Bliss, Osborne Lloyd
Killed in Action 1943-08-24
Service
RCAF
Unit
35 Sqn- Squadron (RAF)
Uno Anima Agimus We Act with One Accord
Base
RAF Graveley
Rank
Warrant Officer 1
Position
Warrant Officer 1
Service Numbers
R/88244
Target
 Berlin Germany
Berlin Germany
First Burial
 Berlin War Cemetery, Charlottenburg, Germany
Berlin War Cemetery, Charlottenburg, Germany
Halifax HR928
Handley Page Halifax
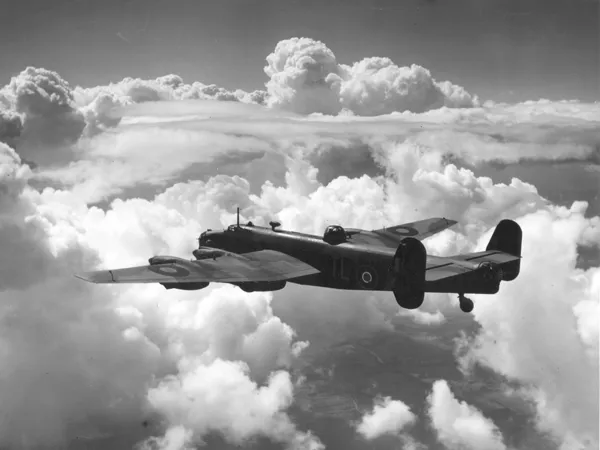

The Handley Page Halifax is a British Royal Air Force (RAF) four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It was developed by Handley Page to the same specification as the contemporary twin-engine Avro Manchester.
The Halifax has its origins in the twin-engine HP56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a capable medium bomber for "world-wide use." The HP56 was ordered as a backup to the Avro 679, both aircraft being designed to use the underperforming Rolls-Royce Vulture engine. The Handley Page design was altered at the Ministry to a four-engine arrangement powered by the Rolls-Royce Merlin engine; the rival Avro 679 was produced as the twin-engine Avro Manchester which, while regarded as unsuccessful mainly due to the Vulture engine, was a direct predecessor of the famed Avro Lancaster. Both the Lancaster and the Halifax would emerge as capable four-engined strategic bombers, thousands of which would be built and operated by the RAF and several other services during the War.
On 25 October 1939, the Halifax performed its maiden flight, and it entered service with the RAF on 13 November 1940. It quickly became a major component of Bomber Command, performing routine strategic bombing missions against the Axis Powers, many of them at night. Arthur Harris, the Air Officer Commanding-in-Chief of Bomber Command, described the Halifax as inferior to the rival Lancaster (in part due to its smaller payload) though this opinion was not shared by many of the crews that flew it, particularly for the MkIII variant. Nevertheless, production of the Halifax continued until April 1945. During their service with Bomber Command, Halifaxes flew a total of 82,773 operations and dropped 224,207 tons of bombs, while 1,833 aircraft were lost. The Halifax was also flown in large numbers by other Allied and Commonwealth nations, such as the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Free French Air Force and Polish forces.Wikipedia
Specifications
Handley Page HP57/59/61/63/71 Halifax
by Peter Allam and Greg Neid
Click to open:
Introduction
The Halifax was the most common heavy bomber employed by Canadians in WW2 -- over 70% of Canadain bomber crews were asigned to the Halifax Bomber. Canada's highest losses of airmen in Halifaxs:
| Killed in action, Killed in Flying Accident | 3,500 | + | |
| Prisoner of War, Interned in a neutral country | 1,200 | + | |
| Shot Down, Evaded Capture | 200 | + | |
| Survived Catasrophic events | 200 | ||
| total | 5,100 | + |
The Halifax was available and flying in 1940. The Lancaster was not available in any significant numbers until mid 1942.
