Patterson, K R
Rescued 1943-07-26


Birth Date: unkown date
Born:
Home:
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RAF
Unit
432 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Saeviter Ad Lucem Ferociously toward the light
Base
Skipton-on-Swale
Rank
Position
Pilot Officer
Service Numbers
Target
 Essen Germany
Essen Germany
Wellington B. Mk. X HE514
Bombing Essen Germany 1943-July-25 to 1943-July-26
(B) Sqn (RCAF) Skipton-on-Swale
Battle of Hamburg
705 aircraft - 294 Lancasters, 221 Halifaxes, 104 Stirlings, 67 Wellingtons, 19 Mosquitoes. 26 aircraft - I0 Halifaxes, 7 Stirlings, 5 Lancasters, 4 Wellingtons - lost, 3·7 per cent of the force. The commander of the American VIII Bomber Command, Brigadier-General Fred Anderson, observed this raid as a passenger in an 83 Squadron Lancaster.
This was an attempt to achieve a good raid on this major target while the effects of Window were still fresh. The raid was successful, with particular damage being recorded In Essen's industrial areas in the eastern half of the city. The Krupps works suffered what was probably it's most damaging raid of the war. The next morning, Doktor Gustav Krupp had a stroke from which he never recovered; this saved him from being charged with war crimes after the war. 51 other industrial buildings were destroyed and 83 seriously damaged. 2,852 houses were destroyed, 500 people were killed, 12 were missing and 1,208 were injured. The 500 dead are recorded as follows: 165 civilian men, II8 women, 22 children, 22 servicemen, 131 foreign workers and 42 prisoners of war.
source: The Bomber Command War Diaries, Martin Middlebrook and Chris Everitt
Wellington BX aircraft HE 514 QO-K, flak damaged, was ditched into the English Channel off Cromer, Norfolk, England returning from a raid to Essen, Germany
Squadron Leader CB Sinton (RCAF)(UK), Sergeant GW Sharpe (RAF), Pilot Officer SA Sinclair (RAF), Sergeant RE Pearce (RAF) and Pilot Officer KR Patterson (RAF) all survived the ditching at sea and were rescued
Wellington HE514
Vickers Wellington
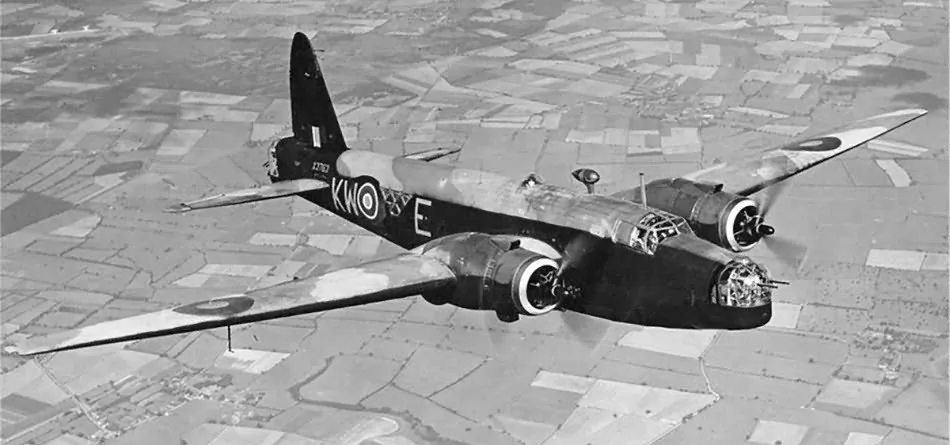

Vickers Wellington B. Mk. III (Serial No. X3763), coded KW-E, No. 425 'Alouette' (B) Squadron, RCAF, late summer of 1942
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson, a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design.
The Wellington was used as a night bomber in the early years of the Second World War, performing as one of the principal bombers used by Bomber Command. During 1943, it started to be superseded as a bomber by the larger four-engined "heavies" such as the Avro Lancaster. The Wellington continued to serve throughout the war in other duties, particularly as an anti-submarine aircraft.
It holds the distinction of having been the only British bomber that was produced for the duration of the war, and of having been produced in a greater quantity than any other British-built bomber. The Wellington remained as first-line equipment when the war ended, although it had been increasingly relegated to secondary roles. The Wellington was one of two bombers named after Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, the other being the Vickers Wellesley.
In August 1936, an initial order for 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft, powered by a pair of 1,050 hp (780 kW) Bristol Pegasus radial engines, was received by Vickers; it had been placed so rapidly that the order occurred prior to the first meeting intended to decide the details of the production aircraft. In October 1937, another order for a further 100 Wellington Mk Is, produced by the Gloster Aircraft Company, was issued; it was followed by an order for 100 Wellington Mk II aircraft with Rolls-Royce Merlin X V12 engines. Yet another order was placed for 64 Wellingtons produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. With this flurry of order and production having been assured by the end of 1937, Vickers set about simplifying the manufacturing process of the aircraft and announced a target of building one Wellington per day.
A total of 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft were built; 150 for the RAF and 30 for the Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) (which were transferred to the RAF on the outbreak of war and used by 75 Squadron). In October 1938, the Mk I entered service with 9 Squadron. The Wellington was initially outnumbered by the Handley Page Hampden (also ordered by the Ministry to B.9/32) and the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley (to B.34/3 for a 'night' bomber) but outlasted both rival aircraft in service. The Wellington went on to be built in 16 separate variants, in addition to two training conversions after the war. The number of Wellingtons built totalled 11,462 of all versions, a greater quantity produced than any other British bomber. On 13 October 1945, the last Wellington to be produced rolled out.Wikipedia
 YouTube Vickers Wellington documentary
YouTube Vickers Wellington documentary
432 (B) Sqn Saeviter Ad Lucem ("Leaside")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Wellington X, Lancaster II, Halifax III, VII)

