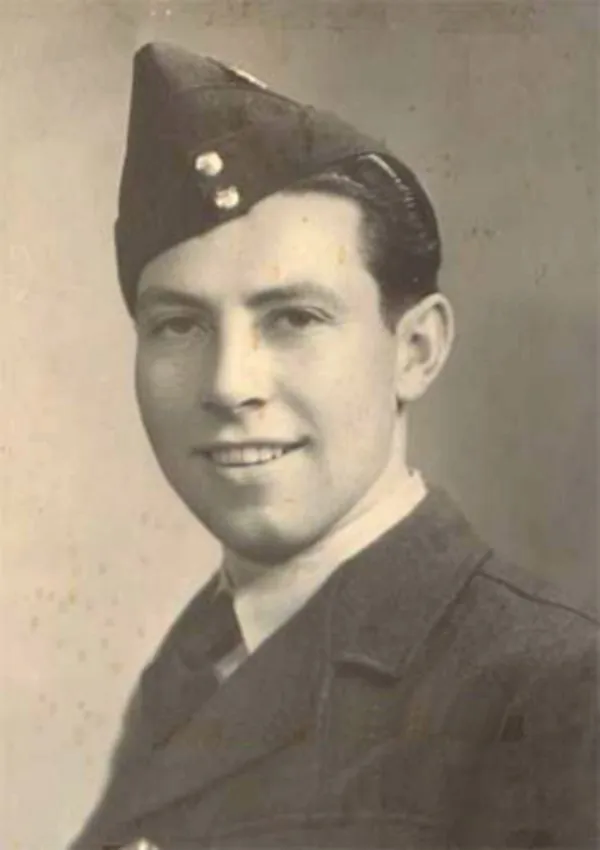
Davis, Harry Llewellyn
Killed in Action 1943-06-01


Birth Date: 1918-October-31
Born: Acme, Alberta
Harry Llwellyn & Rosa Miranda (nee Grimm) Davis
Home: Acme, Alberta (parents)
Enlistment:
Enlistment Date: Unknown
Service
RCAF
Unit
420 (B) Sqn- Squadron
Pugnamus Finitum We fight to the finish
Base
RAF Middleton St George
Rank
Warrant Officer 2
Position
Warrant Officer 2
Service Numbers
R/92672
First Burial
 Runnymede Memorial, Surrey, England.
Runnymede Memorial, Surrey, England.
WO 2 Davis had been injured 1943-01-29 when he had bailed out of 424 Squadron Wellington III BK-436 QB-P that was damaged by flak and ran out of fuel over England returning from an operation to Lorient, France
Aircraft was on transit flight from Portreath to RAF Ras El Ma, North Africa.
Wellington B. Mk. X HE568
Ferry Flight 1943-June-01 to 1943-June-01
420 (B) Sqn (RCAF) Middleton St George
420 Snowy Owl Squadron (Pugnamus Finitum), RAF Middleton St George. 420 Squadron RCAF was detached from Bomber Command from 1943-05-15 until 1943-11-06 and sent to the Middle East. Wellington X aircraft HE 568 lost in a daylight transit flight from RAF Portreath in Cornwall to Ras El Ma, North Africa, when the Wellington was intercepted and shot down over the Bay of Biscay by Oblt Hermann Horstmann of 13/KG 40
Aircrew: Flight Sergeant AT Sodero (RCAF), Flying Officer GH Hubbell (RCAF), Pilot Officer WR King (RCAF), Pilot Officer RS Hollowell (RCAF), Warrant Officer 2nd Class HL Davis (RCAF) as well as Ground Crew: Corporal JF MacKenzie (RCAF) and Leading Aircraftman TA Brookes (RCAF), were all missing, presumed killed in action
The missing have no known graves and are all commemorated on the Runnymede War Memorial
Wellington X HE 568 was one of a group of 20 aircraft transferring air and ground crew to North Africa and one of two aircraft shot down within minutes of each other by German fighters during the transit flight. Please see serial HE 961 for casualty list on that aircraft
Addendum: - FS Sodero was 23 years old at the time of death, not 21 Detail provided by DA Stallard, Trenton, Nova Scotia
Wellington HE568
Vickers Wellington
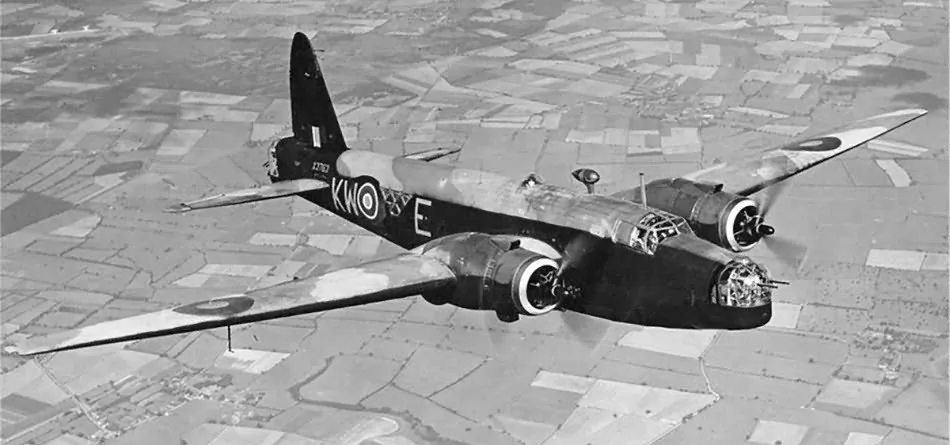

Vickers Wellington B. Mk. III (Serial No. X3763), coded KW-E, No. 425 'Alouette' (B) Squadron, RCAF, late summer of 1942
