Byrne, Kenneth Edward (Sergeant)
Killed in Action 1942-May-09


Birth Date: 1915
Born:
Parents: Son of Patrick J. and Mary C. Byrne, of St. John'S, Newfoundland, Canada.
Spouse:
Home: St John's, Newfoundland
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: unkown date
Service
RAF
Unit
412 Sqn- Squadron
Promptus Ad Vindictam Swift to Avenge
Base
RAF Binbrook
Rank
Sergeant
Position
Wireless Air Gunner
Service Numbers
798555
Crew or Other Personnel
Wellington W5574
Wellington serial: W5574
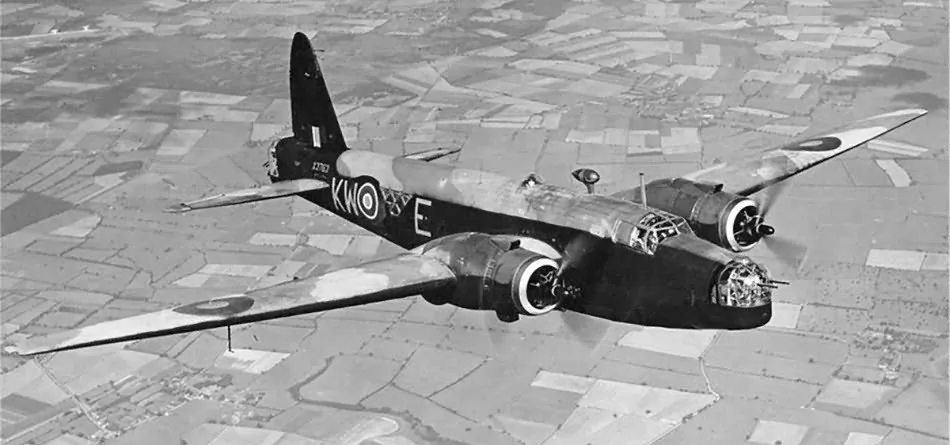

Vickers Wellington B. Mk. III (Serial No. X3763), coded KW-E, No. 425 'Alouette' (B) Squadron, RCAF, late summer of 1942
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson, a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design.
The Wellington was used as a night bomber in the early years of the Second World War, performing as one of the principal bombers used by Bomber Command. During 1943, it started to be superseded as a bomber by the larger four-engined "heavies" such as the Avro Lancaster. The Wellington continued to serve throughout the war in other duties, particularly as an anti-submarine aircraft.
It holds the distinction of having been the only British bomber that was produced for the duration of the war, and of having been produced in a greater quantity than any other British-built bomber. The Wellington remained as first-line equipment when the war ended, although it had been increasingly relegated to secondary roles. The Wellington was one of two bombers named after Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, the other being the Vickers Wellesley.
In August 1936, an initial order for 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft, powered by a pair of 1,050 hp (780 kW) Bristol Pegasus radial engines, was received by Vickers; it had been placed so rapidly that the order occurred prior to the first meeting intended to decide the details of the production aircraft. In October 1937, another order for a further 100 Wellington Mk Is, produced by the Gloster Aircraft Company, was issued; it was followed by an order for 100 Wellington Mk II aircraft with Rolls-Royce Merlin X V12 engines. Yet another order was placed for 64 Wellingtons produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. With this flurry of order and production having been assured by the end of 1937, Vickers set about simplifying the manufacturing process of the aircraft and announced a target of building one Wellington per day.
