 November 1950.
was formed on 12 June 1944, and it was officially renumbered No. 414 on 1 April 1947. The squadron flew Douglas Dakota IIP and IVP aircraft on vertical photographic duty, to photograph 323,754 square miles (838,520 km2) of Canada's North. When this task was completed the squadron was disbanded on 1 November 1950.
The squadron was re-formed as a Fighter unit at Bagotville, Quebec  on 1 November 1952, equipped with Canadair Sabre aircraft. It later joined No. 4 (Fighter) Wing at Baden-Soellingen, Germany
on 1 November 1952, equipped with Canadair Sabre aircraft. It later joined No. 4 (Fighter) Wing at Baden-Soellingen, Germany  in August 1953. In 1956, it was decided to replace one Sabre squadron in each of No. 1 Air Division Europe’s four wings with an all-weather fighter unit. When No. 419 AW(F) Squadron arrived from Canada, No. 414 was deactivated on 14 July 1957 and reactivated as All-Weather (Fighter) at North Bay, Ontario
in August 1953. In 1956, it was decided to replace one Sabre squadron in each of No. 1 Air Division Europe’s four wings with an all-weather fighter unit. When No. 419 AW(F) Squadron arrived from Canada, No. 414 was deactivated on 14 July 1957 and reactivated as All-Weather (Fighter) at North Bay, Ontario  on 5 August 1957. The squadron flew CF-100 and CF-101 aircraft on North American air defence until disbanded on 30 June 1964.
on 5 August 1957. The squadron flew CF-100 and CF-101 aircraft on North American air defence until disbanded on 30 June 1964.
The squadron re-formed once again at RCAF Station St-Hubert, Quebec  , on September 15, 1967 as 414 Electronic Warfare Squadron, with CF-100 aircraft. The unit provided Air Defence Command ground control radar personnel and airborne interceptor crews with training and experiences in combating radar jamming. On 1 February 1968 the squadron was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces. In August 1972, 414 moved to Canadian Forces Base North Bay and stayed there until 1992, when they were split in two with one part going to Canadian Forces Base Comox, British Columbia
, on September 15, 1967 as 414 Electronic Warfare Squadron, with CF-100 aircraft. The unit provided Air Defence Command ground control radar personnel and airborne interceptor crews with training and experiences in combating radar jamming. On 1 February 1968 the squadron was integrated into the Canadian Armed Forces. In August 1972, 414 moved to Canadian Forces Base North Bay and stayed there until 1992, when they were split in two with one part going to Canadian Forces Base Comox, British Columbia  as 414 Composite Squadron and the other part going to Canadian Forces Base Shearwater, Nova Scotia as 434 Composite Squadron. 414 changed its name to Combat Support Squadron in 1993 when it was equipped with the CT-133 Silver Star. In 2002, 414 Squadron was disbanded and its remaining two aircraft retired.
as 414 Composite Squadron and the other part going to Canadian Forces Base Shearwater, Nova Scotia as 434 Composite Squadron. 414 changed its name to Combat Support Squadron in 1993 when it was equipped with the CT-133 Silver Star. In 2002, 414 Squadron was disbanded and its remaining two aircraft retired.
On 7 December 2007 approval was received for the squadron to stand up once more, this time as 414 EWS (Electronic Warfare Support) Squadron. Belonging to the RCAF Aerospace Warfare Centre, the squadron is based in Ottawa and is composed of military Electronic Warfare Officers who fulfill the combat support role, flying on civilian contracted aircraft.