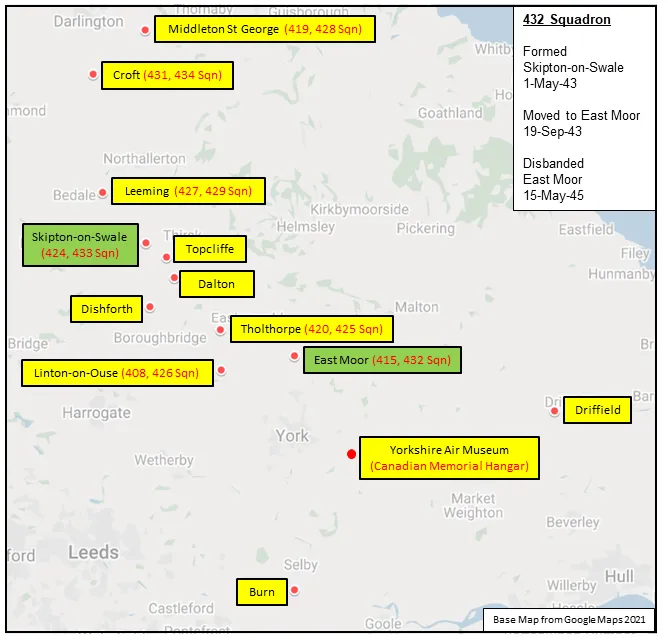
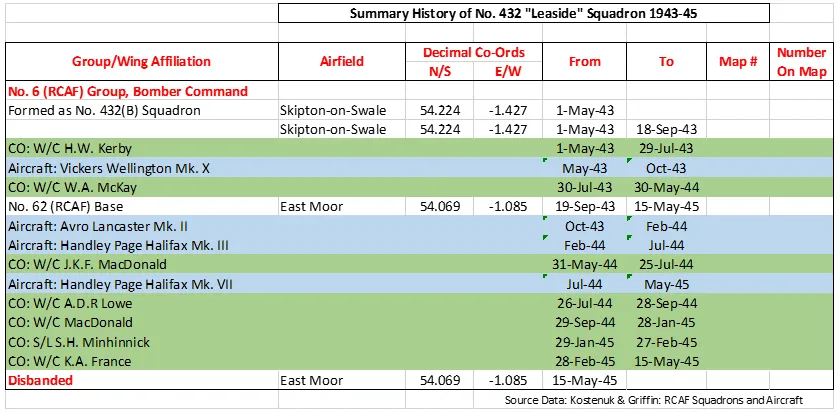
The Squadron was the twelfth RCAF bomber squadron to be formed overseas in WWII. It was formed on May 1, 1943 at Skipton-on-Swale, Yorkshire, UK as a unit of No 6 (RCAF) Group of RAF Bomber Command: indeed, it was the first bomber squadron to be formed directly into No 6 Group. Using the squadron identification letters QO it flew Vickers Wellington Mk X medium bombers until it moved to East Moor, Yorkshire on 19th September 1943, when it re-equipped with Avro Lancaster Mk II aircraft. East Moor was part of No 62 (RCAF) Base. The squadron re-equipped with Handley Page Halifax Mk III aircraft in February 1944, and with Halifax Mk VII in July of that year, and continued with them until the squadron was disbanded at East Moor on May 15, 1945.
In the course of operations the squadron flew 246 missions, involving 3130 individual sorties, for the loss of 73 aircraft. 8980 tons of bombs were dropped. Awards to squadron members included 2 DSOs, 119 DFCs,1 Bar to DFC, 1 CGM, 20 DFMs and 1 Croix de Guerre (France). Battle Honours were: English Channel and North Sea 1943, Fortress Europe 1943-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1944, Ruhr 1943-45, Berlin 1943-44, German Ports 1943-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1943.Moyes, Kostenuk and Griffin
Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum PDF)
Maps for Movements of 432 Squadron 1943-45
432 Squadron History Summary 1943-45
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Canuck)
The squadron was re-formed at Bagotville, Quebec as an All-Weather Fighter unit on 1 October 1954. The squadron flew Avro CF-100 Canuck aircraft on North American Air Defence until it was disbanded on 15 October 1961.
 Daily Operations 6bombergroup.ca
Daily Operations 6bombergroup.ca Wikipedia Vickers Wellington
Wikipedia Vickers Wellington