Melrose, John Douglas Fitzgerald "Jack"
Prisoner of War 1942-10-13
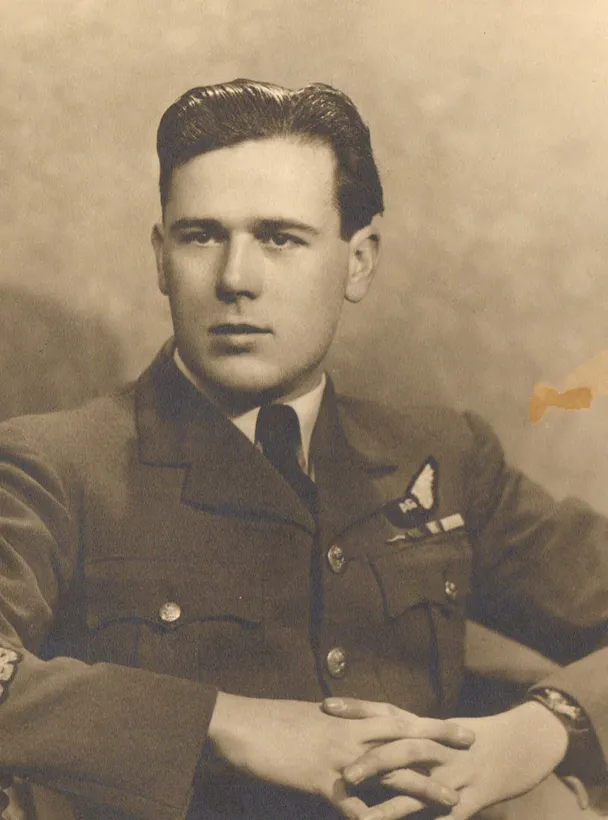

Birth Date: 1921
Born:
Home: Glasgow, Scotland
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: 1939-09-04
Service
RAF
Unit
214 (B) Sqn- Squadron (RAF)
Ultor In Umbris Avenging in the shadows
Base
RAF Chedburgh
Rank
Warrant Officer
Position
Sergeant
Service Numbers
983731
PoW: 842
Home
 Glasgow, Scotland
Glasgow, Scotland
Target
 Kiel Germany
Kiel Germany
Due to the Allied advances in the area, Prisoners of War in were evacuated from Stalag 357 1945-04-06, for a forced march back east. Warrant Officer Melrose managed to escape from the column into the woods where he met up with another escaper an American Sergeant. However, they were quickly captured by a Hungarian soldier who turned them over to a German officer. Belsen Concentration Camp was in the area, operated by the German SS. The SS officers used their two captives to approach British troops in an effort to negotiate a ceasefire that would allow the Germans to leave Belsen and have the British take control of the Camp. Taken into British custody, Melrose was liberated and returned to the UK
Footprints on the Sands of Time, RAF Bomber Command Prisoners of War in Germany 1939-45 by Oliver Clutton-Brock, page 361Stirling Mk. l BK599
Bombing Kiel Germany 1942-October-13 to 1942-October-13
214 (B) Sqn (RAF) RAF Chedburgh
214 Federated Malay States Squadron RAF (Ultor In Umbris) RAF Chedburgh. Stirling I aircraft BK 599 BU-R was coned by searchlights, struck by flak and attacked by night fighter pilot Oberfeldwebel Karl Fleischmann of the 6/NJG 3, crashing near Felde, Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Only two of the crew of seven managed to bale before the crash
Davison, Phalempin, Dempsay, Cameron, and Murray had previously survived the ditching of #22 Operational Training Unit Wellington Ic aircraft X 9701 LT-D 1942-06-25 returning from an operation over Germany. They survived adrift in their dinghy for several days until picked by air-sea rescue until 1942-07-01
 [Royal Air Force Serial and Image Database]...
[Royal Air Force Serial and Image Database]...
 No 214 (FMS) Squadron RAF - Crews and Losses - Short Stirling
No 214 (FMS) Squadron RAF - Crews and Losses - Short Stirling
Stirling BK599
Short Stirling

In June 1944, this Short S.29 Stirling B Mk. IV (Serial No. LK589), coded V3, RAF, was flown across the Atlantic as part of a navigation training exercise and did a tour of bases in Eastern Canada. It is shown here at Malton, Ontario. It was flown back to the UK after a two-week visit.
The Short Stirling was a British four-engined heavy bomber of the Second World War. It has the distinction of being the first four-engined bomber to be introduced into service with the Royal Air Force (RAF).
The Stirling was designed during the late 1930s by Short Brothers to conform with the requirements laid out in Air Ministry Specification B.12/36. Prior to this, the RAF had been primarily interested in developing increasingly capable twin-engined bombers but had been persuaded to investigate a prospective four-engined bomber as a result of promising foreign developments in the field. Out of the submissions made to the specification Supermarine proposed the Type 317, which was viewed as the favourite, whereas Short's submission, named the S.29, was selected as an alternative. When the preferred Type 317 had to be abandoned, the S.29, which later received the name Stirling, proceeded to production.In early 1941 the Stirling entered squadron service. During its use as a bomber pilots praised the type for its ability to out-turn enemy night fighters and its favourable handling characteristics whereas the altitude ceiling was often a subject of criticism. The Stirling had a relatively brief operational career as a bomber before being relegated to second line duties from late 1943. This was due to the increasing availability of the more capable Handley Page Halifax and Avro Lancaster, which took over the strategic bombing of Germany. Decisions by the Air Ministry on certain performance requirements (most significantly to restrict the wingspan of the aircraft to 100 feet) had played a role in limiting the Stirling's performance; the 100ft limit also affected earlier models of the Halifax (MkI & MkII) though the Lancaster never adhered to it.
During its later service, the Stirling was used for mining German ports; new and converted aircraft also flew as glider tugs and supply aircraft during the Allied invasion of Europe during 1944"“1945. In the aftermath of the Second World War, the type was rapidly withdrawn from RAF service, having been replaced in the transport role by the Avro York, a derivative of the Lancaster that had previously displaced it from the bomber role. A handful of ex-military Stirlings were rebuilt for the civil market.Wikipedia
 Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)
Library and Archives Canada Service Files (may not exist)






 Wikipedia Short Stirling
Wikipedia Short Stirling