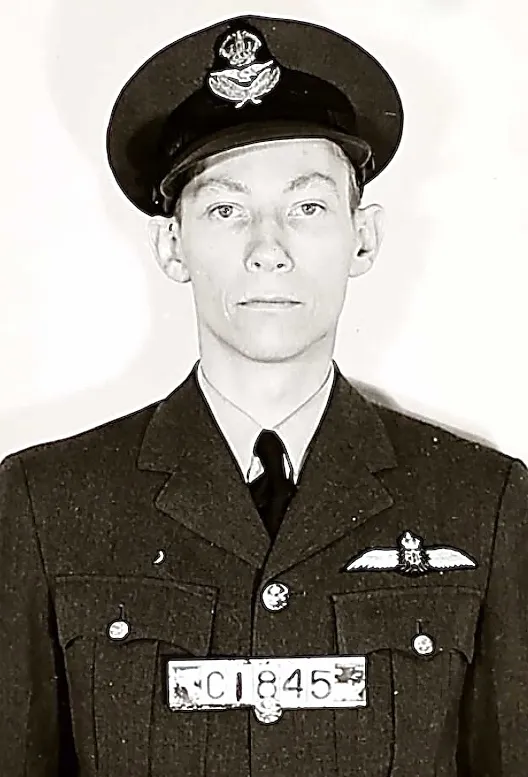
Wilson, Robert Hipwell
Killed in Action 1943-11-13


Birth Date: 1917
Born:
Son of Cecil Hubert and Mary Ellen Wilson, of Orillia, Ontario, Canada; husband of Catherine Wilson.
Home: OriIlia, Ontario
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
423 Sqn- Squadron
Quaerimus Et Petimus We search and strike
Base
Rank
Flight Lieutenant
Position
Flying Officer
Service Numbers
C/1845
Home
 OriIlia, Ontario
OriIlia, Ontario
First Burial
 Runnymede Memorial Surrey, Uk
Runnymede Memorial Surrey, Uk
Short Sunderland

Short Sunderland, coded Z, 15 Apr 1943
The Short S.25 Sunderland was a British flying boat patrol bomber, developed and constructed by Short Brothers for the Royal Air Force (RAF). The aircraft took its service name from the town (latterly, city) and port of Sunderland in North East England.
Developed in parallel with the civilian S.23 Empire flying boat, the flagship of Imperial Airways, the Sunderland was developed specifically to conform to the requirements of British Air Ministry Specification R.2/33 for a long-range patrol/reconnaissance flying boat to serve with the Royal Air Force (RAF). As designed, it served as a successor to the earlier Short Sarafand flying boat. Sharing several similarities with the S.23, it featured a more advanced aerodynamic hull and was outfitted with various offensive and defensive armaments, including machine gun turrets, bombs, aerial mines, and depth charges. The Sunderland was powered by four Bristol Pegasus XVIII radial engines and was outfitted with various detection equipment to aid combat operations, including the Leigh searchlight, the ASV Mark II and ASV Mark III radar units, and an astrodome.