Manufacturers
| English Electric Co Ltd | 2,145 | |
| Handley Page Ltd | 1,592 | |
| Rootes Securities Ltd | 1,070 | |
| London Passenger Transport Board | 710 | |
| Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | 661 | |
| total | 6,178 |
Variants
The Mark IV was never built.
| Prototype | 2 | |
| Mark I | 84 | |
| Mark II | 1,977 | |
| Mark III | 2,090 | |
| Mark IV | 0 | |
| Mark V | 904 | |
| Mark VI | 468 | |
| Mark VII | 408 | |
| Mark VIII | 100 | |
| Mark IX | 145 | |
| total aircraft | 6,178 |
Engines
The Merlin XX and 22 are equivalents.
| Merlin X, XX/22 (86 and 2,881) | 2,967 | |
| Hercules XVI, 100 (2,643 and 568) | 3,211 | |
| total (4 per aircraft) | 6,178 |
Aircraft Origin
The origins of the Halifax lay in the twin-engine H.P.56 proposal of the late 1930s, produced in response to the British Air Ministry's Specification P.13/36 for a medium bomber for 'world-wide use'. Handley Page initially envisioned a design using of two Rolls-Royce Vulture X-24 engines, but as the airframe design developed and the Vulture's shortcomings became more apparent, the twin-engine H.P.56 evolved into the larger and more capable H.P.57 Halifax powered by four Rolls-Royce Merlin engines. The first flight took place at RAF Bicester on 25 October 1939, the aircraft entering RAF service just over a year later on 13 November 1940.
Ventral Turret
In service it quickly became apparent that the Boulton Paul Type K ventral turret as fitted to early Mk.I aircraft with its twin 0.303-inch calibre machine guns was next to useless, and the turret was replaced on later Mk.Is and early H.P.59 Mk.IIs by two beam gun positions each with twin Vickers Type K 0.303-inch machine guns. In turn the beam guns were also found to be redundant and were soon discontinued.
Rudder Overbalance
However, much more serious deficiencies became apparent following the introduction of the heavier Halifax Mk.II and H.P.63 Mk.V with its Dowty undercarriage and hydraulic system. In addition to poor overall performance, the number of aircraft lost in mysterious circumstances began to rise alarmingly. Following a protracted investigation, the cause was eventually traced to irrecoverable loss of control due to rudder overbalance and was cured by the introduction of the distinctive large rectangular D-Type fins and rudders.
Performance Improvements
Loss of performance in the Mk.II & V was addressed by a number of means including replacement of the front turret by a metal and later Perspex one-piece nose, and replacement of the bulbous drag-inducing Boulton Paul two gun Type C mid-upper turret with the lower profile four gun Type A turret. Improved engine cowlings, more powerful Merlin engines and a general airframe clean-up also helped to somewhat restore the Mk.II and V's performance.
Bristol Hercules Engines
A further improvement of the Merlin-powered Halifax known as the Mk.IV was planned but never built, the design featuring increased wingspan and even more powerful Merlins in completely redesigned and repositioned nacelles. However, a study of the advantages of the sleeve valve 14-cylinder Bristol Hercules radial engine convinced Handley Page to discontinue Merlin Halifax development and instead introduce the Hercules-powered H.P.61 Mk.III. Initially built with 98 ft 10 in wingspan, the Mk.III soon received the still-born Mk.IVs 104 ft 2 in wings, the new mark proving to be the turning point in the Halifax's fortunes.
Later in the war, the Halifax H.P.63 Mk.VI with more powerful fuel-injected Hercules 100 series engines, improved flying controls and systems proved to be the pinnacle of wartime Halifax development, the mark outperforming the Lancaster in some respects. Unfortunately, the Hercules 100 wasn't available in sufficient quantities, and so the Mk.VI airframe was also built with lower powered Hercules XVIs as the Halifax H.P.63 Mk.VII.
.5-inch (50 calibre) Machine Guns
The advantages of the 0.5-inch calibre machine gun over the 0.303-inch calibre were well known and following a protracted turret development programme, some Mk.VII & IX aircraft were fitted with Boulton Paul Type D rear turrets with twin 0.5-inch guns. The final bomber variant was the H.P.71 Mk.IX. Like the earlier variants the IX could also be used for glider towing and paratrooping, and for the latter task the Mk.IX featured an elongated and repositioned paratroop exit aperture.
A - Glider Tug and Transport
B - Bomber
C - Cargo and Passenger
GR - Coastal Command
Met - Meteorological
Series Designations
In addition to the basic mark number the Halifax Mk.I, II & V also had a series number eg. series 1, series 1a, series 2. The series number is not included in our database because it is not easily or accurately determined.
