Burns, William
Killed in Action 1943-10-22
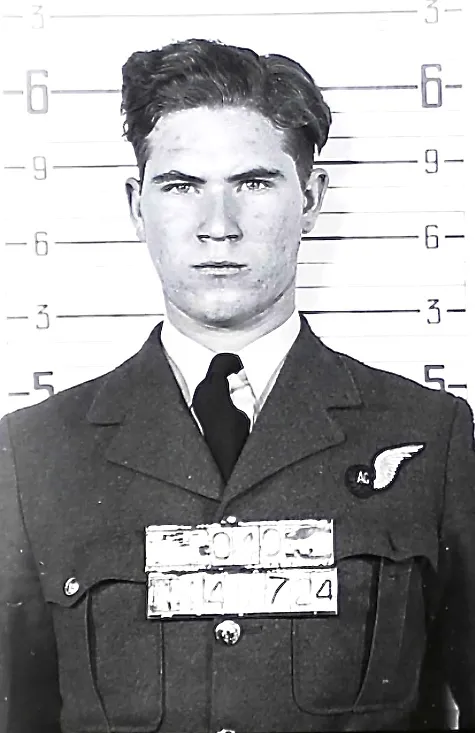


Birth Date: 1922-March-16
Born:
Son of William C. D. and Annie Burns, of Roblin, Manitoba, Canada.
Home: Roblin, Manitoba
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
431 (B) Sqn- Squadron
The Hatiten Ronteriios Warriors of the Air: Iroquois
Base
RAF Tholthorpe
Rank
Flight Sergeant
Position
Flight Sergeant
Service Numbers
R/140724
Halifax B/Met.Mk.V LK639
Bombing Kassel Germany 1943-October-22 to 1943-October-22
(B) Sqn (RCAF) Tholtthorpe
Battle of Berlin
569 aircraft - 322 Lancasters, 247 Halifaxes. The German controller was again successful in assessing the target and 43 aircraft- 25 Halifaxes, 18 Lancasters - were lost, 7·6 per cent of the force.
The initial 'blind' H2S marking overshot the target but 8 out of the 9 'visual' markers correctly identified the centre of Kassel and placed their markers accurately. Although German decoy markers may have drawn off part of the bomber force, the main raid was exceptionally accurate and concentrated. The result was the most devastating attack on a German city since the firestorm raid on Hamburg in July and the results at Kassel would not be exceeded again until well into 1944. The fires were so concentrated that there was a firestorm, although not as extensive as the Hamburg one.
It is impossible to list all the damage. 4,349 separate dwelling blocks containing 26,782 family living units (flats/apartments) were destroyed and 6,743 more blocks with 26,463 'units' were damaged. 63 per cent of all Kassel's living accommodation became unusable and 100,000-120,000 people had to leave their homes. The fire · services dealt with 3,600 separate fires. The intensity of the destruction is illustrated by the fact that more buildings were completely destroyed than those classed as 'lightly damaged' and there were more 'large' fires (1,6oo}than small ones (1,000); in most raids the lightly damaged buildings and small fires outnumbered serious incidents several times over
. In addition to dwelling-houses, the following properties were destroyed or badly damaged: 155 industrial buildings, 78 public buildings, 38 schools, 25 churches, 16 police and military buildings (including the local Gestapo), I 1 hospitals. The Kassel records do not provide any further detail about the industrial damage caused but R.A.F. photographic reconnaissance showed that the Kassel railway system and its installations were severely hit and all 3 Henschel aircraft factories seriously damaged; as these were making V-1 flying bombs at the time, this was a most useful result of the raid and had a major effect upon the eventual opening and scale of the V-1 campaign, comparable to the recent raid on Peenemimde which set back the V-2 rocket programme.The Kassel records give the number of dead recovered up to the end of November as 5,599, of which 1,817 bodies were unidentifiable and the records go on to add that the 'Missing Department' (the Vermisstensuchstelle) was still trying to trace 3,300 people. 459 survivors, however, had been recovered from ruined houses 'after many days of heavy work'. 3,587 people were injured - 800 seriously - and a further 8,084 people were treated for smoke and heat injury to their eyes.