The Sunderland was one of the most powerful and widely used flying boats throughout the Second World War. In addition to the RAF, the type was operated by other Allied military air wings, including the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF), South African Air Force (SAAF), Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF), French Navy, Norwegian Air Force, and the Portuguese Navy. During the conflict, the type was heavily involved in Allied efforts to counter the threat posed by German U-boats in the Battle of the Atlantic.Wikipedia
 YouTube Short Sunderland (1940-1949)
YouTube Short Sunderland (1940-1949)
423 Sqn Quaerimus Et Petimus ()
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Sunderland III, Liberator VI, VII)

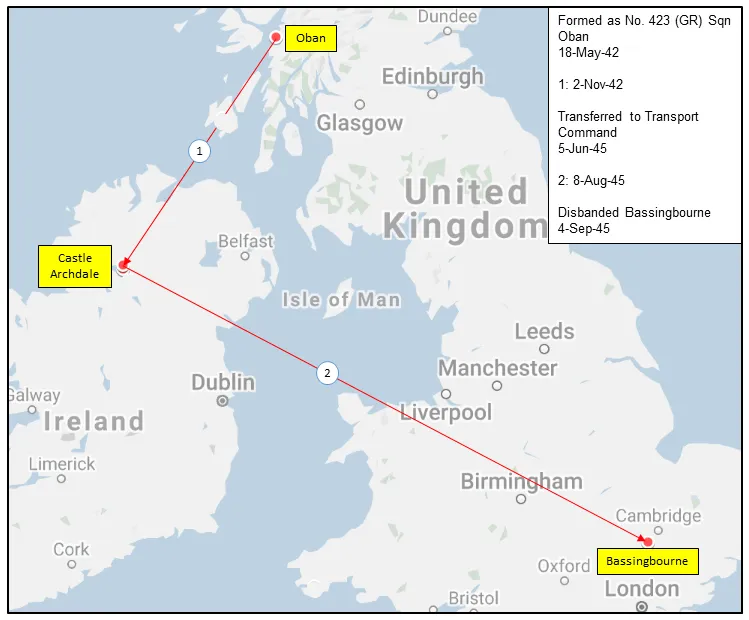
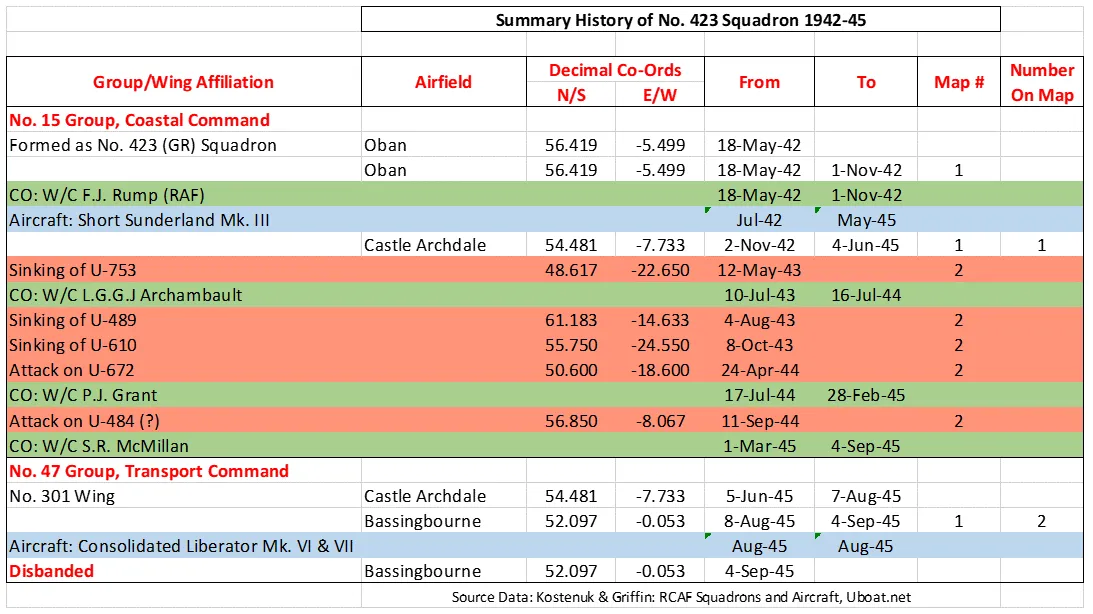
The squadron was formed as a General Reconnaissance unit at Oban, Scotland  , on 18 May 1942. It was the RCAF's 21st, and sixth and last Coastal squadron formed overseas in WWII. The unit flew Short Sunderland flying boats as convoy escorts and on anti-U-boat missions. It remained at Oban until November 1942, when it transferred to Castle Archdale in Northern Ireland
, on 18 May 1942. It was the RCAF's 21st, and sixth and last Coastal squadron formed overseas in WWII. The unit flew Short Sunderland flying boats as convoy escorts and on anti-U-boat missions. It remained at Oban until November 1942, when it transferred to Castle Archdale in Northern Ireland  .
.
When hostilities terminated in Europe, the squadron was re-designated as a Transport unit and was slated to move to the Far East as part of the "Tiger Force" that was assembling to carry on the war with Japan. To this end, the squadron was equipped with Consolidated Liberator aircraft, but the termination of hostilities with Japan meant that the squadron was no longer required in the transport role, and it was disbanded at Bassingbourn, Cambridgeshire, England  , on September 4, 1945.
, on September 4, 1945.