The Vickers Wellington was a British twin-engined, long-range medium bomber. It was designed during the mid-1930s at Brooklands in Weybridge, Surrey. Led by Vickers-Armstrongs' chief designer Rex Pierson, a key feature of the aircraft is its geodetic airframe fuselage structure, which was principally designed by Barnes Wallis. Development had been started in response to Air Ministry Specification B.9/32, issued in the middle of 1932, for a bomber for the Royal Air Force. This specification called for a twin-engined day bomber capable of delivering higher performance than any previous design.
The Wellington was used as a night bomber in the early years of the Second World War, performing as one of the principal bombers used by Bomber Command. During 1943, it started to be superseded as a bomber by the larger four-engined "heavies" such as the Avro Lancaster. The Wellington continued to serve throughout the war in other duties, particularly as an anti-submarine aircraft.
It holds the distinction of having been the only British bomber that was produced for the duration of the war, and of having been produced in a greater quantity than any other British-built bomber. The Wellington remained as first-line equipment when the war ended, although it had been increasingly relegated to secondary roles. The Wellington was one of two bombers named after Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, the other being the Vickers Wellesley.
In August 1936, an initial order for 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft, powered by a pair of 1,050 hp (780 kW) Bristol Pegasus radial engines, was received by Vickers; it had been placed so rapidly that the order occurred prior to the first meeting intended to decide the details of the production aircraft. In October 1937, another order for a further 100 Wellington Mk Is, produced by the Gloster Aircraft Company, was issued; it was followed by an order for 100 Wellington Mk II aircraft with Rolls-Royce Merlin X V12 engines. Yet another order was placed for 64 Wellingtons produced by Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft. With this flurry of order and production having been assured by the end of 1937, Vickers set about simplifying the manufacturing process of the aircraft and announced a target of building one Wellington per day.