source: The Bomber Command War Diaries, Martin Middlebrook and Chris Everitt
Halifax BV aircraft LK 639 SE-E missing during night operations, a raid against aircraft manufacturing plants and rail facilities in Kassel, Germany. The cause of the loss of this aircraft and crew is unknown, they were lost without a trace
FS LB Russell (RCAF), FS W Burns (RCAF), Sergeant JF Challis (RAFVR), FE Skinner (RAFVR), H Priestly (RAFVR), Flying Officer RP Wissler (RAFVR) and Sergeant DJ McCarthy (RAF) were all missing, presumed killed. They have no known graves and are all commemorated on the Runnymede War Memorial
Halifax LK639
Handley Page Halifax
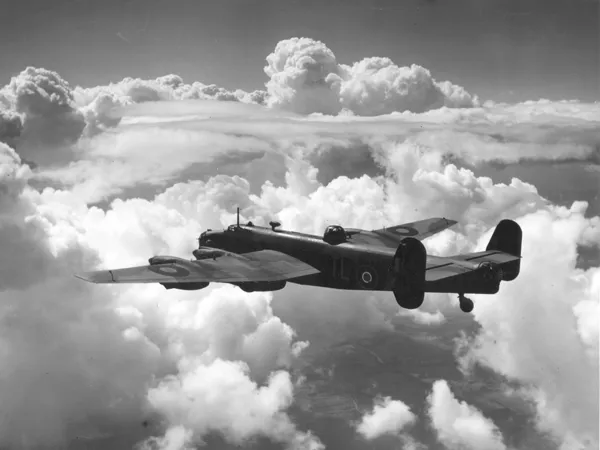

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces.Wikipedia
 National Air Force Museum of Canada
National Air Force Museum of Canada
431 (B) Sqn The Hatiten Ronteriios ("Iroquois")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington X, Halifax V, III, Lancaster X)

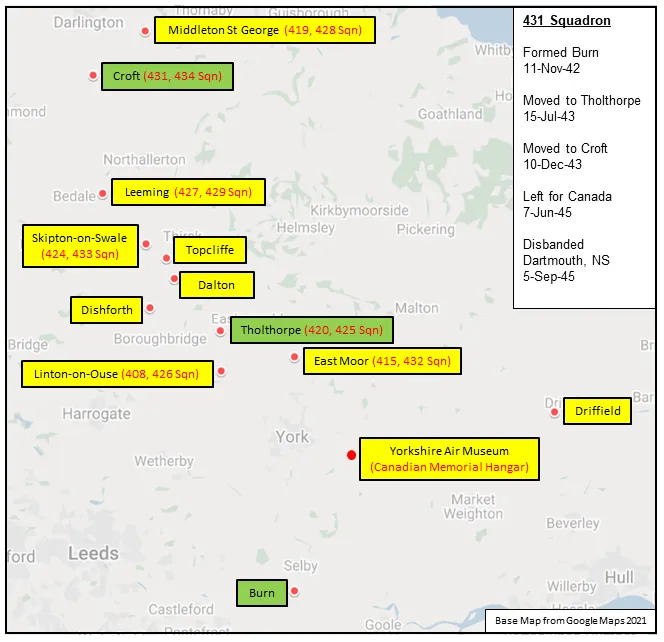
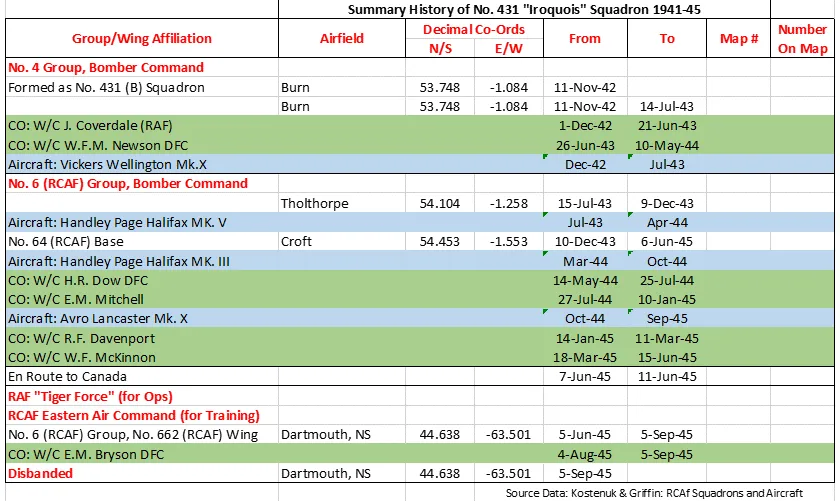
The Squadron was formed in November 1942 as the RCAF's 11th bomber squadron to be formed overseas, at Burn, Yorkshire, UK , as a bomber unit of No 4 Group of RAF Bomber Command. With squadron code letters SE it flew Vickers Wellington Mk X aircraft. In July 1943 it moved to Tholthorpe, Yorkshire , to become part of No 6 (RCAF) Group, at the same time re-equipping with Handley Page Halifax Mk V bombers. It moved again in December 1943 to become part of No 64 (RCAF) Base at Croft, Yorkshire , where it remained until the end of the war. Another change of aircraft, to Halifax Mk. III was made in March of 1944, and finally the squadron was equipped with Canadian-built Avro Lancaster Mk X aircraft from October 1944. After the termination of hostilities in Europe, it was earmarked to form part of the Tiger Force to attack Japan and left for Canada in June 1945. The Japanese surrender following the dropping of the atomic bombs made Tiger Force redundant, and the squadron was disbanded at Dartmouth, Nova Scotia in September of 1945.