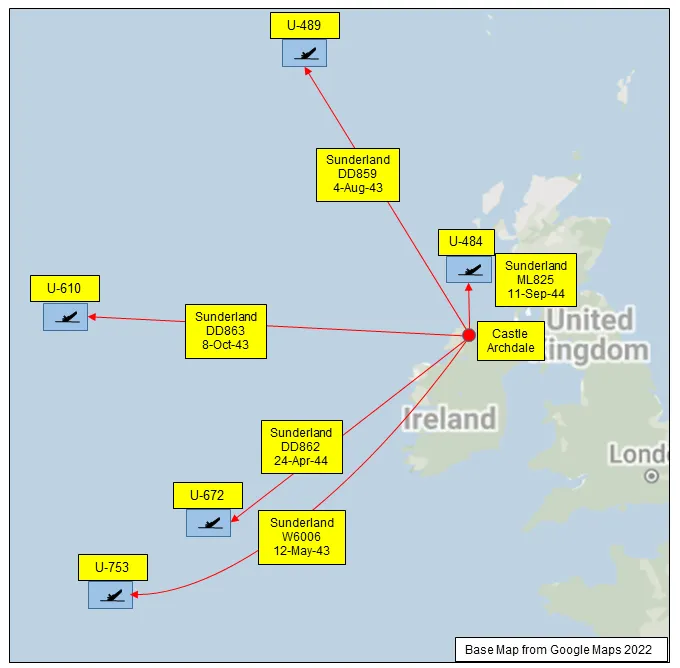
The squadron claimed the sinking of a number of U-boats. Flight Lieutenant J. Musgrave and crew shared with destroyers HMCS Drumheller and HMS Lagan the sinking of what was thought to be U-456 on May 12, 1943 (later research established that the U-boat sunk was U-753, see link below). On August 4, 1943, Flying Officer A.A. Bishop and crew sank U-489; on October 8. 1943 Flying Officer A.H. Russell and crew sank U-610; on April 24, 1944 Flying Officer F.G. Fellows and crew sank U-311 (later research showed that the boat attacked was U672, see link below, and that it was damaged but not sunk); on September 11, 1944 it was claimed that Flying Officer J.N. Farren and crew shared in the sinking of U-484 with HMCS Dunver and HMCS Hespeler. Later research showed that this was probably a non-submarine target (see link below). In the course of the war, the squadron won 4 DFCs and 1 DFM. Battle Honours were: Atlantic 1942-45, English Channel and North Sea 1944-45, Normandy 1944, Biscay 1944.Wikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin, uboat.net
Maps for Movements of 423 Squadron 1942-45
 |  |
423 Squadron History Summary 1942-45
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Canuck 3B & 4B, Sea King, Cyclone)
The squadron was re-formed on 1 June 1953 at RCAF Station St Hubert, Quebec flying the Avro CF-100 Canuck in a continental defence role. It was transferred to RCAF Station Grostenquin, France
flying the Avro CF-100 Canuck in a continental defence role. It was transferred to RCAF Station Grostenquin, France  in February 1957 where it replaced No. 416 Squadron which flew Sabres. The squadron was disbanded in 1962 when the RCAF's CF-100s were removed from service. In 1974, it was re-formed a final time as No. 423 Anti-Submarine Squadron. In 1995 its name was changed to 423 Maritime Helicopter Squadron. It flew CH-124 Sea King helicopter, which it used in support of Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) warships during the 1991 Gulf War and in the Arabian Sea after the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks. It now operates the Sikorsky CH-148 Cyclone since January 2018. On 30 April 2020, an RCAF CH-148 from 423 Squadron, attached to HMCS Fredericton and based at the Shearwater Heliport
in February 1957 where it replaced No. 416 Squadron which flew Sabres. The squadron was disbanded in 1962 when the RCAF's CF-100s were removed from service. In 1974, it was re-formed a final time as No. 423 Anti-Submarine Squadron. In 1995 its name was changed to 423 Maritime Helicopter Squadron. It flew CH-124 Sea King helicopter, which it used in support of Royal Canadian Navy (RCN) warships during the 1991 Gulf War and in the Arabian Sea after the 11 September 2001 terrorist attacks. It now operates the Sikorsky CH-148 Cyclone since January 2018. On 30 April 2020, an RCAF CH-148 from 423 Squadron, attached to HMCS Fredericton and based at the Shearwater Heliport  crashed in the Ionian Sea during a NATO Mediterranean exercise. All six crew members aboard the aircraft were killed.
crashed in the Ionian Sea during a NATO Mediterranean exercise. All six crew members aboard the aircraft were killed.
 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial
 Wikipedia Short Sunderland
Wikipedia Short Sunderland Harold A Skaarup Web Page
Harold A Skaarup Web Page