A total of 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft were built; 150 for the RAF and 30 for the Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) (which were transferred to the RAF on the outbreak of war and used by 75 Squadron). In October 1938, the Mk I entered service with 9 Squadron. The Wellington was initially outnumbered by the Handley Page Hampden (also ordered by the Ministry to B.9/32) and the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley (to B.34/3 for a 'night' bomber) but outlasted both rival aircraft in service. The Wellington went on to be built in 16 separate variants, in addition to two training conversions after the war. The number of Wellingtons built totalled 11,462 of all versions, a greater quantity produced than any other British bomber. On 13 October 1945, the last Wellington to be produced rolled out. Wikipedia
Unit Desciption
412 Sqn Promptus Ad Vindictam ("Falcon")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Spitfire Mks. IIA, VB, IXB, IXE, XVI, XIV)

The squadron was the tenth of the RCAF's squadrons to be formed overseas in WWII. It was the seventh fighter squadron to be so formed. It was established at Digby, Lincolnshire, England  on June 30, 1941. John Gillespie Magee, the author of the famous aviation poem “High Flight†was serving with 412 Squadron when he was killed in a mid-air collision in his Spitfire in 1941. The squadron flew Spitfire aircraft in the defence of Great Britain, formed part of the Canadian Kenley Wing within No. 11 Group, Fighter Command. It was re-equipped with the Spitfire lXb in November 1943 and began operating over northern France in preparation for operation Overlord, the D-Day landings. It was during late 1943 that the ace George “Screwball†Beurling scored his last air victory while serving with the squadron. Shortly after D-Day, on June 19, 1944, the squadron moved to France