Mk.II & V
The basic series number of all the rest of the Mk.IIs & Vs was Series 1. Some early production airframes were built as straight Series 1s and later modified, and some later production airframes were built with one or both of the key suffix-changing modifications already incorporated. Regardless of whether the change/s occurred during or post-manufacture, a suffix was supposed to be added to the series number when the following changes occurred:
- Replacement of the front turret with the one-piece metal fairing (Mod.398 aka Tollerton nose, Tempsford nose or Z-fairing) - this added the suffix (Special) after the series number i.e. Series 1 (Special).
- Installation of Merlin 22 engines and Morris radiators along with modified engine cowlings - this added the letter 'A' to the series number i.e. Series 1A.
However
- Some late production Mk.II Series 1 (Specials) were fitted with Morris radiators and Merlin 22s but retained the designation Series 1 (Special).
- Some Series 1 aircraft were fitted with the previous type of Gallay radiators but were designated as Series 1A.
- Aircraft with the Mod.452 Perspex nose but without Morris radiators/Merlin 22s were not Series 1A, and the actual designation of such aircraft i.e. Series 1 or Series 1 (Special) is unknown.
NOTE - In period as now, it was widely but incorrectly believed that an aircraft became a 1A when the one-piece Perspex nose was added, but an airframe became a Series IA only when Merlin 22 & Morris radiators were installed - addition of the one-piece Perspex nose (and the large D-Type fins) made no change to the series suffix.
To add to the confusion production records are not only incomplete but sadly in a great many instances they also do not record whether a particular airframe was a Series 1, Series 1 (Special) or Series 1A. And if that wasn't enough many aircraft were field modified and the modification/s were not recorded, which of course means that many airframes could and did start life without a series suffix and gain one later when the engine or nose type changed, yet the records don't reflect the changes!
The bottom line is that unfortunately it's impossible to list the series/engine sub-model breakdowns of the Mk.II & V Series 1 aoircraft. Really the best that can be said is that early Mk.IIs and Vs had Merlin XXs and the later ones had Merlin 22s.
Meteorological Variant
Predicting the weather was a significant problem. The weather generally flows west to east in the northern hemisphere, so ascertaining the weather as far out as possible in the Atlantic Ocean gave indications of future weather events in Britain and on the continent.
The main variant was the MET V which looked very similar to a Coastal Command GR Mk.V. The aircraft themselves were fitted with very sensitive air temperature and humidity measuring equipment, plus radio altimeters to allow the crews to fly very accurately at selected altitudes, and they also carried an extra crew member who recorded the weather data. Towards the end of the war the Halifax MET V was supplemented by the MET III and VI.
From airfields located on the west coast of the UK including Tiree on the Isle of Skye, Stornoway on the Isle of Lewis, Brawdy in Wales and Chivenor in Devon the aircraft regularly flew extremely long duration meteorological reconnaissance flights over the Atlantic.
The weather forecasts used for D-Day planning were partly based on data provided by the MET Halifax squadrons.