A total of 180 Wellington Mk I aircraft were built; 150 for the RAF and 30 for the Royal New Zealand Air Force (RNZAF) (which were transferred to the RAF on the outbreak of war and used by 75 Squadron). In October 1938, the Mk I entered service with 9 Squadron. The Wellington was initially outnumbered by the Handley Page Hampden (also ordered by the Ministry to B.9/32) and the Armstrong Whitworth Whitley (to B.34/3 for a 'night' bomber) but outlasted both rival aircraft in service. The Wellington went on to be built in 16 separate variants, in addition to two training conversions after the war. The number of Wellingtons built totalled 11,462 of all versions, a greater quantity produced than any other British bomber. On 13 October 1945, the last Wellington to be produced rolled out.Wikipedia
 YouTube Vickers Wellington documentary
YouTube Vickers Wellington documentary
420 (B) Sqn Pugnamus Finitum ("Snowy Owl")
History of the Squadron during World War II (Aircraft: Hampden I, Wellington III, X, Halifax III, Lancaster X)

420 Squadron RCAF was the fourth RCAF bomber unit formed overseas in WWII. It was formed at Waddington, Lincolnshire, UK on December 19, 1941 as a unit of No 5 Group of RAF Bomber Command flying Handley Page Hampden Mk 1 aircraft, with the squadron code letters PT. In early August 1942 the squadron transferred to No 4 Group of Bomber Command, and was based at Skipton-on-Swale, Yorkshire : at this time it was equipped with Vickers Wellington Mk. III aircraft. In October 1942 it moved to Middleton St. George, Durham , where on January 1, 1943 it became a unit of the newly-created no. 6 (RCAF) Group of Bomber Command. It remained there until May 1943, when, by now flying tropicalized Wellington Mk X aircraft, it flew to Tunisia in North Africa to join No 331 (RCAF) Wing of No. 205 Group. From the bases of Kairouan/Zina and Hani East Landing Ground (both locations approximate)it attacked targets in Sicily and Italy as part of the invasion force. In October, the squadron returned by sea to England, leaving its aircraft behind, and rejoined 6 Group at Dalton, Yorkshire, re-equipping with Handley Page Halifax Mk. III aircraft. The squadron finally moved to Tholthorpe, Yorkshire in December 1943, where it remained until the end of hostilities in Europe. From April 1945 the squadron re-equipped with Lancaster Mk. X aircraft, although they were not used operationally. In June 1945 the squadron flew its aircraft to Debert, Nova Scotia , where it disbanded in September of 1945