in a fighter and ground support role. It then supported the Allied armies, moving through France, the Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany. It was one of four RCAF day fighter units retained in Germany as part of the British Air Forces of Occupation before being disbanded at Utersen, Germany
on June 30, 1941. John Gillespie Magee, the author of the famous aviation poem “High Flight†was serving with 412 Squadron when he was killed in a mid-air collision in his Spitfire in 1941. The squadron flew Spitfire aircraft in the defence of Great Britain, formed part of the Canadian Kenley Wing within No. 11 Group, Fighter Command. It was re-equipped with the Spitfire lXb in November 1943 and began operating over northern France in preparation for operation Overlord, the D-Day landings. It was during late 1943 that the ace George “Screwball†Beurling scored his last air victory while serving with the squadron. Shortly after D-Day, on June 19, 1944, the squadron moved to France in a fighter and ground support role. It then supported the Allied armies, moving through France, the Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany. It was one of four RCAF day fighter units retained in Germany as part of the British Air Forces of Occupation before being disbanded at Utersen, Germany  on March 21, 1946.
on March 21, 1946.
In the course of hostilities, the squadron flew 12,761 sorties for the loss of 63 aircraft and 62 pilots, of whom 21 were killed, 14 presumed dead, 11 POW. The squadron claimed 106 enemy aircraft destroyed, 11 probably destroyed and 46 damaged. On the ground, they claimed 282 motor vehicles and 22 locomotives. The squadron had 5 aces (shot down 5 or more enemy aircraft): Flight Lieutenant D.C. Laubman DFC & Bar; Flight Lieutenant W.J. Banks,DFC & Bar; Flying Officer D.R.C. Jamieson DFC & Bar; Flying Officer P.M. Charron; Flight Lieutenant R.I.A. Smith DFC. Overall, the squadron was awarded 7 Bars to DFC, 16 DFCs and 4 MiD. Battle Honours were: Defence of Britain 1941-44, Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin