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | 69 ft 9 in (21.25 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 98 ft 10 in (30.12 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,250 sq ft (116.12 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021, Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | Mk. I Series 1: 33,860 lb. (15,359 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | Mk.I Series 1 (early): 55,000 lb (24,970 kg) Mk.I Series 1 (late): 58,000 lb (kg) Mk.I Series 2 & 3: 60,000 lb (27,240 kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | Mk.I Series 1 & 2: 1,392 Imp gal (6,328 L) Mk.I Series 3: 1,636 Imp gal (7,437 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Rolls-Royce or Ford UK built Merlin X liquid-cooled V-12 piston engines with power output of 1,130 hp (840 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3-bladed Rotol hydraulic constant-speed fully feathering metal or wooden bladed propellers with diameters between 12 and 13 ft (3.65 and 3.96 m) | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 255 mph (410 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 195 mph (313 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,860 mi (2,993 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 18,000 ft (5,486 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type C nose turret, two twin beam mounted .303-inch (7.7 mm) Vickers Gas Operated "K" machine guns and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | Boulton Paul Type K ventral turret with two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns (briefly fitted in small numbers to some early Halifax Mk.I aircraft) | |||||||
| Bomb load: | 7,500 lb (3,401) consisting of combinations of 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 1,000 lb GP, 500 lb GP or 250 lb GP bombs, or various quantities of 4 lb incendiaries installed in Small Bomb Containers 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR9F: HF R/T radio transceiver T1083: High frequency W/T transmitter R1082: High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5000 Mk.II: IFF Friend or Foe radar identification system | |||||||
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | Pre-Mod.452 (Perspex nose): 69 ft 9 in (21.25 m) Post-Mod.452: 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 98 ft 10 in (30.12 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,250 sq ft (116.12 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021 Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | Mk. II Srs 1A: 35,270 lb. (16,000 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 60,000 lb (27,240 kg) Series 1A: 63,000 lb (kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 1,882 Imp gal (8,555 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Rolls-Royce or Ford UK built Merlin XX or 22 liquid-cooled V-12 piston engines with power output between 1,280 hp (831 kW) and 1,435 hp (897 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3 or 4-bladed Rotol hydraulic constant-speed fully feathering wooden bladed propellers with diameters between 12 and 13 ft (3.65 and 3.96 m) | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 254 mph (408 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 190 mph (305 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,900 mi (3,057 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 22,000 ft (6,705 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | (earlier aircraft only): Two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type C nose and mid-upper turrets, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret (later aircraft only): Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type A mid-upper turret, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine gun in nose (Coastal Command aircraft (GR variant) only) | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 4,000 lb HC, 250 lb, 500 lb, 1,000 lb bombs, or various sizes of incendiary bombs installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 8 x 250lb (113 kg) depth charges 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR9F: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1083: High frequency W/T transmitter R1082: High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF ARI 5119 ASV Mk.III: Centimetric radar ship/submarine target finding system | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5000/5025/5640 IFF Mk.II & III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5171/5625/5672/5769 Mandrel: Freya and W�rzburg radar jamming system ARI 5538/5557 Boozer Mk.I & II: Passive radar warning receiver ARI 5122 Monica Mk.I: Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S | |||||||
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | Early production aircraft: 98 ft 10 in (30.12 m) Late production aircraft: 104 ft 2 in (31.75 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 98 ft wingspan - 1,250 sq ft (116.12 m2) 104 ft wingspan - 1,280 sq ft (118.91 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021, Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | 37,870 lb (17,178 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 65,000 lb (29,484 kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 1,986 Imp gal (9,028 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Bristol Hercules Mk.VI or XVI air-cooled 14-cylinder radial piston engines with power output of between 1,615 hp (1,204 kW) and 1,675 hp (1,235 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3-bladed de Havilland Hydromatic constant-speed fully feathering metal bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m) diameter | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 277 mph (445 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 225 mph (362 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,700 mi (2,735 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 20,000 ft (6,096 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type A mid-upper turret, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine gun in a ventral Preston Green mount One 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mk.II machine gun in nose | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 4,000 lb HC, 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 1,000 lb MC, 500 lb MC or 250 lb MC bombs, or various quantities of 4 lb incendiaries installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF ARI 5119 ASV Mk.III: Centimetric radar ship/submarine target finding system | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5000/5025/5640 IFF Mk.II & III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5171/5625/5672/5769 Mandrel: Freya and W�rzburg radar jamming system ARI 5538/5557 Boozer Mk.I & II: Passive radar warning receiver ARI 5122/5281 Monica Mk.I, III & V ('Lulu'): Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S TR3549 Airborne Cigar (ABC): Night fighter radio control jamming system ARI 5549 Carpet II: Wurzburg radar jamming system | |||||||