In the course of operations the squadron flew 2584 sorties (including 11 bringing PoWs back to England) at a cost of 72 aircraft destroyed. Approximately 14000 tons of bombs were dropped. Aircrew awards were 1 DSO, 63 DFCs, 10 DFMs, 2 CGMs and 1 MiD. Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943-44, Baltic 1943-44, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1943-44, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1943-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1944.Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 431 Squadron 1942-45
431 Squadron History Summary 1942-45
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Tutor)
No. 431 (Fighter) Squadron re-formed at RCAF Station Bagotville, Quebec on 18 January 1954, using the new Canadair Sabre. The squadron was formed on a temporary basis until there were enough new CF-100s available to fulfill RCAF squadron needs. No. 431's duties included aerial combat training and displaying the capabilities of jet operations to the public at air shows: the team from No. 431 Squadron consisted of four Sabres and a solo aircraft. This was the first Sabre team to be authorized to perform formation aerobatics in Canada. 431 squadron was disbanded on 1 October 1954.
In 1969, Colonel O.B. Philp, base commander of CFB Moose Jaw and former leader of the defunct Golden Centennaires aerobatic team, considered using several of the leftover Golden Centennaire CT-114 Tutor aircraft for another team. These Tutors were still fitted for aerobatic flying. Philp, at this point, did not receive approval to form the new team; however, approval had been given for single Tutors to provide simple flypasts at local football games. To further the cause of an aerobatic team, Philp began informal enhanced formation practice for the instructors at 2 Canadian Forces Flying Training School with the aim of providing multi-aircraft flypasts at special events. In 1970, four-aircraft formations began providing flypasts at fairs and festivals, as well as Armed Forces Day at CFB Moose Jaw . In July 1970, a white Tutor was introduced to the formation for flypasts. Four white Tutors were finally flown together at the Abbotsford Air Show, followed by a flypast in Winnipeg. Known as the "2 Canadian Forces Flying Training School Formation Team", or informally as the "Tutor Whites", the team grew in size to seven aircraft in 1971 using eleven pilots, and gradually gained recognition. Formation flypasts were replaced with more complicated manoeuvres, and more aircraft were added as the team matured. A contest to give the air demonstration team a formal name was held at Bushell Park Elementary School at CFB Moose Jaw, and resulted in the name "Snowbirdsâ€, which was formally adopted on 25 June 1971. The Snowbirds were officially authorized to be designated the "Canadian Forces Air Demonstration Team" on 15 January 1975, and were formed into their own squadron by reactivating 431 Squadron (renamed 431 Air Demonstration Squadron) on 1 April 1978. .Wikipedia
And the rest is history……………………
 Roblin, Manitoba
Roblin, Manitoba Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com Daily Operations 6bombergroup.ca
Daily Operations 6bombergroup.ca
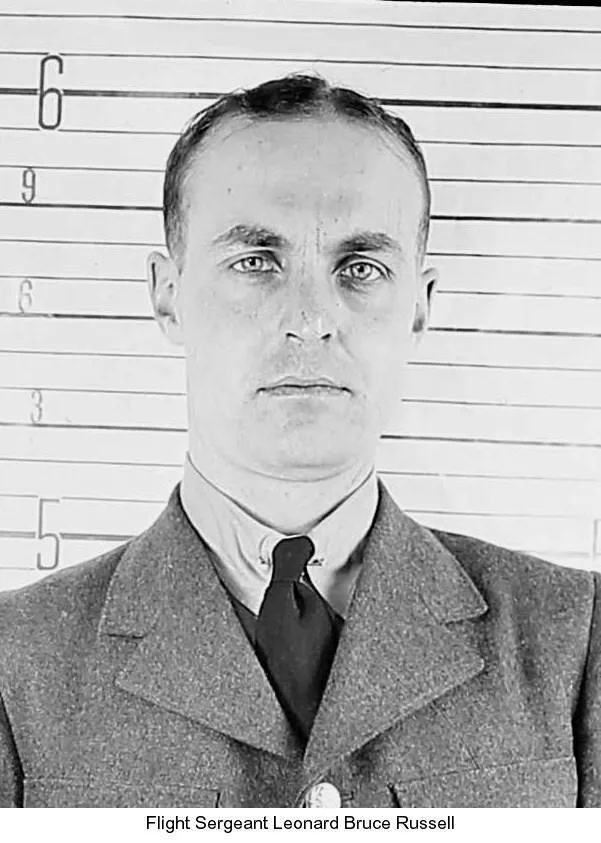



 Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII
Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII Wikipedia Halifax Bomber
Wikipedia Halifax Bomber