Maps for Movements of 412 Squadron 1941-46
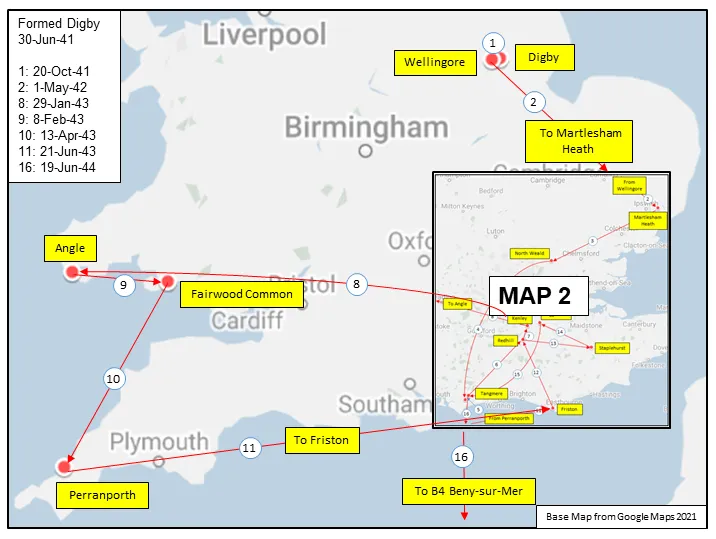
MAP 1: 412 Squadron Movements 1941-44 (right-click on image to display enlarged in new tab)
|
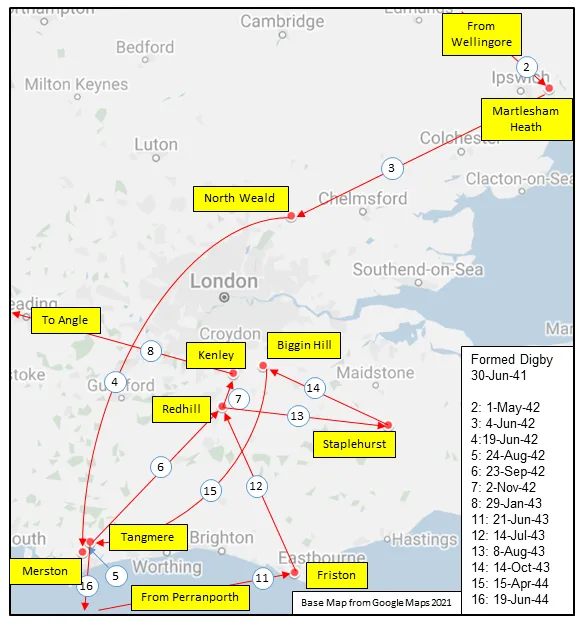
MAP 2: 412 Squadron Movements Detail of Map 1
|
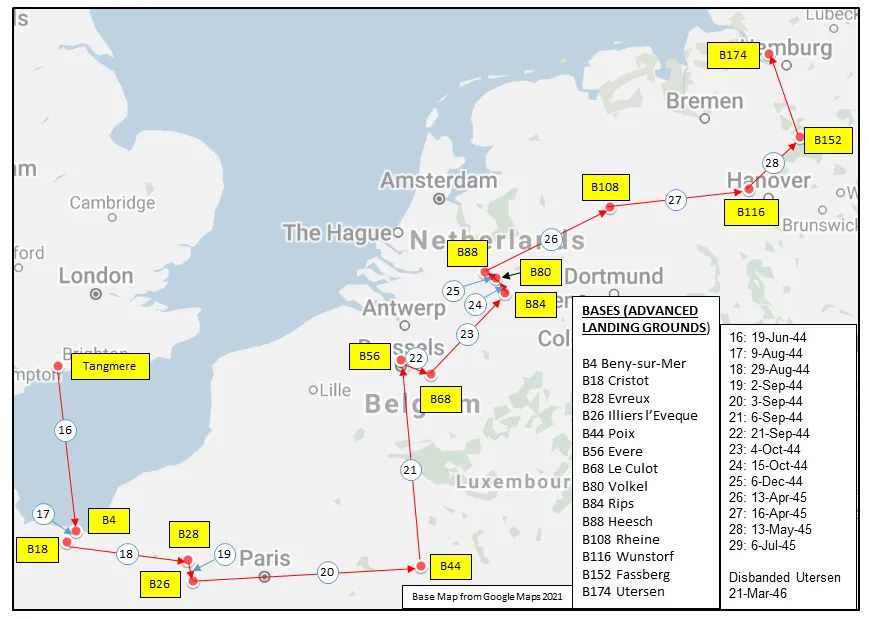
MAP 3: 412 Squadron Movements in Europe 1944-46
|
412 Squadron History Summary 1941-46
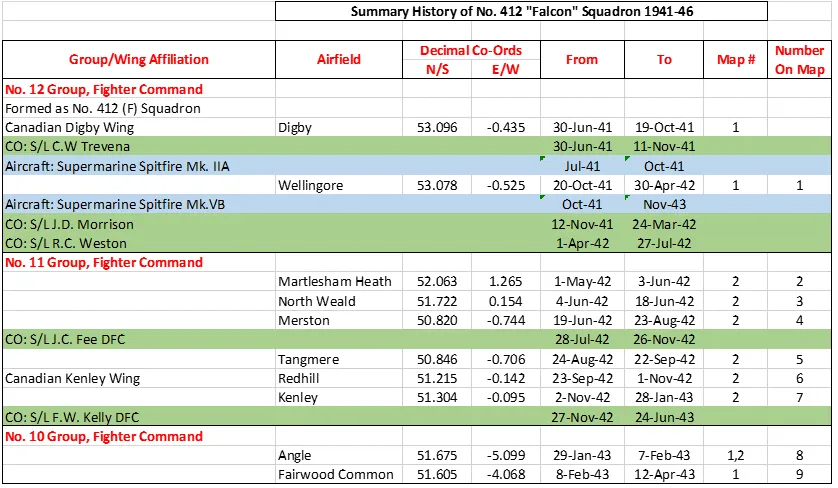
412 Squadron History Summary 1941-46 Page 2
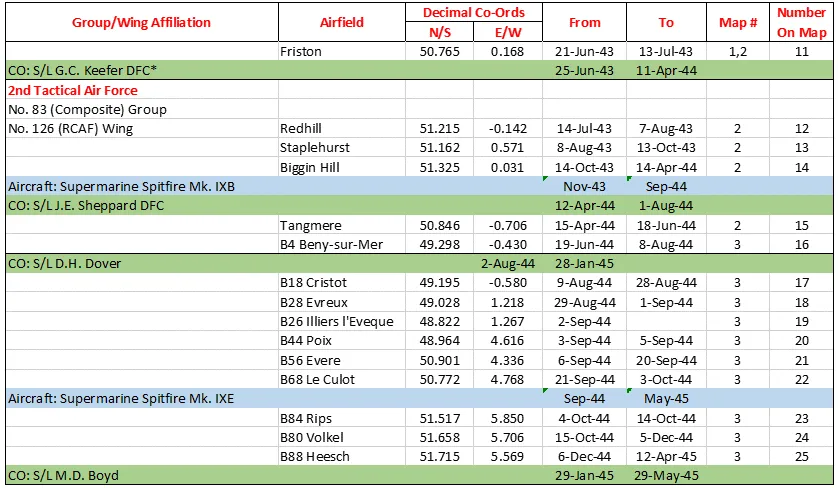
412 Squadron History Summary 1941-46 Page 3
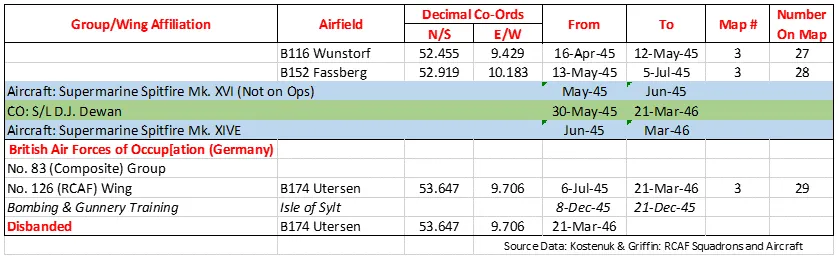
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: CC-117 Falcon, CC-144 Challenger and CC-109 Cosmopolitan)
After the Second World War, Number 12 Communications Flight was reassigned as 412 Squadron on 1 April 1947, and renamed 412 (Composite) Squadron based at Rockcliffe, Ontario  . In 1955, the squadron moved to Uplands, Ontario. Upon unification in 1968, 412 Squadron became the VIP squadron for the Canadian Forces based at CFB Uplands
. In 1955, the squadron moved to Uplands, Ontario. Upon unification in 1968, 412 Squadron became the VIP squadron for the Canadian Forces based at CFB Uplands
Error in opcode: linkgooglemap
and flew the CC-117 Falcon, CC-144 Challenger and CC-109 Cosmopolitan. In the late 1970s a sub-unit was established at CFB Lahr in West Germany; this operation closed in 1993. In 1994, CFB Ottawa (Uplands) closed and 412's fleet was moved to a civilian hangar at Ottawa International Airport. All aircraft are maintained by Transport Canada on behalf of the Canadian Forces. Today, the Squadron performs the VIP and general transport duties with the CC-144 Challenger.