In the course of hostilities, the squadron flew 4186 sorties for the loss of 65 aircraft. 9771 tons of bombs were dropped. The squadron won 38 DFC's, 1 Bar to DFC, and 9 DFM's. Battle Honors were: English Channel and North Sea 1942-44, Baltic 1942, Fortress Europe 1942-44, France and Germany 1944-45, Biscay Ports 1942-44, Ruhr 1942-45, Berlin 1944, German Ports 1942-45, Normandy 1944, Rhine, Biscay 1942-43, Sicily 1943, Italy 1943, SalernoWikipedia, Kostenuk and Griffin, Moyes
 420 Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum (Large PDF)
420 Squadron History (Bomber Command Museum (Large PDF)
 420 Tholthorpe Airfield Operations Record Book
420 Tholthorpe Airfield Operations Record Book
 420 Squadron Operations Record Book
420 Squadron Operations Record Book
Maps for Movements of 420 Squadron 1941-45
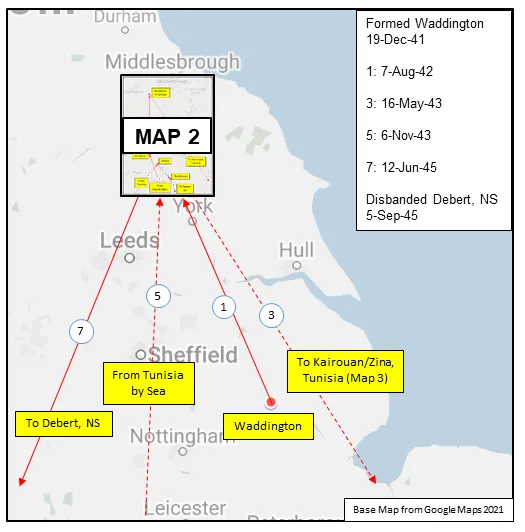 MAP 1: 420 Squadron Movements in England 1941-45 (right-click on image to display enlarged new tab) | 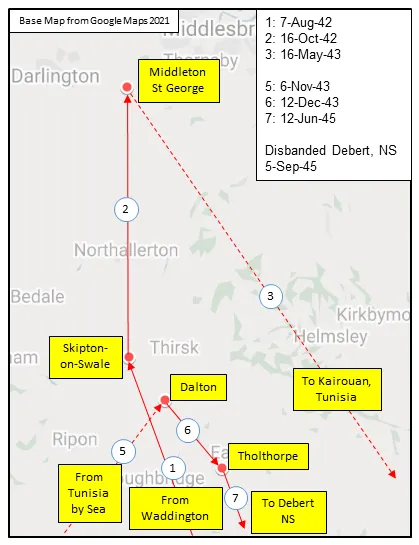 MAP 2: 420 Squadron Movements in Yorkshire and Durham 1942-45 | 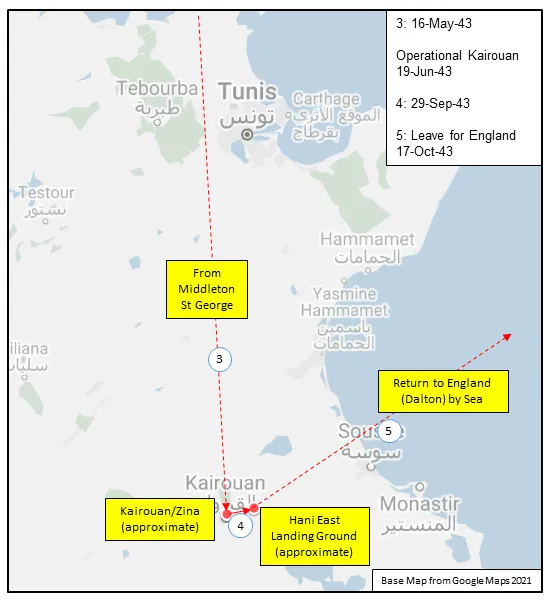 MAP 3: 420 Squadron Movements in Tunisia, North Africa 1943 |
420 Squadron History Summary 1941-45
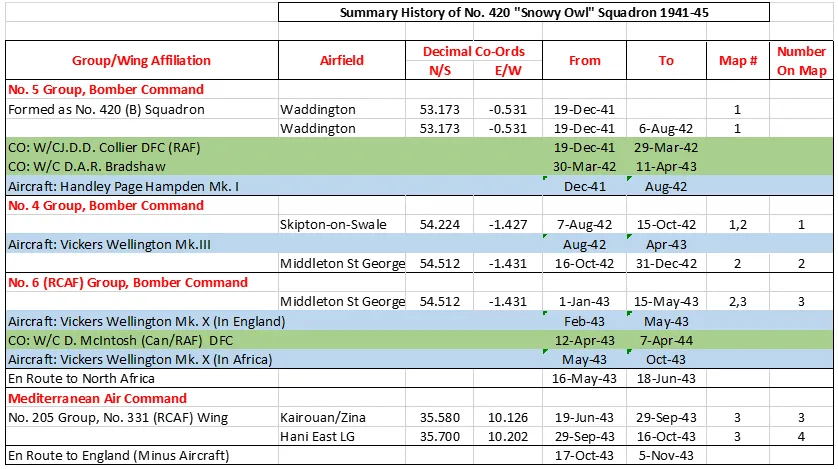
420 Squadron History Summary 1941-45 Page 2
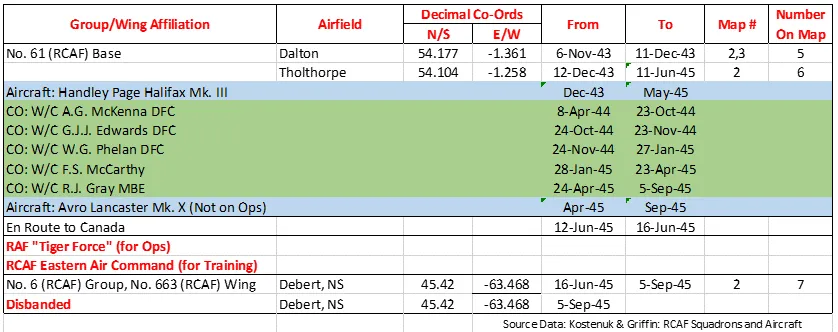
History of the Squadron Post-WWII (Aircraft: Harvard, Mustang, Silver Star, Tracker)
No. 420 Squadron reformed at London, Ontario on 15 September 1948, and flew North American Mustang and Harvard aircraft in a fighter role until the squadron disbanded on 1 September 1956. The squadron was re-formed as an Air Reserve squadron based initially at CFB Shearwater, Nova Scotia flying the de Havilland Canada Tracker aircraft that had once been the backbone of the Canadian Naval Air's anti-submarine program. As an Air Reserve Squadron it participated with regular fisheries patrols. It was one of the few active Air Reserve Squadrons in Canada and was paired with the Regular Force's 880 Squadron. The Squadron was rebased to CFB Summerside, Prince Edward Island when their base was downsized. No 420 Squadron was reduced to nil strength on 15 May 1995.
 Canadian Virtual War Memorial
Canadian Virtual War Memorial Commonwealth War Graves Commission
Commonwealth War Graves Commission www.findagrave.com
www.findagrave.com [Royal air Force serial and Image Database]...
[Royal air Force serial and Image Database]...





 Wikipedia Vickers Wellington
Wikipedia Vickers Wellington