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | Pre-Mod.452 (Perspex nose): 69 ft 9 in (21.25 m) Post-Mod.452: 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 98 ft 10 in (30.12 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,250 sq ft (116.12 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021 Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | Mk. II Srs 1A: 35,270 lb. (16,000 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 60,000 lb (27,240 kg) Series 1A: 63,000 lb (kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 1,882 Imp gal (8,555 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Rolls-Royce or Ford UK built Merlin XX or 22 liquid-cooled V-12 piston engines with power output between 1,280 hp (831 kW) and 1,435 hp (897 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3 or 4-bladed Rotol hydraulic constant-speed fully feathering wooden bladed propellers with diameters between 12 and 13 ft (3.65 and 3.96 m) | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 254 mph (408 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 190 mph (305 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,900 mi (3,057 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 22,000 ft (6,705 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | (earlier aircraft only): Two 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type C nose and mid-upper turrets, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret (later aircraft only): Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type A mid-upper turret, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine gun in nose (Coastal Command aircraft (GR variant) only) | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 4,000 lb HC, 250 lb, 500 lb, 1,000 lb bombs, or various sizes of incendiary bombs installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 8 x 250lb (113 kg) depth charges 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR9F: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1083: High frequency W/T transmitter R1082: High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF ARI 5119 ASV Mk.III: Centimetric radar ship/submarine target finding system | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5000/5025/5640 IFF Mk.II & III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5171/5625/5672/5769 Mandrel: Freya and W�rzburg radar jamming system ARI 5538/5557 Boozer Mk.I & II: Passive radar warning receiver ARI 5122 Monica Mk.I: Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S | |||||||
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 104 ft 2 in (31.75 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,280 sq ft (118.91 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021, Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | 39,000 lb (17,690 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 68,000 lb 30,844 kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 2,190 Imp gal (9,956 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Bristol Hercules 100 air-cooled 14-cylinder radial piston engines with power output of 1,675 hp (1,235 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3-bladed de Havilland Hydromatic constant-speed fully feathering metal bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m) diameter | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 290 mph (466 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 230 mph (370 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 2,500 mi (4.023 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | Halifax Mk.VI: 22,000 ft (6,705 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type A mid-upper turret, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine gun in a ventral Preston Green mount One .303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mk.II machine gun in nose | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 4,000 lb HC, 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 1,000 lb MC, 500 lb MC or 250 lb MC bombs, or various quantities of 4 lb incendiaries installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5033/5083 GEE Mk.I/II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5640 IFF Mk.III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5122/5281 Monica Mk.I, III & V ('Lulu'): Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S | |||||||
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 104 ft 2 in (31.75 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,280 sq ft (118.91 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021, Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | 37,870 lb (17,178 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 65,000 lb (29,484 kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 2,190 Imp gal (9,956 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Bristol Hercules Mk.VI or XVI air-cooled 14-cylinder radial piston engines with power output of between 1,615 hp (1,204 kW) and 1,675 hp (1,235 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3-bladed de Havilland Hydromatic constant-speed fully feathering metal bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m) diameter | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 277 mph (445 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 225 mph (362 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,700 mi (2,735 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 20,000 ft (6,096 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type A mid-upper turret, and four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machineguns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One .303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mk.II machine gun in nose Boulton Paul Type D rear turret with two 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine guns (some late production aircraft only) | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 4,000 lb HC, 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 1,000 lb MC, 500 lb MC or 250 lb MC bombs, or various quantities of incendiaries installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5083 GEE Mk.II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5640 IFF Mk.III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5122/5281 Monica Mk.I, III & V ('Lulu'): Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S | |||||||
Specs not available
| General characteristics: | ||||||||
| Crew: | 7 (typical) | |||||||
| Length: | 71 ft 7 in (21.82 m) | |||||||
| Wingspan: | 104 ft 2 in (31.75 m) | |||||||
| Wing area: | 1,280 sq ft (118.91 m2) | |||||||
| Height: | 20 ft 9 in (6.32 m) | |||||||
| Airfoil: | Root: NACA 23021, Tip: NACA 23007 | |||||||
| Empty weight: | 37,870 lb (17,178 kg) | |||||||
| Max takeoff weight: | 65,000 lb (29,484 kg) | |||||||
| Fuel capacity: | 2,190 Imp gal (9,956 L) | |||||||
| Powerplants: | 4 x Bristol Hercules Mk.VI, XVI or 100 air-cooled 14-cylinder radial piston engines with power output of between 1,615 hp (1,204 kW) and 1,675 hp (1,235 kW) each | |||||||
| Propellers: | 3-bladed de Havilland Hydromatic constant-speed fully feathering metal bladed propellers, 13 ft (3.96 m) diameter | |||||||
| Performance: | ||||||||
| Maximum speed: | 277 mph (445 km/h) | |||||||
| Cruising speed: | 225 mph (362 km/h) | |||||||
| Range: | 1,700 mi (2,735 km) | |||||||
| Service ceiling: | 20,000 ft (6,096 m) | |||||||
| Armament | ||||||||
| Primary | Four 0.303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mark II machine guns in Boulton Paul Type E rear turret | |||||||
| Alternative/additional: | One .303-inch (7.7 mm) Browning Mk.II machine gun in nose Boulton Paul Type D rear turret with two 0.5-inch (12.7 mm) Browning AN/M2 machine guns (some late production aircraft only) | |||||||
| Bomb load: | Varying between 7,500 and 13,000 lb (3,401 and 5,903 kg) and consisting of combinations of 4,000 lb HC, 2,000 lb AP, 2,000 lb HC, 1,000 lb MC, 500 lb MC & 250 lb MC bombs, or various quantities of incendiaries installed in Small Bomb Containers or Cluster Projectiles 3 x 1,500 lb (839 kg) Parachute Anti-Shipping Mines | |||||||
| Electronics | ||||||||
| Communication and navigation equipment: | TR1196: HF R/T radio transceiver TR1143/SCR522: VHF R/T radio transceiver T1154: Medium and High frequency W/T transmitter R1155: Medium and High frequency W/T & direction finding receiver ARI 5083 GEE Mk.II: Radio navigation system ARI 5560/5564 H2S Mk.II/III: Radar navigation/target finding system TR3190/3160 Lucero Mk.I & II: H2S adapter to permit interrogation of/homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF AN/APN-4 LORAN: Long range radio navigation system AN/AP1 (AYD): Low range radar altimeter SCR-718-C: High range radar altimeter Lorenz Standard Beam Approach: Runway blind approach system ARI 5506/5162/5787 Rebecca Mk.II: Radar interrogator to permit homing onto radar navigation beacons, Eureka beacons & IFF | |||||||
| Radio Countermeasures: | ARI 5640 IFF Mk.III: Friend or Foe radar identification system ARI 5122/5281 Monica Mk.I, III & V ('Lulu'): Active tail warning radar Fishpond: Fighter warning radar add-on to H2S | |||||||
Serial Groups
| Serial & Range (Clickable) | Count | Manufacturer | Location | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L7244 - L9624 | 102 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| R9363 - R9540 | 100 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| V9976 - V9994 | 19 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| W1002 - W7939 | 381 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| BB189 - BB446 | 200 | London Passenger Transport Board | ||
| DG219 - DG424 | 150 | Rootes Securities Ltd | ||
| DJ980 - DJ999 | 20 | Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | ||
| DK114 - DK271 | 130 | Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | ||
| DT476 - DT808 | 250 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| EB127 - EB276 | 100 | Rootes Securities Ltd | ||
| HR654 - HR988 | 250 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| HX147 - HX357 | 150 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| JB363 - JB974 | 127 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| JD105 - JD476 | 223 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| JN882 - JN978 | 83 | London Passenger Transport Board | ||
| JP107 - JP532 | 167 | London Passenger Transport Board | ||
| LK626 - LK999 | 287 | Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | ||
| LL112 - LL615 | 393 | Rootes Securities Ltd | ||
| LV771 - LV999 | 166 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| LW113 - LW724 | 434 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| MZ282 - MZ989 | 585 | London Passenger Transport Board | ||
| NA102 - NA704 | 475 | Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | ||
| NP681 - NP999 | 259 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| NR113 - NR290 | 141 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| PN167 - PN460 | 211 | Fairey Aviation Co Ltd | ||
| PP165 - PP389 | 177 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| RG345 - RG879 | 400 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| RT753 - RT938 | 150 | Handley Page Ltd | ||
| ST794 - ST818 | 25 | English Electric Co Ltd | ||
| TW774 - TW796 | 23 | Handley Page Ltd |



 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com


 Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII
Halifax Heavy Bomber WWII Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page Wikipedia Halifax Bomber
Wikipedia Halifax Bomber National Air Force Museum of Canada
National Air Force Museum of Canada